
Success in mastering complex subjects relies heavily on a solid understanding of key principles and the ability to apply them effectively. Whether you’re tackling theoretical concepts or practical applications, it’s essential to grasp both the basics and advanced material. This guide will help you navigate the most critical topics you need to focus on, ensuring you’re well-equipped to tackle the challenges ahead.
By breaking down the material into manageable sections, we will cover a range of topics designed to sharpen your skills and boost your confidence. From fundamental theories to real-world applications, every area plays a crucial role in your preparation. The goal is to provide clear insights and practical tips that will enable you to approach your upcoming challenges with clarity and expertise.
Stay focused, review key concepts regularly, and practice with real-world examples to strengthen your understanding. With a clear study plan and the right resources, you can approach the material with confidence, knowing you’re ready to tackle any question that comes your way. Preparation is the key to success, and this guide will provide the tools you need to excel.
Preparation Guide for the Subject Assessment
To perform well in any challenging subject, it’s crucial to focus on understanding core principles and mastering problem-solving techniques. This section will guide you through the main topics and strategies that will help you succeed. By reviewing essential material and practicing application methods, you can ensure you’re fully prepared for the assessment ahead.
The following areas are central to your preparation, providing a comprehensive overview of what to focus on:
- Core Concepts: Refresh your understanding of the foundational principles that form the basis of the subject.
- Practical Application: Focus on applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios to improve your problem-solving skills.
- Key Formulas and Definitions: Ensure you’re familiar with the essential formulas and definitions that are often tested.
- Conceptual Connections: Review how different topics are interconnected to better understand the overall framework.
To make your study sessions more effective, consider the following tips:
- Break down complex material into smaller, manageable chunks for easier comprehension.
- Practice with sample problems and previous examples to gain confidence in applying concepts.
- Focus on areas where you feel less confident, but also keep revisiting stronger areas to maintain your knowledge base.
- Work through different types of questions to familiarize yourself with potential problem formats.
By structuring your study sessions around these key areas, you’ll be able to tackle the assessment with a clear understanding and the confidence to succeed.
Key Topics Covered in the Assessment
To achieve success, it’s essential to focus on the main areas of study that are most likely to be tested. These topics are fundamental to understanding the subject in-depth and applying concepts effectively. The following list outlines the core themes that are crucial for your preparation.
Core Principles and Foundations

- Market Structures: Understand the different types of market systems, such as perfect competition, monopolies, and oligopolies.
- Supply and Demand: Grasp the basic law of supply and demand, and how changes affect market equilibrium.
- Consumer Behavior: Learn how consumers make decisions based on preferences, income, and prices.
- Cost Structures: Familiarize yourself with the various cost concepts, such as fixed costs, variable costs, and total costs.
Applications and Real-World Scenarios
- Government Policy: Study the effects of fiscal and monetary policy on national economies.
- International Trade: Understand the concepts of tariffs, trade agreements, and globalization.
- Economic Indicators: Learn about key indicators like GDP, inflation, and unemployment rates.
- Public Goods and Externalities: Examine the role of government in providing public goods and addressing market failures.
These key topics form the foundation for a deeper understanding of the subject and will help you approach the assessment with confidence. By mastering these areas, you’ll be well-prepared to answer a range of questions that assess both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Important Formulas for Assessments
Mastering essential equations is a critical step in preparing for any test. These formulas help simplify complex concepts and allow you to quickly solve problems under time pressure. Understanding how and when to use these calculations is just as important as knowing the concepts themselves. Below are the most relevant formulas you should be familiar with.
Basic Equations for Analysis

- Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): PED = (% change in quantity demanded) / (% change in price)
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP = C + I + G + (X – M), where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government spending, and (X – M) is net exports.
- Marginal Cost (MC): MC = Change in total cost / Change in output
- Average Total Cost (ATC): ATC = Total cost / Quantity produced
Advanced Formulas for In-Depth Problems
- Unemployment Rate: Unemployment rate = (Number of unemployed people / Labor force) x 100
- Inflation Rate: Inflation rate = ((New CPI – Old CPI) / Old CPI) x 100, where CPI is the Consumer Price Index.
- Consumer Surplus: Consumer surplus = 1/2 x Base x Height, where base is the quantity and height is the price difference from the demand curve.
- Profit Maximization: Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost
By thoroughly understanding and practicing these formulas, you’ll be better equipped to solve problems efficiently and accurately. Ensure that you not only memorize these equations but also understand their application in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Microeconomics Principles
Grasping the fundamental concepts of market behavior and decision-making at the individual and firm level is essential for navigating more advanced material. These principles lay the groundwork for understanding how resources are allocated and how agents within the market interact. By focusing on the core ideas, you’ll build a strong foundation for analyzing various market structures and economic scenarios.
Key Concepts in Microeconomic Theory
- Demand and Supply: The interaction of buyers and sellers in determining the prices and quantities of goods and services.
- Utility Maximization: The process by which consumers seek to allocate their limited resources to maximize satisfaction.
- Market Equilibrium: The point at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, leading to stable prices.
- Opportunity Cost: The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision.
Types of Market Structures
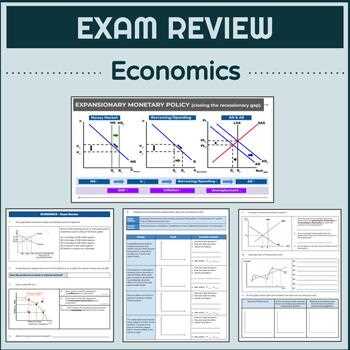
Market structures describe the competitive environment in which firms operate. Understanding these structures helps to analyze pricing, output, and efficiency within different industries. The four main types include:
| Market Structure | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect Competition | Many firms, identical products, easy market entry | Farmers’ markets |
| Monopolistic Competition | Many firms, differentiated products, some control over prices | Restaurants, clothing brands |
| Oligopoly | Few large firms, high barriers to entry, interdependent pricing | Airlines, automobile manufacturers |
| Monopoly | One firm controls the market, no close substitutes, high barriers to entry | Utility companies |
By understanding these core principles, you’ll be able to analyze how decisions are made within different types of markets and how economic agents interact with each other. This knowledge is essential for evaluating the efficiency and outcomes of various economic systems.
Macroeconomic Theories You Should Know
Understanding the broader forces that shape national economies is essential for analyzing economic trends, policies, and the behavior of entire markets. These theories provide insights into how economies function as a whole, focusing on elements such as growth, inflation, unemployment, and government interventions. Familiarity with these key frameworks will allow you to assess and interpret the health of an economy more effectively.
Classical and Neoclassical Models
Classical economics emphasizes the role of free markets in promoting efficient resource allocation, with the belief that economies tend to self-correct over time. The neoclassical approach builds on this by introducing the concept of utility maximization, where individuals and firms make decisions that lead to optimal outcomes in competitive markets.
- Invisible Hand: A concept introduced by Adam Smith, suggesting that individual actions driven by self-interest can lead to beneficial outcomes for society.
- Say’s Law: The idea that supply creates its own demand, implying that production will always generate enough income to purchase the goods and services produced.
Keynesian Economics
Keynesian theory argues that total spending in an economy (aggregate demand) is the primary driver of economic growth and employment levels. It advocates for government intervention through fiscal and monetary policies to stabilize the economy, especially during periods of recession. According to this theory, in times of economic downturns, the government must step in to boost demand and increase output.
- Government Spending: In times of economic slowdowns, increased government spending can help stimulate demand and reduce unemployment.
- Multiplier Effect: An increase in government expenditure can lead to a larger overall increase in economic activity.
By studying these macroeconomic frameworks, you will gain a better understanding of how large-scale economic forces interact and how government policies influence national growth and stability. This knowledge is crucial for evaluating both short-term and long-term economic conditions.
Types of Market Structures Explained

Market structures describe the competitive environment within which businesses operate, affecting pricing, production levels, and overall efficiency. Understanding the different types of market structures is essential for analyzing how firms compete and make decisions. Each structure has its own characteristics, influencing how companies interact with consumers and each other. Below are the main types of market structures that you should be familiar with.
- Perfect Competition: This is a market structure where many firms sell identical products, and there is free entry and exit from the market. No single firm has any influence over the market price, and consumers have full information about prices and products.
- Monopolistic Competition: In this structure, many firms sell similar but not identical products, giving them some control over prices. Companies engage in non-price competition by differentiating their products through branding, quality, or other features.
- Oligopoly: A market dominated by a few large firms, each of which has significant control over the market. Oligopolistic companies may compete or collaborate, and barriers to entry are high, making it difficult for new firms to enter the market.
- Monopoly: A market structure where a single firm controls the entire supply of a good or service, with no close substitutes available. Monopolies can set prices and produce at their own levels of output, often leading to inefficiency and higher prices for consumers.
Each market structure has different implications for consumer choice, pricing, and market efficiency. Understanding these differences is essential for evaluating how markets function and how firms in each structure make strategic decisions.
Strategies for Time Management

Effective time management is crucial when preparing for any assessment. It allows you to approach each section methodically, ensuring that you complete all tasks while maintaining focus and quality. By allocating your time wisely and prioritizing key areas, you can maximize your performance and reduce stress. Below are some strategies to help you manage your time efficiently during an assessment.
- Understand the Time Limit: Before starting, get a clear understanding of the total time available and the number of questions or tasks. This will help you allocate time for each section based on its difficulty and weight.
- Divide and Conquer: Break the assessment into smaller sections or tasks. Allocate specific time slots to each part and stick to it, ensuring that no section is neglected.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Start with the questions you are most confident about. This will give you quick wins, boost your confidence, and free up time for the more challenging sections later.
- Leave Time for Review: Always reserve a few minutes at the end to go over your work. Use this time to check for any errors or areas where you might improve your responses.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Time management isn’t just about keeping track of the clock. Stay calm, avoid rushing, and ensure each response is thoughtful and well-constructed.
By applying these strategies, you’ll be able to navigate your tasks more effectively, ensuring you stay on track and complete everything within the allotted time. Proper preparation combined with good time management can make a significant difference in your overall performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam
Many individuals make avoidable errors during assessments that can negatively impact their performance. By recognizing these common pitfalls, you can take steps to avoid them, ensuring a more efficient and effective approach. Identifying and addressing these mistakes beforehand can help you manage your time better and improve the overall quality of your responses.
Rushing Through Questions
One of the most common mistakes is rushing through questions in an attempt to finish quickly. While time management is crucial, hurrying can lead to careless mistakes, overlooked details, and incomplete answers. Take your time to read each question carefully and ensure that your responses are thorough and well-considered.
Ignoring Instructions
Failure to read and follow instructions precisely can result in losing valuable marks. Always read the directions carefully before answering any question. For example, some questions may require specific formats, or you may be asked to provide detailed explanations rather than simple answers. Misinterpreting instructions can lead to unnecessary errors.
- Not Reviewing Your Work: Failing to leave time for review often leads to overlooked mistakes, such as typos, miscalculations, or incomplete answers.
- Overlooking Important Details: Skipping over important facts or ignoring specific aspects of a question can cause your response to be incomplete or inaccurate.
- Spending Too Much Time on One Section: Focusing too much on difficult questions at the expense of easier ones can disrupt your overall time management.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your performance reflects your preparation and knowledge. Stay calm, be mindful of your approach, and use your time wisely to achieve the best possible results.
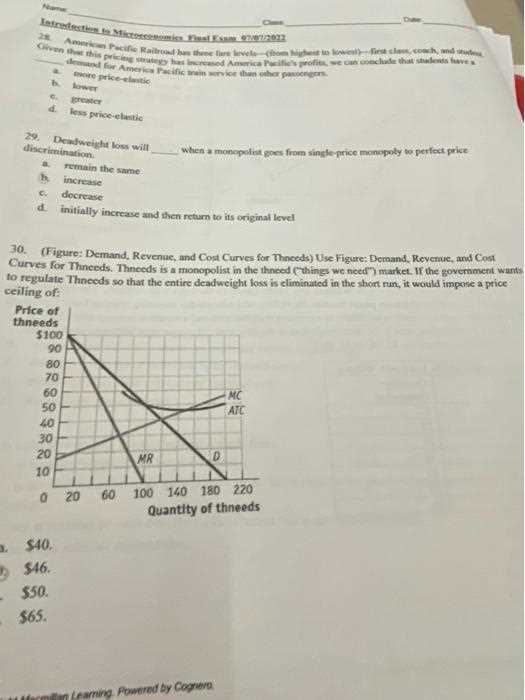
Essential Graphs and Diagrams to Study
Understanding visual representations of data is crucial for grasping core concepts. Graphs and diagrams are powerful tools that can simplify complex information and make abstract ideas more tangible. By familiarizing yourself with key visuals, you can better understand relationships and trends that might otherwise seem difficult to comprehend.
Here are some of the most important graphs and diagrams to focus on:
- Supply and Demand Curves: These graphs show how the price and quantity of goods in a market are determined. Being able to interpret shifts in these curves is essential for understanding market behavior.
- Production Possibility Frontiers (PPF): The PPF illustrates the trade-offs between two different goods or services. This diagram helps to analyze opportunity costs and resource allocation.
- Cost Curves: These diagrams represent the costs incurred by a firm at different levels of production. Key curves include average total cost, marginal cost, and average variable cost.
- Aggregate Demand and Supply: This graph shows the total demand and total supply in an economy. It’s important for understanding the equilibrium level of output and the effects of fiscal and monetary policies.
- Market Structures Graphs: These graphs compare different types of market conditions, such as perfect competition, monopolies, and oligopolies, highlighting how prices and output levels vary in each structure.
Familiarizing yourself with these visuals will not only help with theoretical understanding but also improve your ability to answer application-based questions efficiently. Make sure to practice interpreting and drawing these graphs to solidify your knowledge.
Reviewing Supply and Demand Curves
Understanding the dynamics of supply and demand is essential for analyzing market behavior. These curves represent the relationship between the quantity of a good or service available and its price, as well as the quantity consumers are willing to purchase at those prices. By mastering the interpretation of these curves, you can better understand how price changes affect market equilibrium and resource allocation.
Supply Curve: The supply curve shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity producers are willing to supply. As prices rise, producers are more willing to increase production, leading to a higher quantity supplied. This curve typically slopes upward from left to right.
Demand Curve: The demand curve illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity consumers are willing to buy. Generally, as prices fall, demand increases, meaning consumers are more likely to purchase the product. The demand curve typically slopes downward from left to right.
The point where the supply and demand curves intersect is known as the market equilibrium. At this point, the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and the market is in balance. Any shifts in the curves can result from changes in external factors like income, preferences, or production costs.
- Shifts in the Demand Curve: Factors like consumer income, the prices of related goods, or changes in consumer preferences can cause the demand curve to shift left or right, indicating an increase or decrease in demand at all price levels.
- Shifts in the Supply Curve: Changes in production costs, technological advancements, or input prices can shift the supply curve. A rightward shift indicates an increase in supply, while a leftward shift signifies a decrease.
Mastering these curves is fundamental for understanding market mechanics and predicting how changes in factors like price or production will affect supply and demand. Understanding the concepts of equilibrium, shifts, and price elasticity will also enhance your ability to interpret real-world economic situations.
Monetary and Fiscal Policy Overview
Government actions aimed at influencing economic activity are essential for maintaining stability and promoting growth. These policies are tools that policymakers use to regulate the economy, manage inflation, and reduce unemployment. By adjusting variables like interest rates, taxation, and government spending, authorities can control economic expansion and contraction to ensure the smooth functioning of the market.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to control the money supply and interest rates in an economy. By manipulating these factors, the central bank aims to achieve objectives such as controlling inflation, stabilizing currency value, and promoting full employment. Key tools include:
- Interest Rates: Central banks can adjust interest rates to influence borrowing and spending. Lower interest rates make loans cheaper, stimulating demand, while higher rates can slow down an overheated economy.
- Open Market Operations: This involves buying or selling government securities to regulate the amount of money circulating in the economy.
- Reserve Requirements: The central bank may adjust the reserve requirements for commercial banks, controlling the amount of money they can lend out to businesses and consumers.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence economic conditions. Through changes in tax rates or public expenditure, governments can stimulate or cool down economic activity. There are two primary types:
- Expansionary Policy: This policy seeks to increase government spending or decrease taxes to stimulate demand during periods of economic downturns.
- Contractionary Policy: This aims to reduce government spending or increase taxes to slow down an overheated economy, typically to control inflation.
Both monetary and fiscal policies are crucial for managing the overall health of an economy, but they often work in tandem, influencing each other and reinforcing efforts to achieve economic stability.
Real-Life Applications of Economic Concepts

Understanding fundamental principles of how markets operate can help us make sense of everyday decisions, from personal finance to global trade. These concepts are not only theoretical but are deeply embedded in the choices made by individuals, businesses, and governments alike. By applying these ideas, we can better navigate real-world challenges, such as setting prices, determining wages, or evaluating policy impacts on growth.
Price Determination in the Market
Price setting is a critical concept that affects the entire economy. From consumer goods to services, prices are influenced by the balance of supply and demand. In everyday life, this concept can be seen in action when grocery stores adjust prices based on demand for certain items, or when airlines change ticket prices depending on how many seats are left on a flight. Understanding how supply and demand curves affect these prices can help consumers make better purchasing decisions.
| Factor | Effect on Price |
|---|---|
| Increased Demand | Prices tend to rise as more consumers compete for a limited quantity of goods or services. |
| Decreased Supply | Reduced availability of a product or service leads to higher prices as sellers take advantage of scarcity. |
| Government Intervention | Price controls, such as minimum wages or rent limits, can distort the natural market price. |
Impact of Government Policies
Government policies, such as taxes, subsidies, and tariffs, directly affect the economy. For example, when a government imposes a tax on a product like tobacco, the cost of that product increases for consumers, which can lead to decreased demand. On the other hand, subsidies can encourage the production of certain goods, such as renewable energy, by lowering costs for producers and consumers. These actions are intended to steer economic activity in a desired direction, whether that’s reducing harmful consumption or encouraging innovation.
In personal finance, understanding economic principles allows individuals to make smarter investment choices, like when to buy or sell stocks based on market trends, or how to manage debt and savings in response to interest rate changes set by central banks.
Key Terms Every Student Must Know

Understanding the fundamental concepts in this field is essential for grasping how markets function and the role of policy in shaping economies. These terms form the building blocks that help explain broader principles and phenomena, whether you’re analyzing price fluctuations, understanding government intervention, or predicting market behavior. Mastery of these terms is crucial for any student looking to succeed in their studies and apply these concepts in real-world scenarios.
- Scarcity: Refers to the basic economic problem that arises because resources are limited while human wants are virtually limitless.
- Opportunity Cost: The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision. It’s the value of what you give up in order to choose another option.
- Supply and Demand: Fundamental concepts that explain how the price of goods and services is determined in a competitive market. Supply refers to how much the market can offer, while demand refers to how much consumers want it.
- Market Equilibrium: The point where the quantity of a good demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in a stable market price.
- Elasticity: Measures how the quantity demanded or supplied of a good changes in response to a price change. A product is said to be elastic if demand or supply changes significantly with price changes.
These key terms provide a foundation for more advanced concepts and are regularly encountered in everyday discussions about market conditions, government policies, and business strategies. A clear understanding of these terms allows students to think critically about various issues, both theoretically and practically.
Preparation Tips for Success

Effective preparation is key to performing well in any assessment. It’s not just about memorizing facts; it’s about understanding the material deeply and being able to apply it in various contexts. By organizing your study sessions and adopting productive strategies, you can boost your confidence and improve your performance. Here are some essential tips to help you succeed when it’s time to demonstrate your knowledge.
Time Management
Managing your time efficiently ensures you cover all necessary topics without feeling rushed. It helps reduce stress and allows for thorough understanding and retention of key concepts.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions well in advance. Break down the topics into manageable sections and allocate time for each one.
- Prioritize Difficult Areas: Focus on the areas that are most challenging for you. Give them extra time and effort to ensure mastery.
- Avoid Cramming: Study consistently over time instead of cramming at the last minute. Spacing out your sessions allows for better retention.
Active Learning Techniques
Engage with the material actively to enhance your understanding and memory. Active learning techniques encourage deeper processing of the content, making it easier to recall when needed.
- Practice with Past Material: Review old tests, quizzes, or practice questions to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions.
- Teach Someone Else: Teaching or explaining concepts to others helps reinforce your understanding and highlight any gaps in your knowledge.
- Use Mnemonics: Create mnemonic devices to remember complex information, such as formulas or key terms.
By following these tips and adopting a structured approach to your studies, you’ll increase your chances of success and feel more confident on assessment day. Preparation isn’t just about working hard–it’s about working smart.
Analyzing Economic Trends and Data

Understanding patterns and data is crucial for assessing the health and direction of markets and industries. By interpreting various statistics, we can uncover insights that inform decisions and forecast future outcomes. This process involves identifying key indicators, recognizing trends, and applying analytical techniques to interpret the information effectively. In this section, we will explore the fundamental aspects of analyzing such data and how to draw meaningful conclusions from it.
Key Indicators to Track
Certain indicators serve as reliable signals for assessing the state of an economy or a specific market. By monitoring these regularly, you can gain a better understanding of performance and predict future trends.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A primary indicator used to measure the total value of goods and services produced within a country. It reflects the overall economic activity.
- Unemployment Rate: A crucial measure of labor market health, indicating the percentage of the workforce that is actively seeking work but unable to find employment.
- Inflation Rate: This measures the rate at which prices for goods and services rise, which impacts purchasing power and cost of living.
Understanding Trends and Patterns
Trends reflect long-term movements in data that indicate potential changes in economic conditions. Recognizing these trends early can help forecast shifts in markets or economic environments.
- Long-Term Trends: These trends are typically observed over several years or decades and can show significant shifts in the economy, such as changes in consumer behavior or technological advancements.
- Short-Term Fluctuations: Short-term data can reveal immediate changes, often influenced by external factors such as policy changes, global events, or seasonal shifts.
- Volatility and Cycles: Markets and industries experience periodic cycles of growth and decline. Understanding these cycles helps predict future fluctuations and make informed decisions.
By mastering the analysis of economic data and trends, you gain valuable insights that allow you to make more informed decisions, whether for personal, corporate, or governmental purposes. This skill is key to interpreting the vast amounts of information available and applying it effectively to future planning and strategy.
Best Resources for Final Exam Revision

Preparing for an important assessment requires access to the right tools and materials. With the abundance of resources available, it can be challenging to select the most effective ones. In this section, we explore various study aids that will help you master the necessary concepts and boost your chances of success. From online platforms to textbooks and interactive guides, these resources are designed to cater to different learning styles and needs.
Utilizing a mix of materials will allow you to approach the subject from different angles, reinforcing your understanding. Whether you prefer reading, watching tutorials, or practicing with mock tests, there is a resource for every type of learner. Here are some of the best options available:
- Online Learning Platforms: Websites like Khan Academy, Coursera, and edX offer free courses and tutorials on a variety of topics. These platforms often provide video lectures, quizzes, and study guides tailored to help you grasp key concepts.
- Textbooks and Guides: Comprehensive textbooks can be invaluable for in-depth learning. Consider using recommended reading materials that break down complex theories and offer step-by-step explanations of key ideas.
- Practice Papers and Past Questions: Many students find it beneficial to practice using past papers. These not only give you a feel for the format but also help you identify common question types and frequently tested concepts.
- Flashcards and Apps: Tools like Quizlet can help reinforce key terms and concepts with interactive flashcards. They offer a quick way to review definitions and theories on the go.
- Study Groups and Forums: Joining a study group or online forum can provide additional perspectives on difficult topics. Discussing concepts with peers often enhances your understanding and allows you to clarify any doubts.
By selecting the right mix of resources, you can tailor your preparation to your own learning style and give yourself the best chance of success. Stay organized, stay consistent, and use these resources to build confidence ahead of your assessment.
Practice Questions for Assessment Preparation
One of the most effective ways to prepare for a major test is by practicing with sample questions that mirror the types of problems you will encounter. This section focuses on providing a variety of questions designed to reinforce your understanding and test your grasp of essential concepts. By solving these questions, you can identify areas where you need more practice and improve your problem-solving skills under timed conditions.
The following table provides a set of practice questions that cover a range of important topics. These questions are designed to challenge your knowledge and give you a better sense of what to expect. Take the time to work through them, and be sure to review your responses thoroughly to gain the most benefit from your practice.
| Question | Topic | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Explain the relationship between supply and demand in a competitive market. | Market Dynamics | Easy |
| Calculate the elasticity of demand given a price change and quantity change. | Price Sensitivity | Medium |
| Analyze the effects of a government-imposed price ceiling on consumer surplus. | Government Interventions | Medium |
| Describe the impact of monetary policy on national output and inflation. | Policy Impact | Hard |
| Compare and contrast the characteristics of perfect competition and monopoly. | Market Structures | Hard |
As you work through these questions, try to articulate your answers clearly and logically. This practice will help you strengthen your understanding and improve your performance on the actual test. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering any subject and achieving success.