
As you approach the culmination of your studies, it’s essential to focus on the key topics that will help you succeed. A strong understanding of critical events, influential individuals, and transformative movements will provide you with the foundation needed for a well-rounded performance.
By thoroughly reviewing pivotal moments and their lasting impacts, you’ll not only enhance your recall but also deepen your ability to make connections between different subjects. Grasping cause and effect relationships and recognizing patterns will be invaluable as you tackle a range of questions.
Make sure to prioritize your efforts by focusing on areas that have been repeatedly highlighted throughout the course. With careful preparation and a strategic approach, you’ll be well-equipped to demonstrate your knowledge effectively.
Comprehensive Test Preparation Strategies
In this section, we focus on the essential elements that will be required to succeed in your upcoming assessment. By reviewing the most significant topics, events, and figures, you will be able to approach your test with confidence. It’s crucial to understand the connections between different periods and how specific developments shaped the course of human progress.
Key Events and Figures
Familiarity with major milestones and influential personalities is vital. From the early civilizations to modern times, identifying their roles in shaping global society will ensure you are prepared for a variety of questions. These elements are often highlighted in multiple-choice and essay formats, requiring both memorization and analytical thinking.
Strategies for Effective Study

To make the most of your study time, it’s important to focus on areas that are both broad and deep. Concentrate on understanding the context of significant events, rather than just memorizing dates or names. Analyzing causes and effects, as well as recognizing recurring themes across time periods, will help you connect the dots and answer complex questions more easily.
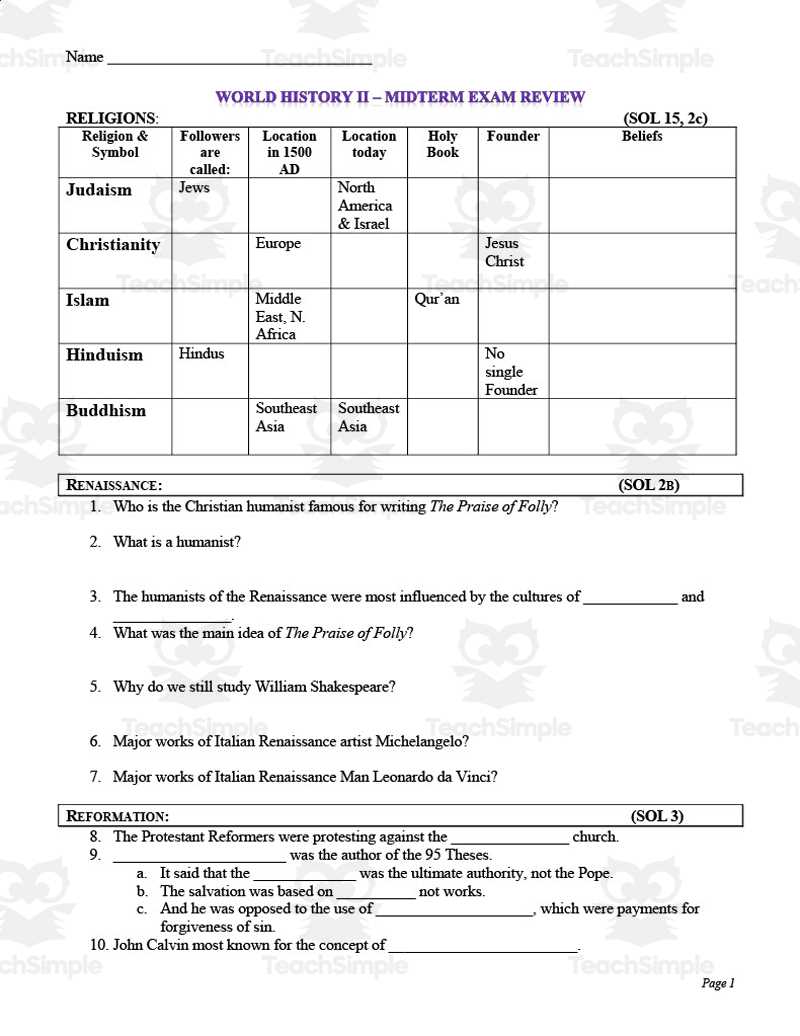
| Topic | Key Figures | Important Dates |
|---|---|---|
| Political Revolutions | Napoleon Bonaparte, Thomas Jefferson | 1789, 1776 |
| Global Conflicts | Winston Churchill, Adolf Hitler | 1914-1918, 1939-1945 |
| Technological Advancements | Alexander Graham Bell, Nikola Tesla | 1876, 1888 |
Key Topics to Focus On
Focusing on the right areas during your preparation will make a significant difference in your performance. Concentrating on pivotal themes and important developments will help you build a strong foundation for understanding the broader context of each subject. These key topics not only serve as the core of the material but also represent the most frequently tested concepts that require in-depth knowledge.
Major Civilizations and Their Influence

Understanding the contributions of ancient and modern civilizations will give you a solid grasp of cultural, political, and economic transformations over time. The development of societies such as Mesopotamia, Greece, Rome, and China has shaped the modern world in countless ways. Pay close attention to their innovations, governance structures, and global impact.
Revolutions and Social Change
Revolutions are often at the heart of many critical shifts in global dynamics. Be sure to review the causes, events, and outcomes of key uprisings like the French and Industrial Revolutions, as well as movements for social justice. These events not only transformed nations but also altered social and economic structures worldwide.
Important Dates and Events
Memorizing key dates and understanding the events that occurred on those days is a crucial part of preparing for any comprehensive assessment. Major milestones in human development often coincide with specific years or periods, marking shifts in power, technology, and society. Recognizing these moments and their implications will help you connect different topics and better understand the evolution of global affairs.
Critical Milestones in Political Change
Revolutions, treaties, and the rise and fall of empires have shaped the political landscape of nations. Pay attention to the dates of significant revolutions such as the French Revolution or the signing of important treaties like the Treaty of Versailles, as they had far-reaching effects on international relations and national boundaries.
Technological and Scientific Breakthroughs
Significant innovations often coincide with periods of rapid societal transformation. Familiarize yourself with the years in which key technological advances, such as the Industrial Revolution, the invention of the printing press, or the discovery of electricity, occurred. These moments not only changed industries but also transformed daily life across the globe.
Major Historical Figures
Throughout time, certain individuals have had a profound impact on shaping societies and events. These key figures often drive the course of revolutions, political changes, and cultural shifts, leaving legacies that are still felt today. Understanding their contributions and influence is essential for grasping the larger narrative of global development.
Influential Leaders and Statesmen

Figures such as Napoleon Bonaparte, Abraham Lincoln, and Winston Churchill played pivotal roles in defining the political landscape of their respective eras. Their decisions shaped the fate of nations and their leadership styles continue to be studied as examples of power and strategy.
Visionaries and Innovators
In addition to political leaders, there are those whose scientific, technological, and philosophical contributions changed the trajectory of human progress. Innovators like Leonardo da Vinci and Marie Curie, or thinkers like Karl Marx, have influenced various aspects of human thought, advancing fields such as art, science, and economics. Their ideas sparked revolutions of the mind that paved the way for modern advancements.
Understanding Historical Movements
Throughout time, various movements have reshaped societies and cultures, often leading to significant political, economic, and social transformations. These movements, whether they are revolutions, reform efforts, or shifts in philosophy, have a lasting impact on the direction of civilizations. Understanding the underlying causes and outcomes of these changes is essential for recognizing their broader significance in shaping the modern world.
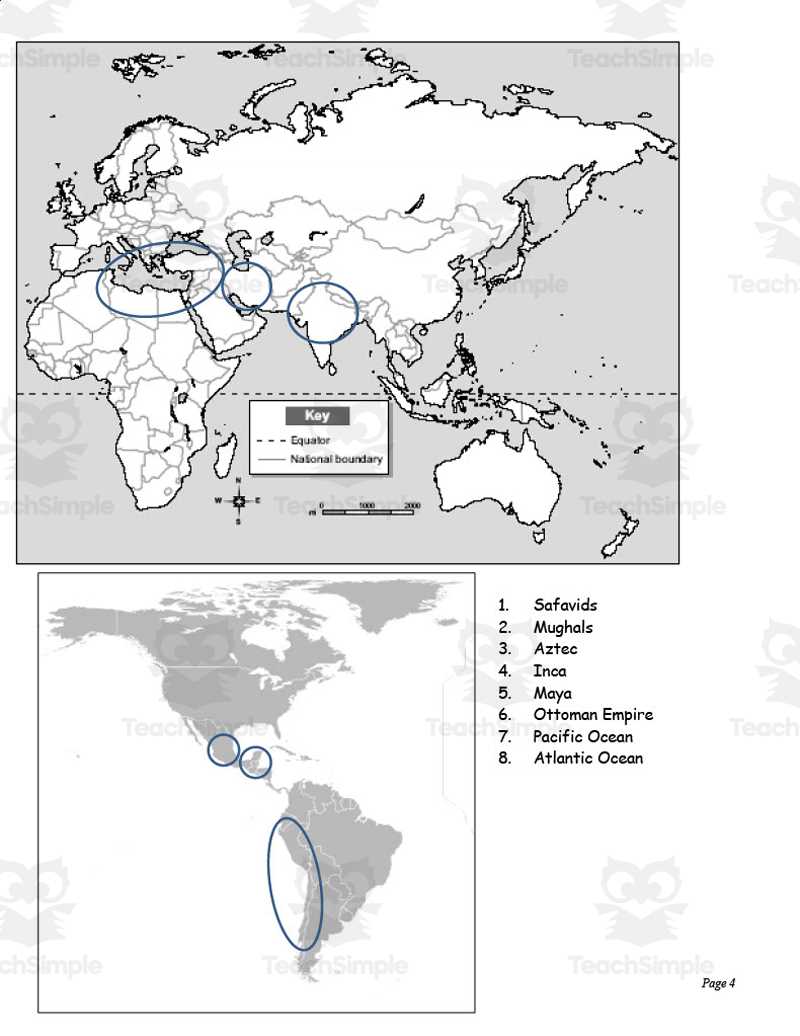
| Movement | Key Figures | Primary Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Renaissance | Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo | Revival of classical learning, artistic innovation, and humanism |
| Enlightenment | John Locke, Voltaire | Advancement of reason, individual rights, and scientific thought |
| Industrial Revolution | James Watt, Henry Ford | Technological advancement, mass production, and urbanization |
| Social Movements | Martin Luther King Jr., Susan B. Anthony | Equality, civil rights, and social justice |
Geography and Historical Context
The geographical features of regions significantly influence the course of human events. Mountains, rivers, and coastlines have shaped settlements, trade routes, and military strategies throughout time. Understanding how natural landscapes interact with human actions helps to explain the rise and fall of empires, the spread of cultures, and the development of civilizations.
Key Geographic Features and Their Influence
The location of a civilization often determined its access to resources, trade, and communication. Consider how geography played a role in major historical events:
- Rivers: The Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates enabled agriculture and early urbanization.
- Mountains: The Himalayas and Alps served as natural barriers for defense and cultural isolation.
- Oceans and Seas: The Mediterranean and the Atlantic facilitated trade, exploration, and empire expansion.
Environmental Factors and Societal Development
Different environments created varying challenges and opportunities for societies. For example:
- Desert regions like the Sahara required adaptation in terms of resource management and survival.
- Forested areas provided materials for construction and fuel but also created challenges for transportation and expansion.
- Tropical climates offered abundant resources but often brought disease and environmental instability.
Influence of Ancient Civilizations
Ancient cultures laid the foundation for many aspects of modern society, including politics, philosophy, architecture, and technology. Their innovations and ways of life had lasting impacts that shaped the trajectory of subsequent civilizations. Understanding how these early societies influenced the world is essential for appreciating the developments that followed and continue to affect us today.
| Civilization | Major Contributions | Legacy |
|---|---|---|
| Mesopotamia | Writing, Legal Systems, Agriculture | Foundation of organized governance and early technology. |
| Ancient Egypt | Architecture, Medicine, Mathematics | Advancements in engineering, preservation techniques, and cultural influences. |
| Ancient Greece | Philosophy, Democracy, Art | Development of political thought and cultural standards still relevant today. |
| Ancient China | Paper, Gunpowder, Silk | Technological innovations and cultural exchanges that shaped the modern world. |
Exploring Global Conflicts and Wars
Throughout human civilization, conflicts and wars have played pivotal roles in shaping political boundaries, economies, and social structures. From territorial disputes to ideological battles, these events have often been catalysts for change, transforming the course of nations and impacting generations. Understanding the causes, key players, and consequences of major conflicts helps us grasp the profound influence they have had on the world.
Major Wars and Their Impact
Several key conflicts throughout history have had lasting effects on both the countries involved and global relations. These wars often arose from a combination of political, economic, and social factors, including territorial expansion, resource competition, and ideological differences. Below are some of the most significant wars:
- World War I: A global conflict that altered the political landscape of Europe, leading to the fall of empires and the creation of new nations.
- World War II: A devastating war that reshaped international alliances and sparked the Cold War, while also accelerating technological and military advancements.
- The Cold War: A prolonged period of tension between major global powers, marked by proxy wars, nuclear arms competition, and ideological rivalry.
- The Korean War: A significant conflict that led to the division of Korea and had long-term effects on the balance of power in East Asia.
Consequences of Global Conflicts
The aftermath of major conflicts often leads to significant social, political, and economic changes. The effects of wars can include:
- Redrawing of national borders and the creation of new states.
- Economic devastation and the shift of global power dynamics.
- Mass migrations and the displacement of populations.
- Technological advancements spurred by military needs, such as aerospace and medical innovations.
Economic Systems Through History
Throughout time, societies have developed various systems to manage the production, distribution, and consumption of resources. These systems are shaped by factors such as geography, culture, and technological advancements, and they evolve to address the needs of a population. The transformation of these economic structures over time reflects changing values, priorities, and interactions among nations and peoples.
Early Systems and Barter Economy
In the earliest stages of human development, economies were often based on direct exchanges of goods and services, known as barter. As societies grew more complex, the need for more organized systems emerged. Early civilizations, such as those in Mesopotamia and Egypt, introduced basic forms of trade, but wealth was still largely tied to agricultural productivity and manual labor.
Feudalism and Agrarian Societies
During the medieval period, many regions operated under feudal systems, where land ownership and control were the primary means of economic power. Under this system, peasants worked the land in exchange for protection and a share of the harvest. This structure created a rigid social hierarchy and limited social mobility, but it remained a dominant economic model for centuries.
Capitalism and Market Economies
With the rise of the Industrial Revolution came the advent of capitalism, a system in which private individuals or corporations control the means of production. This marked a shift from agrarian economies to those driven by factories and mass production. Entrepreneurs and industrialists became central figures in these systems, and market competition led to increased innovation and productivity.
Socialism and Collective Ownership
In response to the inequalities created by capitalism, various socialist systems emerged, advocating for collective ownership and control of resources. In these systems, governments play a larger role in regulating industries and ensuring that wealth is distributed more evenly across society. Socialist ideas were particularly influential in the 20th century, with examples such as the Soviet Union and the rise of welfare states in Europe.
Social Structures in Different Eras
The organization of societies has varied greatly across time, with each era bringing its own systems of hierarchy and social roles. These structures often reflect the values, economic conditions, and political systems of the time. Understanding the social hierarchies of different periods helps us comprehend how power, wealth, and influence were distributed, and how these distributions shaped the lives of individuals within those societies.
Class Systems in Ancient Civilizations
In early civilizations, social stratification was often rigid, with individuals assigned to specific roles based on birth or occupation. Rulers, priests, and elites held significant power, while the majority of the population worked as farmers, artisans, or laborers. This division was often reinforced by religious or cultural beliefs, with the higher classes believed to possess divine favor or inherent superiority.
Feudal Society in the Middle Ages
During the medieval period, the social structure was heavily influenced by the feudal system. Power and land were concentrated in the hands of a few nobles, while the majority of the population, known as serfs or peasants, worked the land. This hierarchical system was maintained through a network of obligations, with peasants offering labor in exchange for protection. The Catholic Church also played a central role in maintaining the social order, acting as both a religious and political authority.
Technological Advancements and Impact

Throughout human progress, innovation in tools, machinery, and methods has shaped societies in profound ways. These developments not only improve efficiency and convenience but also redefine the way people live, work, and interact with their environment. From the earliest tools to the rise of digital technology, advancements in technology have consistently driven change and opened new possibilities for individuals and communities alike.
Revolutionary Inventions and Their Influence
Key technological breakthroughs have significantly altered human existence, often paving the way for further progress. Some of the most transformative inventions have had long-lasting effects on social structures, economies, and global relationships.
| Invention | Era | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| The Printing Press | Renaissance | Revolutionized the spread of knowledge, making books more accessible and fueling the Renaissance, Reformation, and Scientific Revolution. |
| The Steam Engine | Industrial Revolution | Powered factories, ships, and trains, drastically increasing production capacity and leading to urbanization and economic growth. |
| The Internet | Late 20th Century | Transformed communication, business, and access to information, shrinking the world and creating the digital age. |
Impact on Society and Economy
Technological advancements have had a dual effect on both social structures and economic systems. On one hand, new innovations create new opportunities for individuals and businesses, driving economic growth and improving living standards. On the other hand, they can also exacerbate inequalities, creating divides between those who have access to technology and those who do not.
The Role of Religion in History
Throughout time, belief systems have played a central role in shaping the actions of individuals and entire societies. Religion often provided the moral and ethical framework for law, governance, and daily life. It has influenced social structures, sparked movements, and at times, even fueled conflict. The intertwining of religious belief with political power has often defined the trajectory of civilizations, guiding leaders and communities toward certain goals while shaping cultural identities.
Religion as a Source of Authority
In many ancient and medieval societies, religion provided the legitimacy needed for rulers to govern. Monarchs often claimed divine right, asserting that their authority came directly from a higher power. Religious institutions, such as the Catholic Church in Europe or the temples in ancient Egypt, wielded significant political power, influencing decisions on matters of war, law, and governance.
Religious Movements and Social Change
Religious ideas have often been the catalyst for large-scale social movements, challenging established hierarchies and prompting reform. For instance, the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century led to religious and political upheaval, while the spread of Buddhism and Christianity across Asia and Europe prompted shifts in cultural norms and practices. These movements not only transformed religious landscapes but also had profound effects on education, science, and art.
Revolutions and Political Changes
Throughout time, dramatic shifts in governance and social structures have often been sparked by the collective actions of individuals and groups demanding change. Revolutions and political upheavals have reshaped entire societies, leading to the fall of old regimes and the establishment of new systems of rule. These moments of transformation have altered the course of nations and created lasting legacies that continue to influence the political landscape today.
Key Movements and Their Outcomes
Revolutions have frequently been driven by the desire for freedom, equality, or justice. Whether the cause was economic hardship, political corruption, or social inequality, these movements aimed to challenge entrenched power structures. Notable revolutions such as the French Revolution, the American Revolution, and the Russian Revolution brought about fundamental changes to political institutions, often leading to the rise of new ideologies and government systems.
Impact on Governance and Society
Revolutions often led to the creation of more inclusive political systems, but they could also result in instability, conflict, or authoritarian rule. The spread of ideas like democracy, republicanism, and communism during these periods had far-reaching effects on global governance. New forms of government emerged, challenging long-standing monarchies and empires, and reshaping the role of the individual within society.
Colonialism and Imperialism Effects

The expansion of powerful nations across the globe has had profound and lasting impacts on the regions they dominated. Colonialism and imperialism altered not only the political and economic structures of colonized territories but also reshaped cultural identities and social dynamics. These systems of control often involved exploitation of resources, suppression of local populations, and imposition of foreign governance and economic systems, creating legacies that continue to influence global relations today.
In many regions, colonial powers imposed new borders, disregarding existing ethnic, cultural, and political divisions. This often led to long-term conflicts, as newly formed nations struggled with the challenges of nation-building. Economic exploitation also played a central role, as colonies were used to extract raw materials, while local populations were subjected to forced labor or economic policies that benefited the colonizers.
Furthermore, the spread of imperialist ideologies shaped the development of global trade, the spread of new technologies, and the exchange of cultural practices. While this led to the spread of new ideas and technologies, it also caused significant disruption to indigenous cultures and societies. The effects of these practices are still felt today, as former colonies continue to grapple with the challenges of development, inequality, and the consequences of their colonial pasts.
Reforms and Social Movements
Throughout time, individuals and groups have organized to challenge societal norms and demand changes to improve living conditions, human rights, and equality. These movements have been instrumental in transforming governments, social structures, and cultural attitudes. Whether through political activism, legal reforms, or grassroots organizing, the impact of social movements has been profound, reshaping the way societies function and how individuals interact within those systems.
Key Movements and Their Goals
Social movements often arise in response to inequality, discrimination, or political repression. They seek to address issues ranging from civil rights and women’s rights to labor conditions and environmental protections. Some of the most notable movements include:
- Civil Rights Movement – Aimed at ending racial segregation and discrimination, particularly in the United States.
- Women’s Suffrage Movement – Focused on securing voting rights for women in many countries around the world.
- Labor Movements – Advocated for better working conditions, fair wages, and workers’ rights.
- Environmental Movements – Raised awareness about the need to protect natural resources and address climate change.
Impact of Social Movements

Reforms driven by these movements have led to significant changes in laws, policies, and social attitudes. For example, the abolition of slavery, the granting of voting rights to women, and the establishment of labor rights are all outcomes of widespread social mobilization. Additionally, these movements have encouraged more inclusive political systems, pushing for greater representation and fairness in governance.
While progress has been made, many movements continue to fight for further reforms. The struggles for equality, justice, and environmental sustainability are ongoing and remain at the forefront of global activism today.
Historical Perspectives on Democracy

The concept of governance by the people has evolved over millennia, influencing political structures and the relationships between rulers and the ruled. Over time, various cultures and societies have experimented with different forms of self-rule, each contributing to the modern understanding of democracy. From the ancient city-states to the rise of representative governments, the idea of a political system where power is vested in the people has played a crucial role in shaping civilizations and fostering political participation.
Origins and Early Models

The foundations of democratic principles can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where the ideas of citizen participation and public decision-making began to take form. Early examples include:
- Athenian Democracy – Often regarded as the birthplace of direct democracy, where citizens could vote on laws and policies directly in assemblies.
- Roman Republic – Introduced a mixed system of governance, combining elements of democracy, aristocracy, and monarchy, with elected officials representing the people.
- Medieval Assemblies – Early parliaments and councils in Europe were precursors to more representative forms of government, where nobility and clergy had a voice in decision-making.
Modern Developments and Challenges
The modern era saw the rise of more structured and formal systems of democracy, particularly with the expansion of voting rights and the establishment of political parties. Key developments in the spread of democratic ideals include:
- Enlightenment Thinkers – Philosophers such as John Locke, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and Montesquieu promoted ideas about individual rights, the separation of powers, and the social contract, which influenced the creation of modern democratic systems.
- American and French Revolutions – Both revolutions played a pivotal role in establishing the principles of popular sovereignty and the idea of citizens’ rights, serving as models for democratic movements worldwide.
- Universal Suffrage – Over time, democratic systems extended voting rights to all citizens, regardless of gender, race, or social class, further expanding political participation.
While democracy has made significant strides globally, challenges remain. Issues such as voter suppression, political polarization, and the balance between majority rule and minority rights continue to shape the ongoing debate about democratic governance.
Tips for Success

Achieving success in a comprehensive assessment requires more than just memorization. It involves effective preparation, time management, and strategic approaches to problem-solving. By organizing your study efforts and focusing on key concepts, you can maximize your performance and increase your chances of success. Below are some practical tips to help you prepare and excel.
Effective Study Strategies
- Create a Study Schedule: Organize your time in advance to ensure you cover all the necessary material. Break your study sessions into manageable chunks, and allocate time for review.
- Active Learning: Engage with the material actively by summarizing key points, creating flashcards, or teaching concepts to someone else. This will reinforce your understanding.
- Prioritize Key Topics: Focus on the areas that are most likely to appear in the assessment, especially those that have been emphasized in class or covered in review materials.
Test-Taking Techniques
- Read Carefully: Read each question thoroughly before answering. Ensure that you understand what is being asked before jumping to conclusions.
- Manage Your Time: Allocate specific amounts of time to each section, and keep track of your progress to avoid spending too much time on any one question.
- Stay Calm and Focused: If you feel stuck, move on to the next question and return to the challenging ones later. A calm mindset will help you think more clearly.
By following these strategies, you can improve both your preparation and performance, leading to a more successful outcome. Remember, consistency and a positive attitude go a long way toward achieving your goals.