
When preparing for a professional networking certification, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of both theoretical knowledge and real-world application. This section focuses on testing your ability to perform key tasks under pressure, simulating the conditions you’ll encounter in the field. The ability to configure, troubleshoot, and manage networking systems efficiently is critical for any network professional.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything from setting up networks to diagnosing and solving issues. With hands-on practice, you can build the confidence and competence needed to succeed. Practical experience not only helps you understand complex concepts but also prepares you for challenges that go beyond theoretical learning. Each task requires attention to detail, precision, and quick problem-solving skills, qualities that are indispensable in the networking industry.
Through proper preparation, you can approach these tests with confidence. The key to mastering these tasks lies in consistent practice, a deep understanding of core networking principles, and the ability to apply knowledge in dynamic environments. With the right approach, success is within reach.
CCNA Practical Testing Guide
This section is designed to help you navigate through the hands-on tasks required for obtaining a networking certification. In a professional environment, being able to perform technical tasks efficiently and correctly is just as important as theoretical knowledge. The ability to configure, troubleshoot, and optimize network systems is a key aspect of your certification journey.
To succeed, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the types of challenges you’ll face. Below are the core areas you should focus on:
- Configuration – Setting up devices, assigning IP addresses, and ensuring proper connectivity.
- Troubleshooting – Identifying and resolving common network issues, from connectivity problems to performance issues.
- Routing and Switching – Managing traffic flow between networks, configuring routers, and optimizing switches.
- Security – Implementing basic security protocols, firewalls, and access controls.
- Network Monitoring – Using tools to assess the health and performance of a network.
Successful preparation involves more than just reading through manuals. You need hands-on practice in real-world scenarios to sharpen your abilities. Setting up lab environments will allow you to experiment with various devices and configurations, simulating the conditions you will face in actual work settings.
Some key steps to follow during preparation:
- Practice regularly – Spend time working with networking equipment and virtual labs to build familiarity.
- Focus on time management – Allocate enough time for each task and avoid rushing through solutions.
- Simulate test scenarios – Recreate real-world network problems and troubleshoot them under test conditions.
- Review and analyze – After each practice session, review your work, learn from your mistakes, and refine your approach.
Approach these practical tasks with a problem-solving mindset. The more comfortable you become with configuring and diagnosing networks, the more prepared you will be for the challenges ahead.
Understanding the Test Format
Understanding the structure of the practical assessment is crucial for effective preparation. This evaluation is designed to measure your ability to perform various network tasks in real-world scenarios. Instead of theoretical questions, you will be required to configure, troubleshoot, and optimize network systems, simulating tasks you might face in a professional environment.
Task Types
The practical evaluation typically involves a combination of different task types that assess various networking abilities. These tasks are designed to simulate real-world challenges and test your practical knowledge under time constraints. Below are the most common types of tasks you can expect:
- Configuration – Setting up devices and networks, assigning IP addresses, and ensuring connectivity.
- Troubleshooting – Diagnosing and solving connectivity and performance issues within a network setup.
- Security Setup – Implementing security measures such as access controls, firewalls, and encryption protocols.
Time Constraints and Structure
The test is time-sensitive, meaning you will need to complete each task within a set time frame. Efficiency is just as important as accuracy, as the ability to solve problems quickly while maintaining precision is essential in real-world network administration. Each task will be graded based on your ability to complete it correctly within the allocated time, as well as your problem-solving approach.
Proper preparation should include time management practices, where you simulate the test environment to familiarize yourself with the pace of completing tasks. In addition, understanding the expectations for each task will help you focus on the right areas and avoid common pitfalls.
Key Skills Required for Success
To excel in a practical network assessment, a variety of technical competencies are necessary. These abilities go beyond just knowing theory–they require hands-on expertise in configuring, maintaining, and troubleshooting network systems. Understanding the key areas and developing proficiency in each will give you the confidence to perform tasks accurately and efficiently under test conditions.
Core Networking Knowledge
Strong foundational knowledge of networking concepts is essential. This includes understanding the principles of IP addressing, subnetting, and routing protocols. Additionally, familiarity with switching technologies and network topologies is necessary to effectively manage and optimize network systems. Without a solid grasp of these core concepts, troubleshooting and configuration tasks will become more challenging.
Problem-Solving and Troubleshooting
In real-world network management, issues are bound to arise, and the ability to quickly identify and resolve these problems is crucial. Troubleshooting requires logical thinking and a methodical approach to diagnosing problems, whether it’s connectivity issues, performance drops, or configuration errors. Mastery of diagnostic tools and commands will allow you to pinpoint issues swiftly and implement solutions effectively.
Along with technical knowledge, success also depends on your ability to stay calm under pressure and manage your time effectively. Preparing for practical tasks means practicing real-world problems in a controlled environment so that when the time comes, you are ready to perform without hesitation.
How to Prepare Effectively
Preparation for a hands-on network evaluation requires more than just passive reading. To perform well, you must engage in active practice, developing the ability to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios. Successful preparation involves building both your technical abilities and your problem-solving approach, ensuring that you are comfortable with the tasks you will encounter.
Follow these strategies to ensure a thorough and efficient preparation process:
- Set Up Practice Labs – Create a lab environment where you can configure devices, experiment with different setups, and troubleshoot issues. Using virtual machines or real hardware can help replicate real-world scenarios.
- Simulate Test Conditions – Practice under time constraints, just as you will in the actual test. This helps you become accustomed to working efficiently while maintaining accuracy.
- Master Networking Commands – Ensure you are familiar with essential commands for device configuration and troubleshooting. The more comfortable you are with network commands, the faster you can complete tasks.
- Review Core Concepts – Continuously review fundamental networking topics such as routing, switching, IP addressing, and network security. Make sure these core concepts are ingrained in your knowledge.
Beyond technical practice, focus on developing strong time management and problem-solving skills. As you work through practice scenarios, think critically about the issues you’re solving and how to do so in the most efficient manner possible.
By incorporating these strategies into your routine, you’ll build the confidence needed to tackle any challenge during the practical test. Remember, the key to success is not just knowing the material, but being able to perform under pressure and solve problems on the spot.
Common Challenges in Hands on Testing
When participating in a practical network assessment, various challenges can arise that test both your technical knowledge and your ability to perform under pressure. Unlike theoretical exams, hands-on tasks require you to think critically and solve problems in real-time, often with time constraints. Identifying and overcoming these obstacles is key to success.
Time Management Issues
One of the most common challenges is managing the time effectively during the test. Many tasks require several steps to complete, and performing these tasks under a time limit can lead to unnecessary stress. It’s important to practice working quickly without compromising accuracy, ensuring that you can efficiently allocate time to each task.
Configuration and Troubleshooting Complexities
Configuring devices and networks can sometimes be more complicated than expected. Simple mistakes in IP addressing, subnetting, or routing can cause issues that take time to identify and fix. Additionally, troubleshooting connectivity or performance problems can be frustrating when the issue isn’t immediately obvious. A systematic approach to diagnosing issues, as well as familiarity with common configuration pitfalls, can help reduce errors and improve performance.
To overcome these challenges, it’s important to practice troubleshooting methods and become familiar with common network configurations. Recreating real-world scenarios in your practice labs will help you gain confidence in resolving unexpected issues.
Being well-prepared for these challenges can make a significant difference in your performance. Keep refining your approach to managing time and troubleshooting effectively, and you’ll be better equipped to handle the pressure of the test environment.
Best Study Resources for the Test

Having the right study materials is essential for preparing for a practical network assessment. To ensure success, it is important to utilize a variety of resources that cover both theoretical concepts and practical hands-on tasks. From textbooks to online labs, the following tools can help reinforce your knowledge and improve your ability to perform under test conditions.
The table below outlines some of the best resources available for your preparation:
| Resource Type | Details | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Books | Comprehensive coverage of networking concepts, theory, and practical configurations. | Understanding fundamentals and in-depth knowledge. |
| Online Courses | Interactive lessons and tutorials with practice exercises and assessments. | Learning at your own pace with guidance from experts. |
| Practice Labs | Simulated environments where you can practice configuring devices and solving network issues. | Hands-on experience with real-world scenarios. |
| Video Tutorials | Step-by-step video guides showing real-time configuration and troubleshooting. | Visual learners who benefit from seeing tasks in action. |
| Flashcards | Quick reference for memorizing commands, configurations, and protocols. | Reinforcing knowledge of essential networking terms. |
By combining these resources, you can develop a well-rounded study plan that includes both theory and practice. The more exposure you have to real-world scenarios and practical configurations, the more prepared you will be for the assessment.
Time Management Tips During the Test
Effective time management is crucial when undergoing a practical network assessment. The ability to complete each task within the allocated time while maintaining accuracy can significantly impact your performance. Developing a strategy for managing your time during the test will help reduce stress and increase your chances of success.
Prioritize Tasks
Start by identifying the tasks that seem most complex or time-consuming. If a task requires more effort or problem-solving, it might be wise to address it early when your energy and focus are at their peak. On the other hand, simpler tasks can be saved for later, ensuring that you tackle the most challenging problems first while you’re still fresh.
Track Time Carefully
It is essential to be aware of the time remaining throughout the test. Consider setting a mental timer or using a clock to keep track of how long you’ve spent on each task. Regularly check your progress to ensure you are staying within the expected time limits. If you’re spending too much time on one task, move on to the next and return to it if necessary. This will ensure that all areas are covered before the time runs out.
By practicing these time management strategies, you can approach the assessment with confidence, knowing that you are equipped to handle the tasks efficiently while minimizing pressure.
Real-World Scenarios in the Test
In a practical network evaluation, the tasks you will face are designed to simulate real-world scenarios that network professionals encounter daily. These scenarios test not only your technical knowledge but also your ability to think critically and solve problems in a dynamic environment. It’s essential to prepare for tasks that require hands-on problem-solving and configuration management, as these situations closely mirror the challenges faced by IT professionals in the field.
Types of Real-World Scenarios
The following types of situations are commonly encountered during practical assessments:
- Network Configuration – You may be asked to configure routing protocols, IP addressing, or virtual LANs (VLANs) to simulate a network setup.
- Troubleshooting Connectivity – Identifying and fixing connectivity issues, such as incorrect IP configurations or faulty cables, is a common challenge.
- Security Implementation – Applying firewall rules, configuring VPNs, and ensuring proper security protocols are set up are also frequent scenarios.
- Device Management – Tasks may include configuring network devices, such as routers and switches, ensuring proper operation and interconnectivity.
How to Approach Real-World Scenarios
To succeed in these types of tasks, it’s important to adopt a methodical approach:
- Understand the Requirements – Before jumping into configuration or troubleshooting, make sure you clearly understand the task at hand and the expected outcome.
- Stay Organized – Break the task down into smaller steps and address each one systematically, ensuring no part of the task is overlooked.
- Test Solutions – After implementing changes, always test your configurations to ensure everything works as expected before moving on.
- Document Changes – Keep track of changes made during the process to help troubleshoot and provide a reference in case issues arise later.
By familiarizing yourself with these real-world scenarios and practicing similar tasks in a controlled environment, you can enhance your ability to solve problems effectively and efficiently during the test.
How to Set Up Lab Environments
Creating a dedicated lab environment for practicing network configurations and troubleshooting is crucial for gaining hands-on experience. A well-organized lab setup allows you to replicate real-world network scenarios, test configurations, and resolve issues before performing them in a high-pressure test setting. By simulating various network conditions, you can build confidence and refine your technical abilities.
There are a few key considerations when setting up your own lab environment:
1. Choose the Right Hardware and Software

To effectively simulate network environments, you’ll need the appropriate hardware and software. While physical devices such as routers and switches are ideal, they can be expensive. Alternatively, you can use network simulators or emulators like GNS3 or Packet Tracer, which allow you to create virtualized networks without requiring expensive equipment. These tools replicate real-world configurations and help you practice common tasks such as routing, IP addressing, and VLAN setups.
2. Design a Realistic Network Topology
Once you’ve selected your tools, designing a network topology is the next step. Start with basic setups such as a small local area network (LAN) and gradually build complexity by adding more routers, switches, and subnets. A good practice is to create a layout similar to those used in actual network environments, so you can gain experience with the configurations you’re likely to encounter.
- Basic Network – Start with a simple LAN and connect it to a router, simulating an internet connection.
- Intermediate Network – Add additional routers and switches to create more complex scenarios involving routing protocols and subnetting.
- Advanced Network – Integrate VPNs, security protocols, and firewall configurations for a more realistic, enterprise-level network simulation.
3. Test and Troubleshoot
The real value of your lab environment comes from testing and troubleshooting. Create problems intentionally within your network to practice identifying and resolving issues. For instance, misconfigure IP addresses or routing protocols and then troubleshoot until you identify and correct the mistake. This process will sharpen your problem-solving skills and prepare you for unexpected challenges.
By setting up a hands-on lab environment, you can gain invaluable practice that will greatly enhance your preparedness for real-world network tasks and assessments.
Practice Labs and Simulations
Practice labs and simulations are powerful tools for mastering the technical concepts and tasks involved in network management and configuration. They allow you to work in a controlled environment where you can experiment with different setups, test configurations, and solve complex issues without the pressure of a live environment. These virtual setups offer a hands-on approach to learning, enabling you to practice real-world scenarios safely and efficiently.
There are several key advantages to using practice labs and simulations:
- Hands-on Experience – Simulations provide the opportunity to engage with networking equipment and software in real-time, helping you develop practical expertise that is difficult to gain through theoretical learning alone.
- Cost-Effective – While setting up a physical network lab can be expensive, simulations offer a cost-effective alternative by allowing you to create complex networks using virtual devices.
- Safe Environment for Experimentation – You can test configurations, troubleshoot issues, and make mistakes without worrying about damaging real equipment or affecting production systems.
- Scalable Learning – Practice labs allow you to start with basic tasks and gradually advance to more complex scenarios, providing a scalable learning experience as you build your skills.
Popular tools for creating practice labs include network simulators such as Packet Tracer and GNS3, both of which allow you to simulate various network topologies, configure devices, and troubleshoot issues in a virtual environment. These tools offer pre-built labs, as well as the flexibility to create custom setups, allowing you to focus on specific areas that need improvement.
By regularly using practice labs and simulations, you can develop a deeper understanding of networking concepts, increase your troubleshooting abilities, and become more confident in handling the challenges you may face in real-world scenarios.
Mastering Networking Fundamentals
A solid understanding of networking fundamentals is essential for success in any network-related field. These foundational concepts form the building blocks for more advanced configurations and troubleshooting techniques. By mastering the basics, you ensure that you can approach any network-related task with confidence and precision, from configuring devices to diagnosing connectivity issues.
Key concepts to focus on include:
- IP Addressing – Understanding IP addressing is crucial for creating, managing, and troubleshooting networks. Learn about IPv4 and IPv6 address structures, subnetting, and network addressing schemes.
- Routing – Routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP are the core of directing traffic through networks. Knowing how they work and how to configure them allows you to create efficient, scalable networks.
- Switching – Mastering switching concepts, including VLANs, trunking, and STP (Spanning Tree Protocol), will help you manage traffic within a local network, optimize performance, and reduce errors.
- Network Security – Learn about securing networks using firewalls, access control lists (ACLs), and VPNs to ensure that data flows safely and securely across your infrastructure.
- OSI Model – The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is fundamental for troubleshooting and understanding how different layers of networking interact with each other, from physical transmission to application-level protocols.
Mastering these basics creates a strong foundation for more advanced concepts, such as network automation, virtualization, and cloud integration. With a deep understanding of networking fundamentals, you’ll be better equipped to solve complex problems, design networks, and manage systems with ease.
Configuration and Troubleshooting Tips
Efficient network configuration and troubleshooting are vital skills for maintaining a stable and secure infrastructure. Understanding common issues, knowing how to configure network devices correctly, and troubleshooting problems quickly are key to ensuring network reliability. This section covers essential tips for both configuring devices and addressing network challenges effectively.
Configuration Best Practices
When setting up network devices, following best practices ensures a smooth and error-free process. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Plan Before You Configure – Always have a clear plan for addressing IP addressing, subnetting, and routing. Design your network carefully to avoid misconfigurations.
- Use Consistent Naming Conventions – Consistent naming of interfaces, devices, and VLANs makes network management easier and reduces confusion in large environments.
- Document Everything – Keep detailed records of configurations, IP addresses, and network maps to make troubleshooting faster and more efficient in the future.
- Verify Configurations – After configuring devices, use tools like ping and traceroute to verify the correctness of your settings and ensure connectivity.
Troubleshooting Strategies
When network problems arise, a systematic approach to troubleshooting can save time and reduce the risk of further issues. Here are essential strategies:
- Use the OSI Model – Break down problems by the layers of the OSI model to isolate issues in specific areas, such as hardware, protocols, or applications.
- Check Physical Connections – Ensure all cables are connected properly, devices are powered on, and interfaces are not administratively down.
- Monitor Logs and Alerts – Examine device logs, error messages, and alert systems to identify signs of potential issues.
- Perform Network Tests – Tools like ping, show commands, and debug commands can help pinpoint connectivity problems or configuration errors.
By following these configuration and troubleshooting tips, you will improve your ability to manage and maintain network devices, ensuring optimal performance and reducing downtime in your network environment.
Essential Networking Commands to Know
Mastering essential network commands is crucial for configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting network devices. These commands help network engineers and administrators to interact with devices, verify configurations, and diagnose problems effectively. Below, we cover the most important commands that are essential for working with networking equipment in day-to-day operations.
Basic Device Configuration Commands
These commands allow you to configure basic settings, such as IP addresses, interfaces, and routing protocols on network devices:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
show running-config |
Displays the current configuration on a device. |
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode to configure the device. |
ip address [IP address] [subnet mask] |
Configures an IP address and subnet mask on an interface. |
interface [interface name] |
Enters interface configuration mode to configure a specific interface. |
no shutdown |
Activates an interface. |
Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Commands
These commands are used to monitor device performance, troubleshoot connectivity issues, and verify network status:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ping [IP address] |
Tests connectivity between devices on the network by sending ICMP packets. |
traceroute [IP address] |
Displays the path packets take to reach a specific destination. |
show ip route |
Displays the routing table of the device. |
show interfaces |
Shows the status and statistics of all interfaces on the device. |
show log |
Displays the system log, useful for troubleshooting issues. |
By familiarizing yourself with these essential commands, you will enhance your ability to configure and manage network devices more efficiently and effectively. These commands form the backbone of most day-to-day tasks for network professionals and are fundamental for troubleshooting and network optimization.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Test
When taking a practical assessment, it’s essential to be mindful of several common pitfalls that can negatively impact performance. Often, candidates make simple mistakes that could have been avoided with careful preparation and attention to detail. By understanding these potential errors, you can approach the challenge with more confidence and improve your chances of success.
1. Failing to Read Instructions Carefully

One of the most common mistakes is not thoroughly reading the instructions provided at the beginning of each task. Skipping or misinterpreting instructions can lead to unnecessary confusion or even incorrect configurations. Always take a few moments to review the requirements before diving into the task.
2. Not Managing Time Effectively
Time management is critical during any practical test. Without a clear strategy for dividing time between tasks, you may end up rushing through critical parts or neglecting important details. Here are some tips to avoid this mistake:
- Set a timer: Allocate specific time slots for each section or task.
- Prioritize tasks: Work on easier tasks first to build confidence, then tackle more complex ones.
- Review at the end: Reserve the last few minutes for reviewing your work and making adjustments.
3. Overlooking Basic Network Configuration
Many candidates get caught up in advanced troubleshooting or configuration tasks, forgetting to check fundamental settings. Always ensure the basics are properly configured, such as:
- IP addresses and subnet masks
- Interface status (e.g., up or down)
- Default gateway configuration
4. Not Verifying Configurations
Once you have completed a configuration task, it’s vital to verify that everything is functioning correctly. Failing to check or test your configuration could result in errors that are difficult to troubleshoot later. Use commands like show running-config and ping to confirm your settings.
5. Ignoring Error Messages
Error messages are there for a reason–they provide valuable information about what went wrong. Avoid ignoring them or glossing over them. Instead, take the time to read and interpret the message carefully, as it may point you directly to the problem.
6. Rushing Through the Troubleshooting Process
When troubleshooting network issues, it’s tempting to rush in with a solution, but this can lead to missed root causes. Take a structured approach to troubleshooting, such as the following:
- Identify the issue clearly.
- Test basic connectivity (e.g., using
pingortraceroute). - Isolate the problem to a specific area (e.g., a particular interface or routing issue).
- Implement changes one at a time and retest.
7. Neglecting to Save or Apply Changes
It’s easy to forget to save your changes, especially when working under time pressure. Always remember to save your configuration after making adjustments to ensure that your work is preserved. Use commands like write memory or copy running-config startup-config to save your progress.
Avoiding these common mistakes will significantly improve your ability to navigate through the test and demonstrate your knowledge and abilities. By being proactive, managing your time efficiently, and focusing on accuracy, you will be well-prepared for any challenges that arise.
How to Handle Exam Stress
Managing stress during a practical assessment is crucial for maintaining focus and performing at your best. High-pressure situations can often cause anxiety, leading to mistakes or missed opportunities. By developing effective strategies for coping with stress, you can stay calm, confident, and clear-headed throughout the entire process.
1. Preparation is Key

The best way to reduce anxiety is thorough preparation. When you feel well-prepared, you’ll approach the tasks with confidence. Make sure to:
- Practice key concepts and tasks regularly.
- Familiarize yourself with the test format and possible scenarios.
- Review common mistakes and troubleshooting methods.
2. Practice Relaxation Techniques
In high-stress situations, it’s essential to know how to relax. Simple techniques like deep breathing can help lower stress levels and clear your mind. Practice these exercises before the test:
- Deep Breathing: Take slow, deep breaths to reduce anxiety and help your mind focus.
- Visualization: Picture yourself successfully completing the tasks and handling challenges with confidence.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and relax your muscles to release physical tension.
3. Time Management to Avoid Pressure
One of the biggest sources of stress is feeling rushed. Managing your time effectively can help alleviate this pressure. Consider these strategies:
- Break the tasks into manageable chunks and allocate specific time for each.
- Prioritize tasks based on difficulty and time required.
- Leave a few minutes at the end to review your work and make adjustments.
4. Stay Positive and Focused

Maintaining a positive mindset is essential for managing stress. Negative thoughts can increase anxiety and hinder your performance. Focus on:
- Self-Encouragement: Remind yourself of your strengths and past successes.
- Staying Present: Concentrate on the task at hand rather than worrying about the outcome.
- Resilience: If you encounter a challenge, stay calm and tackle it systematically instead of getting frustrated.
5. Take Breaks and Stay Hydrated

During long sessions or practice, taking breaks can significantly reduce stress. A quick walk or a few minutes of stretching can recharge your focus. Additionally, staying hydrated helps maintain mental clarity and reduces physical tension. Avoid over-caffeinating, as it can increase anxiety.
6. Seek Support if Needed
If you find yourself overwhelmed, it’s important to reach out for support. Talk to peers, mentors, or instructors who can offer guidance and encouragement. Sometimes, simply voicing your concerns can provide relief and help you regain composure.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll be better equipped to handle stress and approach any practical assessment with a calm and confident mindset. Preparation, relaxation, and mental clarity are all key to performing your best under pressure.
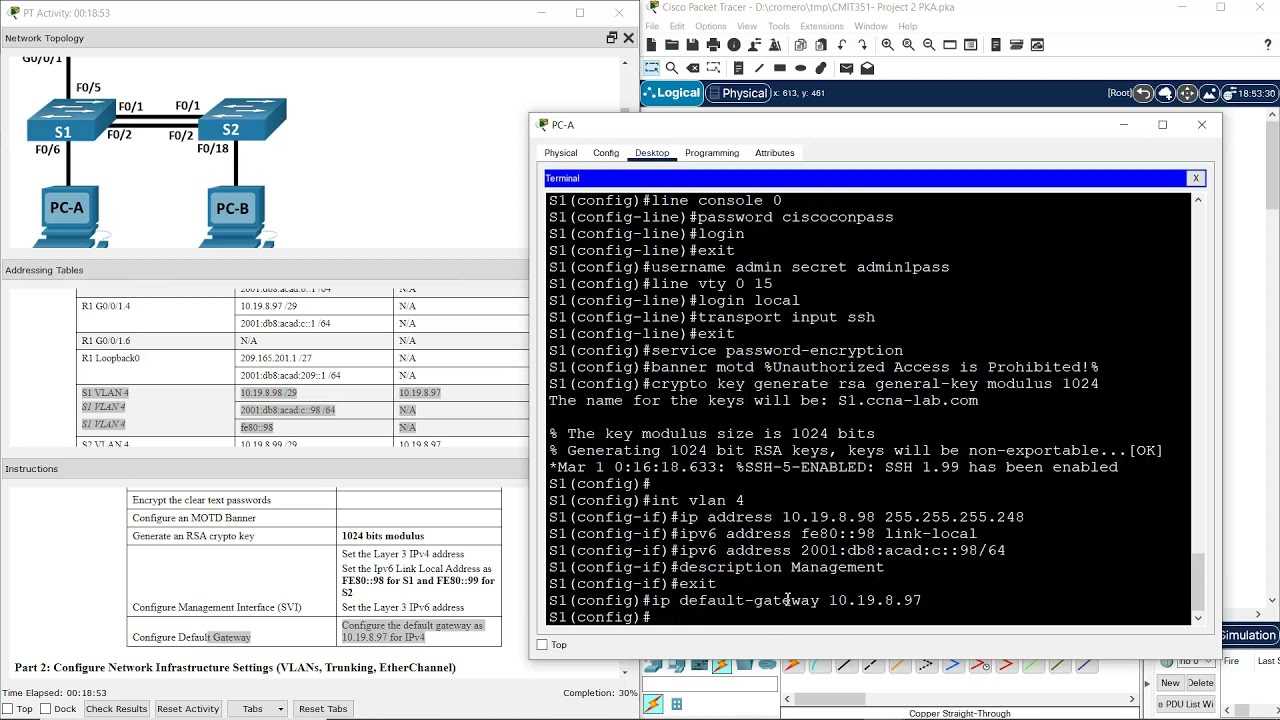
What to Expect on Test Day
On the day of your assessment, it’s important to be prepared both mentally and physically for the challenges ahead. The environment will be structured to simulate real-world situations, providing an opportunity to demonstrate your technical abilities. The key to success is staying organized, managing time wisely, and keeping calm throughout the process. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect.
Pre-Test Preparation
Before you begin, there are a few things to remember:
- Arrive at the testing center early to ensure you have plenty of time to settle in and review any last-minute notes.
- Bring valid identification, as you may be required to verify your identity before starting.
- Prepare mentally by reviewing your study materials briefly, but avoid cramming at the last minute. Trust in your preparation.
Test Environment
The testing area is designed to closely resemble real-world scenarios, with workstations equipped for hands-on tasks. Expect to see:
- Computer terminals or network equipment set up for configuration and troubleshooting tasks.
- Clear instructions on how to approach each task, often accompanied by a timer to track your progress.
- Minimal distractions to ensure that you remain focused on the tasks at hand.
Types of Tasks
During the test, you will be required to complete a series of practical exercises that assess your technical knowledge and ability to apply it. Tasks may include:
- Configuring devices such as routers and switches.
- Setting up network connections and services.
- Diagnosing issues and implementing solutions within given time constraints.
Time Management
Time is an important factor in this type of assessment. You will likely be given a set amount of time for each task, and it’s crucial to manage it efficiently. Here are some tips:
- Read through the instructions thoroughly before starting to avoid mistakes.
- Focus on the most critical tasks first, and leave room for troubleshooting.
- Keep an eye on the clock, but don’t panic if you’re running short on time. Stay calm and proceed methodically.
Post-Test Process
Once you’ve completed the tasks, the next steps typically involve:
- Submitting your work for review. This may involve reviewing your configuration and ensuring that all requirements have been met.
- Receiving feedback either immediately or at a later date, depending on the assessment process.
- Reflecting on your performance to identify areas for improvement, regardless of the outcome.
Test Results
While you might feel anxious about the results, remember that the assessment is designed to gauge your practical abilities. Results may be delivered on the same day or within a few days, depending on the testing center’s procedures.
Commonly Asked Questions on Test Day
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can I use notes during the test? | Generally, no. You are expected to rely on your knowledge and experience. |
| What happens if I make a mistake? | Minor errors are common and typically won’t disqualify you, but the faster you identify and correct mistakes, the better. |
| Can I ask for help if I’m stuck? | Typically, no. You are expected to complete the tasks independently. |
By understanding the structure and expectations of the assessment day, you can approach it with confidence, ready to demonstrate your expertise and problem-solving abilities.
Post-Assessment: Next Steps in Your Career
After completing the assessment, the journey doesn’t end there. It marks a critical point in your professional development, offering numerous opportunities for growth. Whether you passed or need to reattempt, it’s important to plan your next steps carefully to build on the knowledge you’ve gained. This phase is about reflecting on your achievements, identifying areas for improvement, and leveraging your new credentials to advance in your career.
Reflect on Your Performance
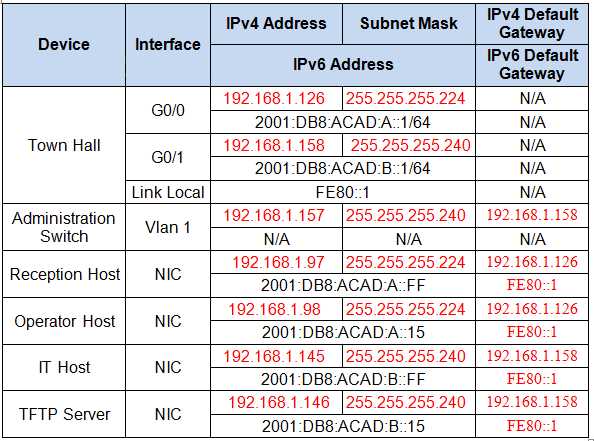
Take time to evaluate how you performed during the assessment. Consider the tasks that went smoothly and those that posed challenges. Self-assessment can help you identify strengths and weaknesses that you can address moving forward. This honest reflection will guide your future learning and preparation efforts, allowing you to enhance the areas that need attention.
Explore Career Opportunities
Upon successful completion of the assessment, you’ll likely be eligible for a range of career opportunities. You may find positions that focus on network management, system administration, or IT support. Use your newly acquired credentials to open doors for job applications, promotions, or even a career shift. Here are some potential pathways:
- Network Engineer – Oversee and manage large-scale network infrastructure.
- Systems Administrator – Handle the configuration, maintenance, and troubleshooting of networked systems.
- IT Support Specialist – Provide hands-on support and troubleshooting for various IT systems and networks.
- Cybersecurity Analyst – Focus on protecting organizational networks and systems from potential threats.
Continue Your Education
Technology evolves rapidly, and staying current is essential for long-term success. Even after achieving this milestone, consider pursuing additional certifications or advanced learning. Specialized areas such as cloud computing, security, or network architecture can further boost your expertise and increase your marketability. Online courses, workshops, and seminars can be valuable resources for continued professional development.
Remember that the completion of this stage in your career is just one stepping stone. By leveraging your knowledge, reflecting on your performance, and setting new goals, you can continue to advance in the dynamic field of IT and networking.