
Preparing for a major assessment in the field of life sciences can be a daunting task, but with the right strategies, you can master the material and feel confident on test day. This section will help you navigate the essential topics, key concepts, and study techniques needed to succeed. Whether you are reviewing terminology, lab techniques, or theoretical principles, this guide provides a clear pathway to effective preparation.
Focus on understanding the core principles and processes that are central to the subject. Pay special attention to critical definitions, fundamental mechanisms, and major frameworks that govern the study of microorganisms. By building a strong foundation in these areas, you will be better equipped to tackle questions and apply knowledge in real-world scenarios.
In this guide, we will break down the content into manageable sections, each designed to highlight the most important concepts you need to master. Whether you are reviewing class notes or practicing with sample questions, this resource will support your learning and help you prepare effectively for your upcoming assessment.
Test Preparation Guide
Mastering the key topics of your upcoming assessment requires a structured approach to studying. Understanding the core concepts and how they interconnect is essential for success. This guide will help you focus on the most important material, offering tips and strategies for effective preparation.
Key Areas to Focus On
Pay attention to the primary areas of focus, including the various biological processes, classifications, and the mechanisms that govern life at the microbial level. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial for answering both theoretical and practical questions. Reinforce your learning with practical examples and review exercises that tie theory to real-world applications.
Effective Study Strategies
Break down your study time into focused sessions. Begin with broad overviews, then narrow down to more specific topics, and regularly test yourself on key facts and concepts. Practice with mock questions to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter. Be sure to review any areas that remain unclear, as strengthening weak points will enhance your overall understanding.
Key Topics for the Assessment
To succeed in your upcoming evaluation, it is essential to focus on the most important themes that form the backbone of the subject. This section highlights the critical areas you should master in order to perform confidently. These topics cover both theoretical knowledge and practical application, helping you connect concepts and approach questions strategically.
Start by reviewing fundamental biological processes, such as cellular function, reproduction, and metabolism. Understand how organisms grow, adapt, and interact with their environments. Next, focus on the classification and identification of various organisms, as this knowledge is often central to many questions. Additionally, be prepared to demonstrate your understanding of immune responses and the factors that influence pathogenicity, as these are common themes in assessments.
Essential Study Materials for Success
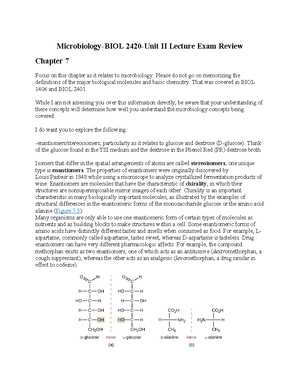
Having the right study resources can make a significant difference in your preparation for the upcoming assessment. Access to comprehensive materials allows you to build a strong understanding of the key concepts and practice applying them. This section outlines the most valuable resources to help guide your studies effectively.
Textbooks and Lecture Notes
Your primary source of information should be the course textbook and notes taken during lectures. These materials cover the core content and often include explanations and examples that clarify complex concepts. Review any summaries, diagrams, and key terms highlighted by your instructor, as these often reflect the most important topics for the test.
Practice Questions and Review Guides
Working through practice questions and sample problems is an effective way to reinforce what you’ve learned and assess your understanding. Many study guides and online resources offer mock questions that mirror the format and difficulty of the actual assessment. These can help familiarize you with the types of questions you may encounter, improving your test-taking confidence.
Understanding Assessment Format and Structure
Familiarity with the structure and format of your upcoming test is crucial for effective preparation. Knowing what types of questions to expect and how the content is organized will help you manage your time and approach each section with confidence. This section breaks down the key elements of the assessment so you can prepare strategically.
Types of Questions
The assessment typically includes multiple question types, such as multiple-choice, short answer, and possibly true/false questions. Each type requires a different approach. Multiple-choice questions often test your ability to recall facts and recognize key concepts, while short-answer questions may assess your understanding of processes and your ability to explain concepts in detail.
Time Management and Strategy
Effective time management during the test is essential. Understand how long you will have for each section and prioritize answering the questions you feel most confident about first. This ensures that you can allocate more time to the more challenging questions without rushing through them.
Common Concepts in Microbial Biology
Understanding the foundational principles of microbial life is essential for mastering this subject. These core ideas form the basis of many questions and applications in the field, covering everything from cellular structures to the way microorganisms interact with their environments. This section highlights the key concepts you need to be familiar with for a thorough understanding of the subject matter.
Cellular Structures and Functions
One of the most important areas to grasp is the structure and function of microbial cells. Knowing the different components, such as the cell wall, membrane, and internal organelles, is crucial. These structures determine how microorganisms grow, reproduce, and respond to their surroundings, making them central to many study areas.
Genetic Material and Replication

Understanding how microorganisms store and replicate genetic material is essential for grasping topics related to inheritance, evolution, and genetic engineering. The processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation in microorganisms play a significant role in their behavior, adaptation, and the spread of resistance traits.
Tips for Efficient Time Management
Effective time management is a critical factor in preparing for any major assessment. By organizing your study time wisely, you can ensure that all important topics are covered without feeling rushed. This section provides strategies to help you make the most of your preparation time.
Plan Ahead
Start your preparation well in advance to avoid last-minute cramming. Break your study material into smaller, manageable sections and allocate specific times to each topic. Use a study calendar to keep track of your progress and ensure that you cover all essential areas before the test.
- Set realistic goals for each study session.
- Review your schedule daily to stay on track.
- Prioritize difficult topics first, when your energy is highest.
Practice Time Management During Study Sessions
During each study session, practice focused time blocks to maintain productivity. The Pomodoro technique, where you work for 25 minutes and take a 5-minute break, is an effective way to stay concentrated and avoid burnout.
- Work in short, intense bursts followed by breaks.
- Avoid multitasking–focus on one task at a time.
- Review what you’ve learned after each study block.
Important Terminology to Know
Mastering key terms is essential to understanding the core concepts in the subject. These terms form the foundation for many of the questions and topics you will encounter. Being familiar with important definitions will help you communicate your understanding clearly and improve your ability to answer questions accurately.
Some of the most critical terms you should focus on include cellular structures, metabolic pathways, and genetic processes. Knowing these terms and how they relate to one another will help you make connections between different areas of study and strengthen your overall knowledge.
- Pathogen – An organism that causes disease in its host.
- Antigen – A substance that triggers an immune response.
- Replication – The process by which an organism’s genetic material is copied.
- Homeostasis – The maintenance of stable internal conditions in an organism.
How to Memorize Key Facts

Memorizing important facts is an essential part of preparing for any assessment in the life sciences. While understanding concepts is crucial, remembering specific details allows you to answer questions accurately and efficiently. This section will guide you through proven techniques to improve retention and recall of key information.
Effective Techniques for Retention
Use a combination of active learning strategies and repetition to reinforce your memory. Instead of passively reading or highlighting, engage with the material by summarizing key points in your own words, creating flashcards, and testing yourself regularly.
- Flashcards – Create flashcards with terms on one side and definitions or explanations on the other. Review them frequently to strengthen your memory.
- Mnemonics – Develop mnemonic devices to help remember complex sequences or lists. For example, use acronyms or rhymes to recall steps in a process.
- Spaced repetition – Review the material at increasing intervals to help solidify your long-term memory.
Visual Learning Tools
Many people find that visual aids help them retain information more effectively. Diagrams, charts, and mind maps can make abstract concepts easier to grasp and recall.
- Diagrams and Charts – Draw diagrams to visualize processes or cycles, helping to understand and remember each step.
- Mind Maps – Create mind maps to connect related concepts, making it easier to understand how they fit together.
Lab Techniques and Assessment Questions
Understanding practical lab techniques is essential for answering questions that require both theoretical knowledge and hands-on application. These skills are often tested through practical scenarios, where you’re expected to demonstrate your ability to interpret and apply what you’ve learned in the laboratory. This section will highlight key lab procedures and how they are typically reflected in assessment questions.
Key Lab Procedures to Focus On

Several laboratory methods are fundamental in the study of microorganisms and their behaviors. You should be familiar with techniques such as staining, culturing, and identifying various organisms. Knowing how to properly conduct experiments and interpret results is crucial for successfully tackling related questions in your assessment.
| Lab Technique | Purpose | Typical Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Gram Staining | To classify bacteria based on their cell wall structure | Describe the steps of Gram staining. What color does Gram-negative bacteria stain? |
| Serial Dilution | To estimate microbial concentration in a sample | Explain how to perform a serial dilution and its purpose in microbial quantification. |
| Antibiotic Sensitivity Test | To determine the effectiveness of antibiotics against bacteria | What does the zone of inhibition indicate in an antibiotic sensitivity test? |
Applying Lab Knowledge to Test Questions
Many assessment questions will ask you to apply your knowledge of lab techniques in specific scenarios. This may involve interpreting experimental data, identifying errors in a procedure, or suggesting improvements based on the results. Practice analyzing lab data and thinking critically about how various techniques can be used to solve real-world problems.
Reviewing Microbial Growth Processes
Understanding the mechanisms behind the growth and reproduction of microorganisms is fundamental to mastering this subject. These processes involve a series of complex steps, from nutrient uptake to cell division, that govern how microbes thrive in various environments. This section provides an overview of key growth processes and how they relate to the broader field of study.
Microbial growth is often measured through changes in population size, and these processes can be influenced by various factors such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability. Familiarity with these growth phases and their significance is essential for interpreting data and answering related questions in assessments.
| Growth Phase | Characteristics | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Lag Phase | No increase in cell number; cells are metabolically active | Nutrient availability, environmental conditions |
| Exponential Phase | Rapid cell division and population growth | Optimal conditions, abundant nutrients |
| Stationary Phase | Growth rate equals the death rate; nutrient depletion | Nutrient limitation, accumulation of waste products |
| Death Phase | Cell death exceeds new cell formation; population declines | Severe nutrient depletion, toxic waste buildup |
By reviewing these key growth phases and their factors, you can better understand the behavior of microorganisms in different environments and apply this knowledge to solve related problems and answer questions effectively.
Pathogen Identification and Diagnosis
Identifying harmful microorganisms and diagnosing infections accurately is a crucial aspect of clinical microbiology. This process involves recognizing specific characteristics of pathogens that distinguish them from one another. Diagnostic methods often rely on the observation of symptoms, laboratory testing, and the use of specialized tools to detect and identify infectious agents. Understanding these techniques is essential for determining the appropriate treatment and managing public health concerns effectively.
Common Methods of Pathogen Identification
There are various laboratory methods used to identify pathogens, each serving a specific purpose depending on the suspected microorganism. These methods can range from simple staining techniques to advanced molecular techniques.
- Culturing – Growing pathogens in controlled environments to observe their characteristics.
- Microscopic Examination – Using light or electron microscopes to examine cellular structures and morphology.
- Biochemical Tests – Analyzing metabolic properties to differentiate microorganisms.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – Amplifying DNA sequences to detect specific pathogens.
Diagnostic Techniques in Practice
Once pathogens are identified, several diagnostic techniques are employed to determine the most effective treatment. These methods can be used to understand how the microorganism interacts with the host, its resistance to drugs, and its role in disease transmission.
- Antigen Detection – Identifying pathogen-specific proteins through immunoassays.
- Serological Tests – Testing for antibodies or antigens in the patient’s blood to indicate infection.
- Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing – Determining the effectiveness of antibiotics against the identified pathogen.
Mastering these identification and diagnostic techniques is vital for effective pathogen control and treatment, ensuring that healthcare professionals can quickly and accurately respond to infectious diseases.
Focus on Immunology Concepts
Understanding the immune system’s function is fundamental to studying how the body defends itself against infections. This branch of biology explores the complex interactions between various components of the immune system, such as cells, antibodies, and molecules, that work together to recognize and eliminate pathogens. By focusing on key immunological concepts, you can better grasp the mechanisms behind immune responses and the ways the body adapts to threats.
The immune system is often divided into innate and adaptive responses. The innate immune system acts as the first line of defense, providing immediate but nonspecific protection. The adaptive immune system, on the other hand, is more specific, developing targeted responses and “memory” to future encounters with pathogens. A deep understanding of these processes is critical for interpreting immune reactions and their role in health and disease.
Familiarity with concepts such as antigen presentation, immune activation, and the roles of various immune cells is essential for analyzing how the body responds to infections and vaccinations. These principles are central to clinical practices and help shape strategies for disease prevention and treatment.
Study Strategies for Complex Topics
Mastering complex subjects requires effective study strategies that allow you to break down intricate concepts and retain detailed information. Approaching challenging material with the right techniques can make all the difference in how well you grasp the material and apply it in different contexts. Whether you are tackling dense theoretical knowledge or detailed practical applications, these strategies will help you stay organized and focused.
Active Learning Techniques
One of the most effective ways to learn complex material is by engaging in active learning. Instead of passively reading or listening, actively work with the content through techniques such as:
- Summarization – Writing summaries of the key points in your own words to reinforce understanding.
- Practice Problems – Applying theoretical knowledge to real-world problems or practice tests to strengthen memory retention.
- Self-Testing – Regularly testing yourself on the material to identify weak areas and improve recall.
Breaking Down the Material
When faced with complex topics, breaking down the content into manageable chunks is essential. Focus on understanding one subtopic or concept at a time, and gradually build your knowledge. This method, often referred to as “chunking,” makes it easier to retain information and see the connections between different concepts. Try the following:
- Mind Mapping – Creating visual diagrams to organize and relate concepts.
- Study Guides – Summarizing key information in concise, organized study guides for quick reference.
By applying these strategies, you can tackle even the most complex subjects with confidence and clarity, ensuring you retain the information needed for success.
Exam Day Tips for Confidence
The day of an important assessment can be stressful, but with the right strategies, you can approach it with confidence and clarity. It’s essential to focus not only on the content you’ve studied but also on how you manage your mindset and preparation on the actual day. Being well-prepared and having a calm, organized approach will ensure you perform at your best.
Preparation the Night Before
How you set yourself up the evening before plays a crucial role in your performance. Here are some steps to take:
- Review Key Concepts: Go over the most important material, but avoid cramming. Focus on areas that need reinforcement.
- Prepare Your Materials: Make sure you have everything you need–pens, ID, calculator, or any required tools–ready to go.
- Get Rest: A good night’s sleep will help you retain information and be mentally sharp during the assessment.
On the Day of the Test
Once the day arrives, following a calm and focused approach is key. Consider the following tips:
- Eat a Balanced Breakfast: Choose foods that will give you sustained energy, like protein and whole grains.
- Arrive Early: Arriving early allows you time to settle in and adjust to the environment before the test starts.
- Stay Calm: Take deep breaths and remind yourself that you’ve prepared well. Confidence comes from knowing you’ve put in the effort.
By maintaining these habits and focusing on your preparation, you can walk into the test with a positive attitude and confidence in your abilities.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Exam

When it comes to taking an important assessment, many students unknowingly fall into traps that can negatively impact their performance. These common mistakes are often related to poor time management, lack of focus, and failure to carefully follow instructions. Recognizing and avoiding these errors can make a significant difference in how well you perform.
Here are some of the most frequent mistakes to be aware of during the assessment:
| Mistake | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Rushing through the questions | Take your time to read each question carefully. Don’t skim over instructions or answers. |
| Misunderstanding the question | Pay close attention to keywords and make sure you fully understand what is being asked before answering. |
| Overthinking simple questions | If you’re unsure, trust your first instinct. Avoid second-guessing unless you’re certain of an error. |
| Skipping difficult questions | Answer the easy questions first, and come back to the more challenging ones with a clear mind. |
| Not managing time effectively | Monitor the time regularly and pace yourself to ensure you’re able to complete the entire assessment. |
| Leaving answers incomplete | Even if you’re unsure, always attempt an answer. A partial response is better than leaving a question blank. |
| Not reviewing your work | If time permits, review your answers before submitting. Look for any obvious mistakes or overlooked details. |
Avoiding these mistakes can help you stay on track and approach the assessment with greater confidence. Being mindful of time management, careful reading, and staying calm will significantly improve your chances of success.
How to Handle Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions are a common format in assessments and can be tricky if not approached correctly. These questions test your ability to understand concepts and identify the most accurate answer from a set of options. By developing a strategy and following a few simple guidelines, you can improve your chances of selecting the correct answer every time.
Steps to Tackle Multiple Choice Questions
Here are some effective strategies to help you navigate through multiple-choice questions with confidence:
- Read the question carefully – Ensure you fully understand what is being asked before looking at the options. Sometimes, the question itself can give you clues about the correct answer.
- Eliminate obviously incorrect answers – Review each option and discard the answers that are clearly wrong. This narrows down your choices and increases your chances of selecting the right one.
- Look for key words in the options – Watch for words like “always”, “never”, “only”, or “most”, as these can help you identify extreme or incorrect answers. Generally, answers with absolute terms are less likely to be correct.
- Consider all options before answering – Don’t rush to choose the first answer that seems correct. Take the time to compare all options before making your final choice.
- Don’t overthink – If you have to guess, trust your initial instinct. Overthinking can lead to confusion and mistakes.
Dealing with Difficult Questions
Sometimes, you may encounter questions that are challenging or unfamiliar. Here’s how to handle them:
- Skip and return later – If you’re unsure, don’t waste too much time on one question. Mark it and move on to others, then come back to it with a fresh perspective.
- Make educated guesses – If you have no idea, try to eliminate one or two answers and then make an educated guess from the remaining choices.
- Use context clues – Look for clues in other questions or the overall theme of the assessment that may help you with the difficult question.
By employing these strategies, you can increase your efficiency and accuracy when answering multiple-choice questions, leading to a more successful outcome in your assessment.
Reviewing Lecture Notes Effectively

Reviewing lecture notes is a critical aspect of reinforcing what you’ve learned in class. It helps solidify concepts and ensures that the material stays fresh in your memory. However, simply reading through your notes isn’t always enough. To make the most of your study time, it’s important to adopt a structured and intentional approach to reviewing.
Organize Your Notes – Before diving into the material, take the time to organize your notes. Categorize them based on topics or themes. This will help you identify the key concepts and spot any areas that need further clarification. Well-organized notes allow for quicker review and make it easier to connect related ideas.
Use Active Recall Techniques – Instead of passively reading your notes, test yourself on the material. Cover the answers and try to recall key points from memory. This method strengthens your ability to retain information and improves long-term memory retention.
Summarize Key Concepts – After reviewing each section of your notes, write a brief summary of the main ideas. This exercise helps reinforce what you’ve learned and highlights any gaps in your understanding. It also serves as a useful reference when you need to review quickly later.
Teach What You’ve Learned – One of the best ways to truly understand a topic is to explain it to someone else. Share what you’ve learned with a friend or study group, or even teach the material out loud to yourself. Teaching forces you to break down complex ideas into simpler terms, which deepens your comprehension.
Space Out Your Review Sessions – Don’t try to cram all your review into one sitting. Break up your study time into shorter, more focused sessions over several days or weeks. Spacing out your reviews allows for better retention and reduces the likelihood of burnout.
Review Regularly – Consistent review is key to retaining information. Make it a habit to go over your notes frequently, even after you’ve covered the entire subject. Regular review ensures that the material stays fresh in your mind and reduces the amount of last-minute studying you’ll need to do.
By applying these strategies, you can make your review sessions more productive and effective, ultimately leading to better understanding and preparation.
Understanding Microbial Genetics for Exam
Grasping the fundamentals of genetic material in microorganisms is crucial for mastering key concepts in the field. Understanding how genes are transferred, expressed, and regulated in microbes helps build a foundation for more advanced topics. These processes not only play a vital role in microbial behavior but also affect how they evolve and adapt to their environments. Properly reviewing these concepts will ensure a strong understanding for any upcoming assessments.
Key Concepts in Microbial Genetics

Microbial genetics focuses on the DNA of microorganisms and the mechanisms by which they replicate, mutate, and express traits. Important areas to review include:
- DNA Replication: Understanding how microorganisms duplicate their genetic material is essential. Pay attention to enzymes like DNA polymerase and helicase, which play a role in unwinding and replicating DNA.
- Mutation and Gene Variation: Learn about how genetic mutations occur, whether through errors in DNA replication or external factors such as radiation. These mutations are crucial for microbial evolution and adaptation.
- Gene Transfer Mechanisms: Familiarize yourself with horizontal gene transfer methods like transformation, transduction, and conjugation, which allow microbes to acquire new genetic traits from other organisms.
- Regulation of Gene Expression: Microbes regulate their gene expression through complex systems, such as operons in bacteria, which help them respond to environmental changes efficiently.
Study Tips for Microbial Genetics
When studying genetic mechanisms, it’s helpful to break down the material into manageable sections. Use these strategies to guide your review:
- Visualize Processes: Draw diagrams of DNA replication, transcription, and translation. These visual representations can help simplify complex processes and make them easier to remember.
- Focus on Key Terminology: Pay attention to the technical terms used in microbial genetics, such as plasmids, operons, and restriction enzymes. Understanding these terms will help you navigate the material more effectively.
- Review Genetic Transfer Mechanisms: Create charts comparing different methods of gene transfer, such as transformation, transduction, and conjugation. Understand the steps involved in each process.
Comparing Genetic Transfer Methods

| Method | Description | Example Organisms |
|---|---|---|
| Transformation | Uptake of naked DNA from the environment | Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Transduction | Gene transfer mediated by a virus | Escherichia coli |
| Conjugation | Transfer of DNA between bacteria through direct contact | Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Understanding the basics of microbial genetics will not only help you answer questions related to gene transfer and expression but also enable you to analyze how microbes adapt to various challenges. With these study tips and a solid grasp of the key concepts, you’ll be better prepared for any assessments on the topic.