
Preparing for the initial assessment in a science course can feel overwhelming, but with the right approach, it becomes manageable. Understanding the core concepts, mastering key techniques, and applying learned knowledge are all crucial components for success.
In this section, we will explore essential topics that are commonly covered in the first test, offering effective study strategies and insights to help you prepare efficiently. From cell structures to pathogen behavior, we’ll guide you through the material you need to know to perform confidently and accurately.
Study smart by focusing on the most important aspects of the subject and reviewing previous coursework to solidify your understanding. Effective preparation is key to achieving the best possible outcome in this crucial early assessment.
Study Guide for the First Test
Preparing for the initial assessment in this scientific discipline requires a clear understanding of core principles and topics. This guide will help you focus on key areas of study, ensuring that you are well-prepared for the first major test. It covers essential concepts, terminology, and methods that will be tested, along with effective study strategies to maximize your chances of success.
Key Concepts to Focus On
- Structure and function of cellular components
- Identification of various microorganisms
- Processes of microbial growth and reproduction
- Pathogen-host interactions and immune responses
- Laboratory techniques for microorganism culture and analysis
Study Strategies for Success
- Review lecture notes: Revisit class materials and highlight key points discussed during lectures.
- Understand key terms: Master the terminology associated with the study of microorganisms and related processes.
- Practice with flashcards: Create flashcards to reinforce important definitions and concepts.
- Work through practice questions: Use practice tests and review problems to assess your understanding.
- Group study sessions: Collaborate with classmates to quiz each other and discuss difficult concepts.
By focusing on these essential topics and applying proven study strategies, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the first major test in this field. Stay organized, stay focused, and approach your studies with confidence to achieve success.
Overview of the First Assessment

The first assessment in this subject will focus on evaluating your grasp of fundamental concepts in the study of tiny organisms and their roles in various biological systems. It will test your understanding of how these organisms function, grow, interact with their environments, and influence both health and disease. A comprehensive understanding of these core topics is essential for progressing in this field.
The table below provides an outline of the key topics that will be covered in the assessment:
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Cellular Components | Understanding the structures and functions of cells, including organelles and their roles in cellular activities. |
| Microbial Growth | Study of how microorganisms reproduce, grow, and adapt to different environmental conditions. |
| Infectious Agents | Learning to identify harmful organisms and understanding their mechanisms of causing diseases. |
| Laboratory Procedures | Mastery of techniques for culturing, isolating, and identifying microorganisms in the lab setting. |
| Immune Response | Grasping how the body’s defense system detects and fights off harmful invaders. |
By focusing on these areas, you will be well-equipped to succeed in the assessment and deepen your understanding of these crucial topics for future learning.
Key Topics to Focus On
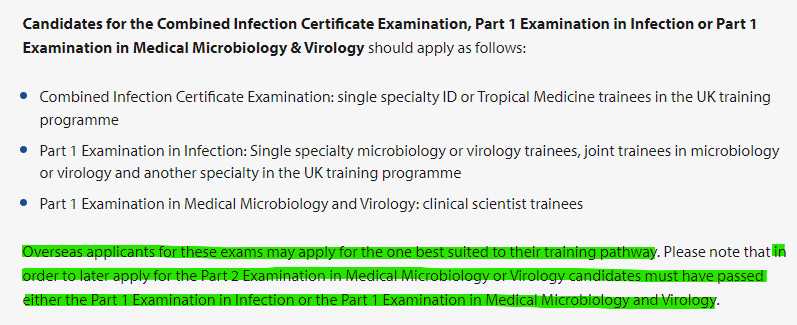
To ensure strong performance in this assessment, it is crucial to concentrate on several core topics. These areas provide the foundational knowledge necessary for understanding the behavior, classification, and impact of microorganisms on living organisms. A deep understanding of these subjects will not only help in answering questions but also serve as a solid base for more advanced studies.
The following topics are particularly important and should be prioritized during preparation:
- Cell Structures: Understand the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, including their organelles and functions.
- Microbial Growth: Study the conditions that influence the replication and survival of microorganisms, including environmental factors and nutrient requirements.
- Pathogen Identification: Learn how to identify harmful microorganisms and the diseases they cause, focusing on their mechanisms of infection.
- Lab Techniques: Familiarize yourself with methods used in isolating, culturing, and identifying various microorganisms in a laboratory environment.
- Immune Responses: Review how the body detects and combats infectious agents through both innate and adaptive immunity.
Focusing on these key areas will enhance your understanding and readiness for the assessment.
Understanding Microbial Cell Structures
Grasping the structural components of microbial cells is essential for understanding their function and behavior. Microorganisms, whether single-celled or multicellular, possess unique characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of life. These structural differences are key to their survival, reproduction, and their ability to interact with their environment and hosts.
Microbial cells are generally divided into two broad categories: those with a simple, single-celled structure and more complex multicellular organisms. The most fundamental structures to focus on include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material, and various organelles or appendages that aid in movement or protection. These components play vital roles in the cell’s life processes, such as nutrient acquisition, waste elimination, and cellular communication.
Key structures to focus on include:
- Cell Wall: Provides shape and rigidity to the cell, often playing a key role in protecting against environmental stress.
- Cell Membrane: Regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell, crucial for maintaining homeostasis.
- Nucleoid: The region where the genetic material is located in prokaryotic cells, typically in the form of a single, circular chromosome.
- Flagella and Pili: Appendages that assist in movement or attachment to surfaces, playing important roles in motility and colonization.
- Ribosomes: Responsible for protein synthesis, a vital function for all cellular activities.
- Cytoplasm: The gel-like substance inside the cell where most metabolic activities occur.
Understanding these structures and their functions will provide insights into how microorganisms adapt, thrive, and cause disease in different environments, making it an essential foundation for further study in this field.
Common Microbial Diseases to Know

Understanding the impact of infectious agents on human health is crucial for recognizing symptoms, diagnosing conditions, and applying appropriate treatments. Various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, are responsible for a wide range of diseases, each with unique characteristics and modes of transmission. Focusing on the most prevalent and clinically significant diseases will provide a solid foundation for further learning in this field.
Among the most commonly encountered diseases are:
- Streptococcal Pharyngitis: Often referred to as strep throat, this bacterial infection is characterized by a sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. It is caused by *Streptococcus pyogenes* and can lead to complications if left untreated.
- Tuberculosis (TB): A serious bacterial infection caused by *Mycobacterium tuberculosis*, primarily affecting the lungs but also capable of impacting other organs. It spreads through airborne droplets from infected individuals.
- Influenza: A viral infection that affects the respiratory system, causing fever, chills, muscle aches, and fatigue. It is highly contagious and spreads easily during flu season.
- HIV/AIDS: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attacks the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to opportunistic infections. If untreated, it progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
- Candidiasis: A fungal infection caused by *Candida* species, often affecting the mouth, skin, or genitals. It can become systemic in immunocompromised individuals.
- Malaria: A parasitic disease transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes. Caused by *Plasmodium* parasites, malaria leads to high fever, chills, and can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Each of these diseases has distinct symptoms and requires specific treatment methods, including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, or supportive care. Recognizing these conditions is vital for both prevention and management in clinical practice.
Important Laboratory Techniques and Methods
In the study of microorganisms and their behaviors, laboratory techniques are essential tools for identifying, analyzing, and understanding various pathogens. These methods provide insight into microbial structures, functions, and interactions with the environment. Mastery of these techniques is critical for accurate diagnostics and the development of treatment strategies.
Some of the most important laboratory methods include:
- Microscopy: A fundamental technique for observing microorganisms at the cellular level. Different types of microscopes, such as light microscopes and electron microscopes, are used to visualize pathogens, their structures, and their behaviors.
- Gram Staining: A method used to differentiate bacterial species based on the properties of their cell walls. It classifies bacteria into two main groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative, which influences the choice of antibiotics.
- Culture Methods: Growing microorganisms on specialized media, such as agar plates, allows scientists to isolate and identify specific species based on their growth patterns, shape, and color.
- Biochemical Testing: This involves testing microorganisms for specific enzymatic activities or metabolic processes. Common tests include catalase, oxidase, and sugar fermentation tests, which help identify bacterial species.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): A technique used to amplify DNA sequences, allowing for the detection and identification of specific microorganisms even in small amounts. It is particularly useful for detecting pathogens in clinical samples.
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing: This method determines the effectiveness of antibiotics against specific microorganisms. It helps in selecting the most appropriate treatment for infections.
By using these techniques, laboratory professionals can gain a better understanding of microbial organisms, their characteristics, and how they interact with their host or environment. These methods are integral to research, diagnostics, and treatment development.
Critical Microscopic Techniques for Exam
In the study of microorganisms, microscopic techniques are indispensable for observing and analyzing the tiny details that define microbial structures and functions. Understanding these methods is essential for accurate identification and classification of pathogens, as well as for recognizing key characteristics that distinguish various species. These techniques help reveal the hidden complexities of cells, tissues, and microorganisms, providing a crucial foundation for research and diagnostics.
Key Techniques for Effective Microscopy

When examining microorganisms, several techniques are particularly important for obtaining high-resolution images and understanding cellular structures:
- Brightfield Microscopy: The most common technique, used for observing stained specimens. The light source illuminates the sample, and the contrast between the sample and background allows for detailed observation of bacterial morphology, such as shape and arrangement.
- Phase Contrast Microscopy: This method is used for observing living organisms without staining. It enhances contrast in transparent specimens by converting phase shifts in light passing through the sample into brightness changes, making internal structures more visible.
- Fluorescence Microscopy: Utilizes fluorescent dyes to stain specific components of cells, such as proteins or nucleic acids. This technique is highly effective for highlighting particular structures within microorganisms and for tracking the movement of molecules in living cells.
Advanced Techniques for Detailed Observation
In addition to basic microscopy, more advanced methods are used for observing finer details and specific characteristics of microorganisms:
- Electron Microscopy: Provides the highest resolution for studying microorganisms at the subcellular level. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) offers detailed 3D views of surface structures, while transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is used for observing internal cellular components.
- Confocal Microscopy: This technique uses a laser to focus on a single point in a specimen, capturing detailed images from different angles. The images are then combined to create high-resolution 3D reconstructions of microbial structures.
- Darkfield Microscopy: Enhances the contrast of unstained specimens by using scattered light to create bright images against a dark background. This is particularly useful for viewing living organisms that are difficult to stain.
Mastering these microscopic techniques allows for a thorough examination of microbial life, from the broadest structural features to the finest cellular details. Understanding these methods is crucial for anyone working in the field of life sciences, providing the foundation for accurate observations and detailed analyses of microorganisms.
Understanding Pathogen Classification
Classifying harmful microorganisms is a crucial step in understanding how they affect living organisms and how they can be controlled. This classification helps researchers and healthcare professionals identify the characteristics and behaviors of different pathogens, which is essential for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. The system of categorization varies based on different attributes such as their structure, mode of transmission, and their effects on the host organism.
Key Classification Criteria

Several factors are used to categorize pathogens, including their morphology, genetic makeup, and their mode of infection. These criteria provide a clearer picture of how pathogens interact with their environments and hosts:
- Type of Organism: Pathogens can be classified into several categories, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Each group has unique characteristics that determine their behavior and methods of causing disease.
- Transmission Routes: Pathogens are often classified based on how they spread from one host to another. Common modes of transmission include respiratory droplets, direct contact, contaminated food or water, and vectors such as insects.
- Host Interaction: Some pathogens primarily infect humans, while others can affect animals, plants, or fungi. The specific interaction between the pathogen and its host can also define its category.
Common Pathogen Categories

Understanding the main categories of pathogens is essential for both prevention and treatment. Below are the primary groups in pathogen classification:
- Bacteria: These are single-celled organisms that can be found in various environments. They can be harmful or beneficial to humans, with harmful strains leading to diseases like tuberculosis, cholera, and pneumonia.
- Viruses: These are much smaller than bacteria and require a host cell to reproduce. Viruses cause diseases such as influenza, HIV, and the common cold.
- Fungi: Fungi are organisms that include yeasts and molds. Some fungal infections are harmless, but others, such as athlete’s foot or candidiasis, can cause illness.
- Parasites: These organisms live in or on a host and rely on it for survival. Common parasitic diseases include malaria, giardiasis, and toxoplasmosis.
Each group of pathogens presents unique challenges in terms of detection, treatment, and prevention. A comprehensive understanding of their classification is essential for effectively managing infectious diseases and developing targeted therapies.
Important Microbial Growth Conditions
For microorganisms to thrive and multiply, they require specific environmental factors. These conditions influence their ability to grow, reproduce, and survive. Understanding the key factors that impact microbial development is essential for both laboratory settings and practical applications in medicine, food safety, and environmental science. The ability to control these factors can help in managing microbial populations and preventing the spread of harmful pathogens.
The main conditions that influence microbial growth include temperature, pH levels, oxygen availability, and nutrient supply. These elements must be carefully balanced to support the needs of different microorganisms.
- Temperature: Temperature plays a crucial role in the rate of growth and the overall survival of microorganisms. Different species have varying temperature ranges in which they are most active. Some thrive in hot environments, while others grow best in cooler conditions.
- pH Levels: Microorganisms also require specific pH levels for optimal growth. While some can survive in highly acidic or basic environments, most prefer a neutral pH, around 7. Extremes in pH can inhibit enzyme activity and hinder metabolic processes.
- Oxygen Availability: Some microorganisms require oxygen for growth, while others thrive in environments with little to no oxygen. This can impact how they metabolize nutrients and produce energy. The classification of microorganisms based on their oxygen requirements includes aerophiles, anaerobes, and facultative organisms.
- Nutrient Availability: Nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur are essential for microbial growth. The availability of these resources determines the ability of microorganisms to multiply and perform essential cellular functions.
In laboratory settings, manipulating these conditions allows researchers to study microbial behavior, cultivate specific strains, and control microbial populations. By understanding and controlling these environmental factors, it becomes possible to optimize conditions for beneficial microorganisms while inhibiting harmful ones.
Memorizing Key Terms and Definitions
Understanding complex concepts often starts with mastering the essential terminology. In many scientific fields, being able to recall and accurately define key terms is fundamental to grasping the broader subject matter. These terms provide the foundation for further study and practical application. Developing effective strategies for memorizing these terms is crucial for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge and enhance their comprehension.
One way to approach memorization is through repetition and active recall. Creating flashcards or engaging in self-quizzing are proven techniques to reinforce memory retention. Visual aids, such as diagrams or charts, can also be helpful in associating terms with specific concepts, making them easier to remember.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Prokaryote | A single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. |
| Eukaryote | A more complex organism whose cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. |
| Pathogen | A microorganism that can cause disease in its host. |
| Antibiotic | A substance used to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. |
| Enzyme | A protein that accelerates chemical reactions in living organisms. |
By frequently reviewing these terms and their meanings, students and professionals alike can build a solid foundation of knowledge. It is also helpful to understand how these terms fit into the larger context of the subject, as this can provide greater clarity and deeper insight into their application.
Study Tips for Success
Achieving success in scientific subjects requires focused preparation and effective study techniques. The process of mastering complex content can be made easier with the right strategies in place. The key to excelling lies in understanding core concepts, practicing application, and reviewing materials regularly. By developing a systematic approach, anyone can improve retention and enhance performance during assessments.
1. Organize Your Study Sessions

One of the most effective ways to prepare is by breaking down the material into manageable sections. Organize your study schedule by prioritizing the most challenging topics and gradually working your way through them. Consistent short study sessions are often more productive than long, irregular ones. Make use of planners or digital tools to structure your time effectively and ensure you cover all key areas before the assessment.
2. Active Learning Techniques
Active learning helps retain information more effectively than passive reading. Techniques such as summarizing concepts in your own words, teaching the material to others, or testing yourself regularly can significantly improve comprehension and memory. Utilize resources such as flashcards, practice questions, or concept maps to reinforce your understanding and identify areas that require further review.
By integrating these methods into your study routine, you can ensure that you’re not only familiar with the material but also prepared to apply your knowledge in a practical setting. Regular practice and active engagement with the content are essential for mastery in any scientific discipline.
Effective Time Management for Studying
Managing study time efficiently is crucial for academic success, especially when dealing with complex subjects that require deep understanding and retention. Organizing your time properly can help reduce stress, prevent last-minute cramming, and allow for more effective learning. A well-structured study schedule encourages consistency and ensures that all important topics are covered without feeling overwhelmed.
1. Set Clear Goals
Before diving into your study sessions, set specific and achievable goals. This will give you direction and help you focus on what needs to be accomplished. Break large topics into smaller, manageable tasks, and prioritize them based on importance or difficulty. Tracking progress by completing these smaller tasks will keep you motivated.
2. Create a Realistic Study Schedule
Effective time management starts with planning. Design a schedule that allocates specific time slots for studying, breaks, and other responsibilities. Be realistic about how much time you can dedicate each day to studying and ensure that you have time for rest and relaxation. Overloading yourself can lead to burnout and reduced efficiency.
3. Use the Pomodoro Technique

This popular time-management method involves studying for a set period (usually 25 minutes), followed by a short break (5 minutes). After completing four cycles, take a longer break (15-30 minutes). This method can help improve focus and productivity by breaking study time into manageable chunks while also allowing for necessary breaks.
4. Minimize Distractions
During study sessions, try to minimize distractions by creating a quiet, organized study environment. Turn off your phone or put it on “Do Not Disturb” mode, and keep away from social media and other non-study related activities. A distraction-free environment helps you concentrate better and makes your study time more effective.
5. Review and Adjust

At the end of each week, review your study plan and assess how well you’ve been sticking to it. Adjust your schedule if needed, making room for areas where you need more time or focus. Flexibility is key in time management, as it allows you to adapt to unforeseen challenges without losing sight of your goals.
By implementing these strategies and staying disciplined with your study routine, you’ll be able to manage your time more effectively, reduce stress, and ultimately improve your academic performance.
Best Resources for Microbiology Preparation
When preparing for an assessment on biological organisms and their processes, having the right resources can significantly improve your understanding and retention of the material. A mix of textbooks, online materials, videos, and practice quizzes can help you grasp complex concepts, clarify doubts, and refine your knowledge. In this section, we will explore some of the most effective resources to assist in your preparation for this subject.
1. Textbooks and Reference Books
Textbooks remain one of the most reliable sources of detailed information. Some highly recommended books include:
- “Essential Microbiology” by James D. Griffin – This book provides a comprehensive overview of microbial biology, with clear explanations and helpful illustrations.
- “Brock Biology of Microorganisms” by Michael T. Madigan – A well-known and widely used resource in many academic programs, it covers the fundamentals of microbial science, including their structure, function, and diversity.
- “Microbiology: An Introduction” by Gerard J. Tortora – A beginner-friendly text that simplifies complex topics while offering detailed coverage of essential principles.
2. Online Learning Platforms and Websites
For interactive and up-to-date learning experiences, online platforms can be invaluable. Some popular options include:
- Khan Academy – Offers free, high-quality lessons on a range of scientific topics, including cellular processes and microbial life.
- Coursera – Provides online courses from top universities on topics related to biology and biological sciences, with specialized courses on pathogens, viruses, and the immune system.
- Quizlet – A great resource for flashcards and quizzes on biological terms and concepts, helping reinforce memory and understanding.
By combining these resources with your study plan, you can deepen your understanding and improve your preparedness for any challenges you may face during your studies. Consistent practice with a variety of materials will give you the confidence needed to excel in your academic goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Exam
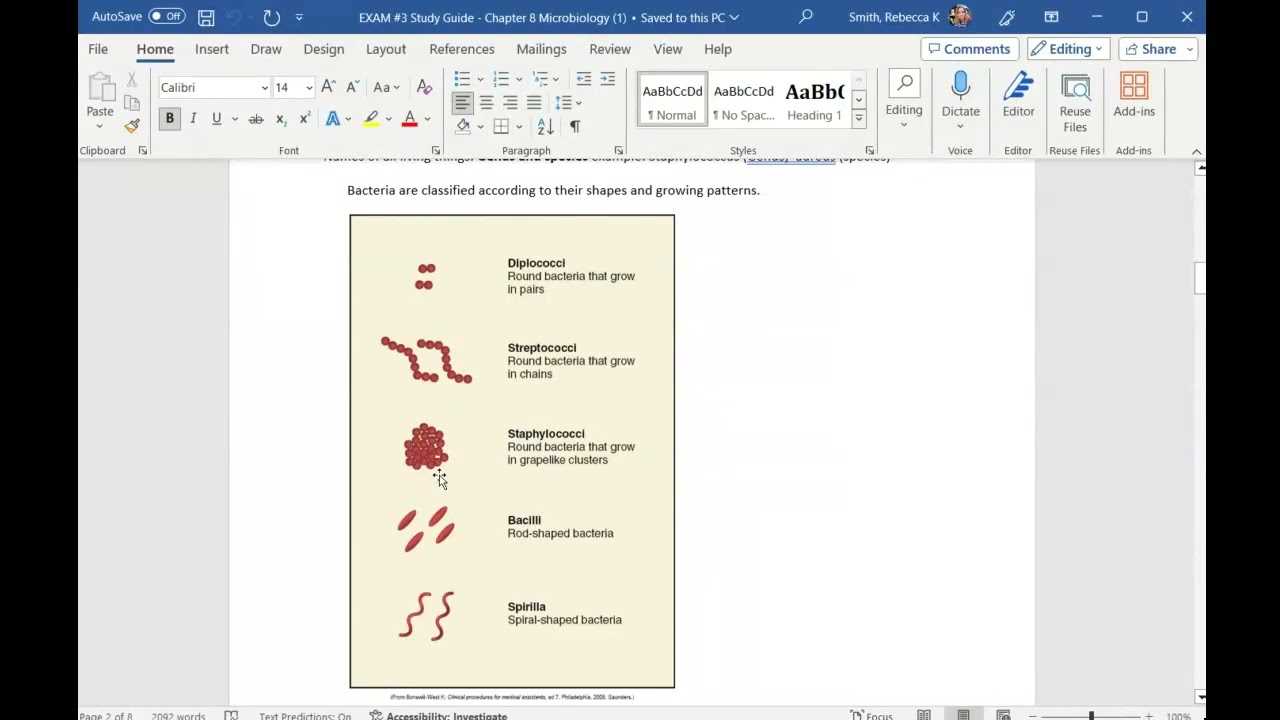
When tackling assessments in biological sciences, certain missteps can hinder performance and affect the outcome. Recognizing and avoiding these mistakes is key to maximizing your success. By being aware of common pitfalls, you can approach the test with a clear and focused mindset, ensuring that you perform to the best of your abilities.
1. Misinterpreting the Question

One of the most frequent errors is misunderstanding what the question is asking. This can lead to incorrect or incomplete answers. Pay close attention to keywords such as “define,” “explain,” or “compare” to understand exactly what is required. Take time to read each question thoroughly before responding.
- Don’t rush through questions; take a moment to interpret each part of the prompt.
- If unclear, try to rephrase the question in your own words to ensure understanding.
2. Lack of Time Management
Another mistake that can negatively impact performance is poor time management. Without allocating time properly, you might spend too long on one section and not complete the rest. It’s important to practice pacing yourself during study sessions and be mindful of how much time you spend on each question.
- Start by answering the questions you are most confident in to ensure you maximize your time.
- Leave more challenging questions for the end, but ensure you don’t run out of time for them.
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you navigate your test more effectively, allowing you to showcase your understanding and knowledge to the fullest. Preparation and awareness are essential for achieving the best results.
Test-Taking Strategies for Microbiology
Success in any biological assessment requires more than just knowledge; it also involves effective strategies for managing the test-taking process. From reading questions carefully to managing time efficiently, utilizing the right techniques can make a significant difference in performance. Below are several strategies designed to help you navigate tests with confidence and precision.
1. Read Each Question Carefully
Misunderstanding a question can lead to avoidable mistakes. Before answering, take the time to carefully read the entire question and any instructions. Pay attention to keywords and details that might indicate what the question is asking.
- Look for words such as “choose,” “identify,” “define,” or “explain” to understand what is being asked.
- If the question is complex, break it down into smaller parts to ensure you address all aspects.
2. Time Management and Pacing
Effective time management is crucial to completing all parts of the assessment. Allocate specific amounts of time to each section and question based on its difficulty and point value.
| Task | Suggested Time Allocation |
|---|---|
| Easy Questions | 1-2 minutes per question |
| Moderate Questions | 3-5 minutes per question |
| Challenging Questions | 5-10 minutes per question |
Be sure to leave time to review your answers at the end, especially for complex questions that require careful consideration.
Incorporating these strategies into your approach will help you stay focused, manage time effectively, and reduce stress during the test. By staying calm and following these methods, you can approach the test with confidence and increase your chances of success.
Reviewing Past Exams and Quizzes
One of the most effective ways to prepare for upcoming assessments is to review previous tests and quizzes. This process not only helps reinforce what you’ve learned, but also provides insight into the structure and types of questions that may appear in future evaluations. By revisiting past materials, you can identify recurring themes, common question formats, and areas where you may need further practice.
1. Analyzing Previous Questions
Reviewing past questions allows you to get familiar with the format and types of concepts that are frequently tested. Pay attention to the following:
- Question types: Are they multiple-choice, short answer, or essay-based? Understanding this can guide your approach when answering similar questions.
- Patterns: Identify topics that appear repeatedly. These are likely to be important areas for future assessments.
- Common mistakes: Recognize areas where you made errors. Understanding these mistakes and correcting them can significantly improve your performance.
2. Simulating Real Conditions
Another helpful approach is to take past quizzes or tests under timed, real-exam conditions. This strategy not only enhances your familiarity with the material, but also builds confidence and improves time management. When simulating test conditions:
- Set a timer: Limit yourself to the same time constraints as the original test.
- Work in a quiet space: Try to replicate the environment of the actual test to minimize distractions.
By practicing in a controlled setting, you can reduce test anxiety and improve your ability to recall information under pressure.
Incorporating the review of past assessments into your study routine can be a powerful tool for reinforcing knowledge, building confidence, and improving your test-taking skills.
Managing Exam Anxiety and Stress
Stress and anxiety are common reactions to high-stakes assessments, but managing these emotions is key to performing at your best. The pressure to succeed can create physical and mental tension, which may affect your concentration and recall. By adopting strategies to reduce stress, you can approach your studies and tests with a clearer mind and greater confidence.
1. Relaxation Techniques
One of the most effective ways to manage anxiety is through relaxation methods that calm the mind and body. Here are a few techniques that can help:
- Deep Breathing: Practice deep, slow breaths to lower your heart rate and relax your muscles. Inhale through your nose for a count of four, hold for four, then exhale through your mouth for four.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Start by tensing and then releasing each muscle group, beginning with your feet and working your way up to your head. This can help alleviate physical tension.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Focus on the present moment without judgment. This helps you stay calm and centered, especially in moments of stress.
2. Effective Time Management
Proper planning and organization can reduce feelings of being overwhelmed. By managing your study schedule wisely, you can avoid last-minute cramming, which is a major source of anxiety.
- Break tasks into smaller chunks: Instead of focusing on the entire subject, break it into manageable parts. This makes studying feel less daunting.
- Set realistic goals: Aim for achievable objectives each study session. This will help maintain motivation and provide a sense of accomplishment.
- Take regular breaks: Incorporate short breaks during study sessions to recharge your mind and body. This helps prevent burnout.
By incorporating relaxation strategies and organizing your time effectively, you can reduce anxiety and enhance your performance during high-pressure situations. Maintaining a balanced approach is essential for achieving success while keeping stress at bay.
Post-Exam Review and Feedback
After completing an assessment, taking the time to reflect on your performance is essential for continuous improvement. Analyzing your results helps identify areas where you excelled and those that need further attention. Feedback from instructors or peers provides valuable insights into how you can enhance your understanding and study methods moving forward.
Reviewing your responses carefully can uncover patterns in the mistakes you made, allowing you to adjust your approach for future evaluations. It is important to not only focus on the content you struggled with but also to celebrate areas where you performed well, reinforcing your strengths.
Feedback sessions are an excellent opportunity to ask questions, clarify misunderstandings, and gain deeper insights into the material. Engaging with instructors or tutors about your performance can guide your preparation for upcoming tasks and provide targeted advice to improve your academic skills.
Incorporating the lessons learned from post-assessment reviews and feedback can lead to better performance, increased confidence, and a more effective study strategy in the future.