
Preparing for a hands-on science evaluation requires a clear understanding of essential concepts, techniques, and skills. The assessment focuses on applying theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, making it crucial to develop both practical and analytical abilities. Success in this type of test depends on how well you can demonstrate your understanding of various scientific principles in a controlled environment.
Effective preparation is key to performing well. It involves reviewing important topics, familiarizing yourself with commonly used tools and methods, and practicing data analysis. By refining these skills, you can approach the test with confidence and clarity, ensuring you’re able to address each challenge competently.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through essential strategies and key areas to focus on. From understanding the core principles to mastering practical techniques, this section will help you approach your upcoming assessment with the right mindset and preparation.
Study Guide for Practical Science Assessment
To succeed in a hands-on scientific assessment, it’s essential to focus on both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This type of test evaluates your ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios, so understanding the key principles and techniques is crucial. Preparation involves mastering important topics, developing efficient workflows, and gaining confidence with commonly used tools.
Key Areas to Focus On
Concentrate on understanding the core concepts that are most frequently tested. These often include identifying common scientific processes, interpreting data, and being able to perform various techniques with accuracy. Being able to demonstrate your ability to explain what you’ve done, and why it matters, is just as important as performing the tasks themselves.
Effective Preparation Strategies

One of the most effective strategies is to simulate the assessment environment by practicing hands-on exercises. This will help you become more comfortable with the equipment and procedures. Additionally, review past materials and test questions to familiarize yourself with the types of tasks and questions you may encounter. Finally, ensure you understand the safety protocols and basic troubleshooting methods to avoid delays or errors during the assessment.
Essential Concepts to Review
Before taking any hands-on scientific evaluation, it’s important to review the key principles that are fundamental to understanding the various processes and techniques. These concepts will help you approach tasks with clarity and confidence, ensuring that you can effectively apply what you’ve learned to practical situations. A solid grasp of these topics will be crucial for demonstrating your competence during the assessment.
Core Scientific Principles

Make sure to revisit the foundational concepts related to the scientific method, data collection, and analysis. Understanding how to properly formulate hypotheses, conduct experiments, and interpret results will be essential. Also, focus on the underlying theories behind common practices, as this will help you make informed decisions while performing tasks.
Tools and Techniques
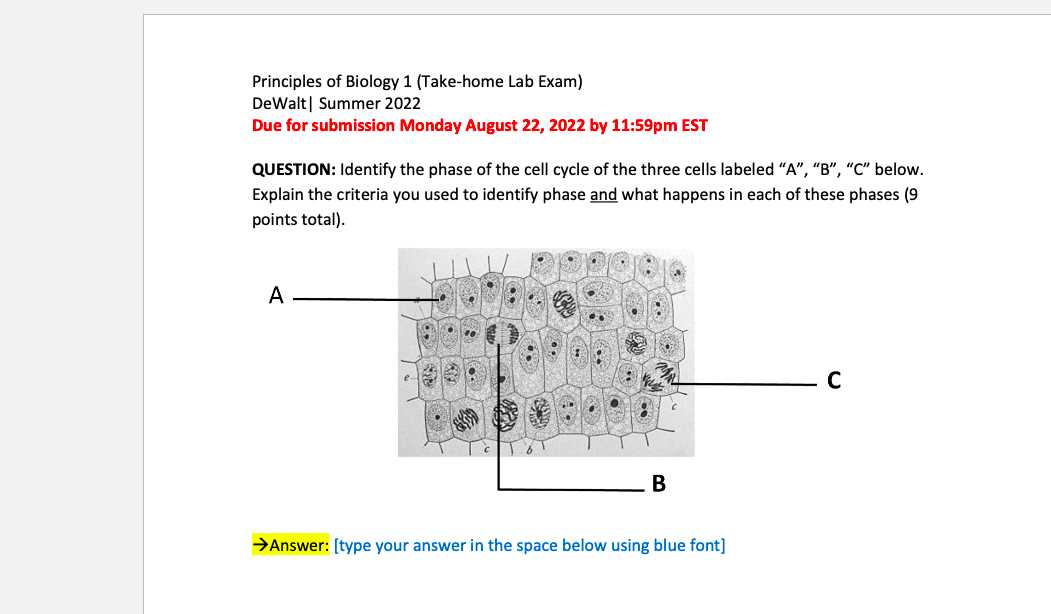
It’s crucial to be familiar with the equipment and techniques you’ll be using. This includes understanding the purpose of various instruments, how to handle them correctly, and how to record and analyze measurements. Be prepared to troubleshoot minor issues with the tools and ensure you can perform basic functions smoothly.
Understanding Safety Protocols
Safety is a critical aspect of any scientific activity. Familiarizing yourself with the proper safety protocols ensures a smooth, secure, and productive experience in any experimental setting. Knowing how to handle materials, equipment, and unexpected situations safely not only protects you but also ensures that the work environment remains secure for everyone involved.
Key Safety Guidelines to Follow
Before beginning any experiment, it is essential to know and follow these basic safety measures:
- Wear protective gear: Always wear gloves, goggles, and lab coats to protect your skin, eyes, and clothing from harmful substances.
- Know emergency procedures: Be aware of the location of fire extinguishers, eyewash stations, and first aid kits. Understand how to respond to different emergencies.
- Handle equipment with care: Use tools and instruments according to their intended purpose to avoid accidents or damage.
- Dispose of materials properly: Dispose of chemicals, biological samples, and other materials according to established guidelines.
Common Safety Hazards
Being aware of potential hazards can help you stay alert and avoid accidents. Some common dangers include:
- Exposure to toxic substances.
- Accidental spills or contamination.
- Improper handling of sharp objects.
- Risk of fire from open flames or electrical equipment.
By adhering to established protocols and staying vigilant, you can maintain a safe environment and ensure the success of your practical tasks.
Common Experiment Types in Science

In any scientific investigation, different types of experiments are conducted to test hypotheses, observe phenomena, and gather data. Each type of experiment serves a specific purpose and requires unique methods and techniques. Understanding these common experiment types is essential for anyone preparing for a practical scientific assessment.
Controlled Experiments
Controlled experiments are designed to isolate the effect of one variable while keeping others constant. These experiments are useful for testing specific hypotheses by ensuring that the results are directly related to the variable being studied. For example, testing the effect of temperature on the growth of a plant involves controlling all other factors, such as light and soil type.
Observational Studies
Unlike controlled experiments, observational studies involve observing and recording data without manipulating variables. These studies are often used when it is impractical or unethical to control the environment. A common example is studying animal behavior in the wild, where researchers observe natural interactions without interference.
Tip: When conducting either type of experiment, always ensure that data collection methods are accurate and reliable to ensure meaningful conclusions can be drawn.
Key Tools and Equipment in the Lab
Having a solid understanding of the tools and equipment used in scientific investigations is essential for carrying out successful experiments. These instruments play a vital role in gathering accurate data, performing tests, and ensuring that processes are executed correctly. Familiarity with the purpose, operation, and proper handling of these tools helps ensure both safety and precision.
Commonly used tools include microscopes for detailed observations, balances for measuring mass, and pipettes for transferring liquids. Other essential equipment such as test tubes, beakers, and Bunsen burners are frequently employed to carry out experiments, and knowing their correct usage is crucial. Each tool has a specific function that contributes to the overall success of the procedure, whether it’s for measuring, observing, or manipulating substances.
It’s important to not only know how to use these tools but also to understand the potential risks associated with them. Proper training and adherence to safety guidelines are key to maximizing their effectiveness while avoiding accidents.
Report Writing Tips
Writing a clear and concise report is a crucial skill in any scientific investigation. A well-written report not only summarizes the experiment and its findings but also helps others understand the methodology and reasoning behind the results. Whether you’re documenting a simple procedure or a complex series of tests, following a structured approach will ensure that your report is both informative and easy to follow.
Start by clearly stating the purpose of your experiment, outlining the objectives, and providing a brief background on the topic. Ensure that each section, from materials and methods to results and conclusions, is logically organized. Be objective in your writing, avoid unnecessary details, and focus on presenting the data in a straightforward manner. Visual aids, such as graphs or tables, can help clarify your findings, but always accompany them with clear explanations.
Lastly, make sure to proofread your report for clarity and accuracy. Well-organized, precise writing will help convey your findings effectively and demonstrate your understanding of the experiment.
How to Analyze Experimental Data
Analyzing experimental data is a key step in drawing meaningful conclusions from your work. Once data is collected, it must be carefully interpreted to understand the results and determine if they support your hypothesis. This process involves organizing data, identifying patterns, and applying appropriate statistical methods to extract insights.
Steps for Analyzing Data

Follow these basic steps to effectively analyze your results:
- Organize the data: Arrange the data in a clear format, such as tables or spreadsheets, to make it easier to compare and evaluate.
- Visualize trends: Use graphs, charts, or histograms to help identify any patterns or relationships between variables.
- Statistical analysis: Apply statistical methods, such as calculating averages, variances, or conducting tests, to assess the significance of the results.
- Interpret the results: Evaluate the findings in the context of your original hypothesis. Determine whether the data supports or contradicts your predictions.
Important Considerations
- Consistency: Ensure that your data collection methods are consistent and reliable across all trials.
- Outliers: Identify and assess any outliers that might affect the overall analysis.
- Context: Always consider the broader context of your experiment when interpreting the data and drawing conclusions.
By following these steps, you can analyze your data systematically, leading to clear, accurate conclusions that contribute to a deeper understanding of the experiment.
Important Scientific Terms to Know

Understanding key scientific concepts is essential for grasping the fundamentals of experiments and their outcomes. Familiarizing yourself with the terminology used in the field helps to communicate findings clearly and accurately. Whether you’re working with cellular processes, genetics, or environmental systems, knowing these terms will enhance your ability to understand and explain various phenomena.
Essential Concepts in Life Sciences
Some of the most important concepts include terms related to cellular structure, genetic material, and metabolic processes. For example, knowing the difference between mitosis and meiosis is crucial for understanding cell division, while understanding terms like enzyme, catalyst, and metabolism helps explain biochemical reactions within organisms.
Terms for Experimentation and Data
In addition to understanding biological processes, it’s important to know terms related to experimentation, such as hypothesis, variable, and control group. These terms are essential when setting up experiments, analyzing results, and drawing conclusions. Familiarity with scientific measurement units and techniques, such as microscopy, titration, and spectroscopy, will also be vital for conducting accurate tests and observations.
Study Strategies for Practical Assessments
Effective preparation for hands-on assessments requires a combination of understanding the theoretical concepts and mastering practical skills. It’s essential to be able to apply what you’ve learned to real-world scenarios, so focusing on both knowledge and technique will ensure success. The following strategies will help you organize your study sessions and feel more confident when performing tasks.
First, review key concepts and terminology. Understanding the underlying principles behind the tasks you might be asked to perform will provide a solid foundation. Make sure to know the correct use of equipment, as well as the steps involved in common procedures. Practicing these tasks, either in class or at home, can significantly improve your familiarity with the tools and techniques involved.
Additionally, creating a study schedule that includes both theoretical review and hands-on practice is essential. Group study sessions can be helpful for discussing concepts with peers and testing each other’s knowledge. Don’t forget to practice under timed conditions to simulate the actual assessment environment. This can help reduce anxiety and improve your time management skills.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

During any practical assessment, it’s easy to overlook key details that can affect your performance. These mistakes can range from small errors in technique to misinterpretations of instructions. By understanding common pitfalls and learning how to avoid them, you can improve your efficiency and accuracy, ensuring a successful outcome.
One of the most frequent mistakes is rushing through tasks without fully understanding the procedure. It’s crucial to take the time to read instructions carefully and ensure you understand the steps involved. Skipping steps or performing them too quickly can lead to inaccurate results or even cause equipment damage. Patience and attention to detail are essential for minimizing errors.
Another common mistake is improper use of equipment. Always familiarize yourself with the tools you’ll be using beforehand. Inaccurate measurements or using the wrong instrument for a task can lead to faulty results. Remember, knowing the purpose of each tool and its correct operation is just as important as understanding the experiment itself.
Lastly, failing to document your observations properly is a mistake that can hinder your ability to analyze and interpret the data later. Always record results immediately and ensure your notes are clear and organized for easy reference.
Preparing for Practical Assessments
Preparing for a hands-on assessment requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. It’s not just about remembering facts but about being able to apply them in real-world situations. Focus on understanding the procedures, mastering the equipment, and being able to think critically under pressure.
Study the Process
Start by reviewing the key procedures and techniques that are likely to be tested. Practice using the necessary tools and equipment, paying attention to each step involved. Understanding the reasoning behind each action will make it easier to recall the correct procedure when needed. This preparation will also help you react quickly and correctly in unfamiliar situations.
Practice Time Management

Practical assessments are often time-limited, so it’s important to practice completing tasks efficiently. Set up mock scenarios where you simulate the actual test environment. Time yourself to ensure you can complete the tasks within the allotted period. This will help reduce anxiety and improve your confidence during the real assessment.
How to Interpret Results
Interpreting the results from any hands-on test requires a careful analysis of the data collected and understanding what it represents. This process goes beyond just reading numbers or observations; it’s about making sense of what the results mean in the context of the experiment. Proper interpretation is key to drawing accurate conclusions and determining whether the hypothesis was supported or not.
Start by reviewing the data carefully. Look for patterns, trends, or inconsistencies that may emerge. For example, if the data shows a clear increase or decrease over time, this could indicate a relationship between variables. It’s also important to consider potential sources of error or bias that may have influenced the results. Double-checking measurements and ensuring consistency can help you make more reliable conclusions.
Once the data is reviewed, compare the findings with your expectations or initial predictions. If the results align with your hypothesis, this can strengthen your understanding. However, if the results differ, it’s important to assess why this may be the case and what it could mean for your understanding of the process. Critical thinking and analysis are crucial in this step to ensure the findings are interpreted in the right context.
Mastering Microscopy Techniques
Microscopy is an essential skill in many scientific investigations, allowing you to observe details too small to be seen by the naked eye. Whether you’re using light, electron, or other types of microscopes, mastering these techniques is crucial for obtaining clear and accurate images. Proper handling and adjustment of the equipment, as well as an understanding of the specimen preparation process, will ensure optimal results.
To begin with, it’s important to correctly set up the microscope. This includes adjusting the light intensity, focusing on the specimen, and selecting the appropriate objective lens for the level of magnification required. Knowing how to handle the microscope gently and efficiently will prevent any damage to both the instrument and the slides you are using.
| Step | Action | Tip |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare the specimen | Ensure the specimen is thin enough for light to pass through or properly stained for contrast. |
| 2 | Focus the image | Start with the lowest magnification and gradually increase to avoid losing focus. |
| 3 | Adjust the light | Use the condenser and diaphragm to optimize the lighting for clear visibility. |
| 4 | Examine the sample | Take note of any unique features and ensure you document everything accurately. |
Practicing these steps will allow you to develop proficiency and gain confidence in using microscopes effectively. Always remember that careful attention to detail is key when observing specimens, as small changes in focus or lighting can dramatically affect the quality of the image.
Practical Tips for Lab Success

Achieving success in hands-on assessments relies on more than just theoretical knowledge. It requires a combination of preparation, attention to detail, and effective execution of tasks. By following certain strategies, you can maximize your performance and ensure a smooth experience in practical scenarios.
- Understand the Basics: Review the fundamental concepts and processes that will be tested. Familiarity with the techniques and tools you’ll use will help you perform tasks more efficiently.
- Stay Organized: Keep your workspace neat and orderly. A clean setup ensures you can access necessary equipment quickly and reduces the risk of errors.
- Read Instructions Carefully: Before beginning any task, take a moment to carefully read all instructions. This helps ensure you fully understand what is required and minimizes mistakes.
- Work Methodically: Break down tasks into smaller steps and follow them in order. This systematic approach reduces confusion and helps you stay focused.
- Practice Time Management: Always keep an eye on the clock. Make sure to allocate enough time for each task and avoid rushing through important steps.
- Ask for Help When Needed: If you’re unsure about a procedure, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification. It’s better to ask questions than to risk making a mistake.
By focusing on these practical tips, you can enhance your efficiency and confidence during hands-on assessments. Consistency and careful planning are key to achieving great results in any practical scenario.
Time Management for Lab Exams
Effective time management is crucial during practical assessments, where every minute counts. Balancing multiple tasks, staying organized, and maintaining focus are key to ensuring you complete all required activities within the given timeframe. By practicing time management, you can increase your efficiency and reduce stress during these assessments.
Tips for Efficient Time Use
- Plan Ahead: Before starting, take a few minutes to review the tasks and identify how much time each will likely take. This will help you prioritize and allocate your time effectively.
- Set a Time Limit for Each Task: For each task, set a specific amount of time. Use a timer or watch to stay on track and avoid spending too much time on any one task.
- Work in Blocks: Break tasks into smaller, manageable chunks. This method helps maintain focus and ensures you stay on schedule throughout the session.
- Leave Buffer Time: Always account for unexpected challenges. It’s a good idea to leave a few minutes at the end to double-check your work or address any issues that arise.
- Stay Focused: Avoid distractions. Focusing on the task at hand helps you complete it faster and more accurately, without losing valuable time.
How to Handle Unexpected Delays

- Stay Calm: If you encounter an issue or delay, remain composed. Panicking will only waste time and hinder your ability to think clearly.
- Adapt Quickly: If something isn’t going as planned, adjust your approach. Prioritize critical tasks and skip over less important steps if needed.
- Ask for Assistance: If you’re running out of time and need help with a procedure, asking for assistance can save you time and ensure you’re on the right track.
With these time management strategies, you can confidently navigate practical assessments, ensuring you stay focused and complete all tasks within the allotted time.
Reviewing Past Exam Questions
Reviewing previous assessment questions is one of the most effective ways to prepare for upcoming practical tests. By familiarizing yourself with the types of tasks and questions typically asked, you can identify patterns, understand what is expected, and tailor your preparation accordingly. This approach helps reduce anxiety and boosts confidence when facing similar challenges in future assessments.
Benefits of Reviewing Past Questions
- Identify Common Topics: Reviewing past questions helps you pinpoint frequently tested concepts and topics, allowing you to focus your study efforts on the areas most likely to appear.
- Understand Question Format: By practicing with past questions, you can become accustomed to the format and wording of tasks, which can improve your response time and accuracy during the actual assessment.
- Improve Time Management: Knowing what to expect can help you manage your time more efficiently, giving you a clear idea of how long to spend on each task.
How to Effectively Review Past Questions
When reviewing past questions, it’s important to analyze not just the questions themselves, but also the structure of your responses. Here’s a strategy to help you get the most out of this practice:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Review the question thoroughly and ensure you understand what is being asked. |
| Step 2 | Identify key concepts and terminology in the question. Make a note of any areas that you may need to revise. |
| Step 3 | Attempt to answer the question on your own before reviewing the model response or reference materials. |
| Step 4 | Compare your answer to the correct response and assess areas for improvement. |
| Step 5 | Use your analysis to guide your study plan, focusing on weak points and reinforcing your strengths. |
By following this method, you can transform past assessments into powerful tools for your preparation, ensuring that you are well-equipped to tackle the challenges ahead.