
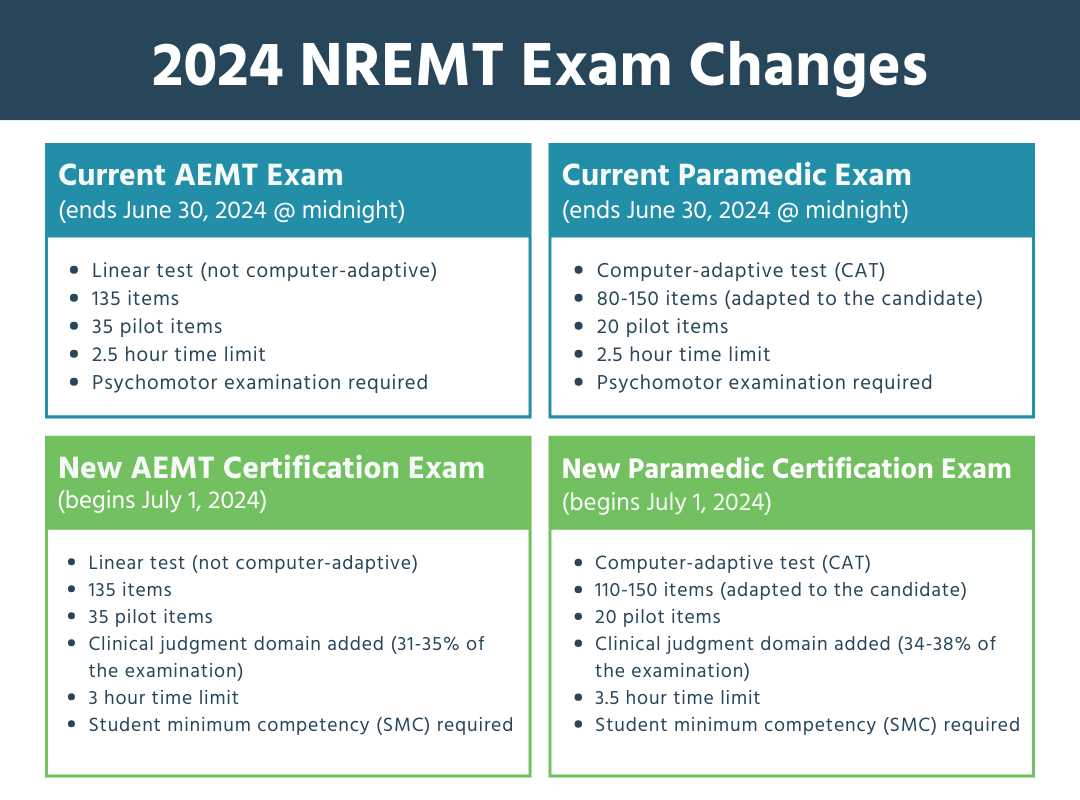
When preparing to enter the field of emergency care, hands-on assessments are crucial in evaluating a candidate’s readiness to respond to real-life situations. These evaluations require individuals to demonstrate their ability to perform essential medical procedures and make quick decisions under pressure.
Success in these evaluations not only tests technical knowledge but also the ability to stay composed during high-stress situations. Candidates must be able to efficiently assess patients, apply appropriate treatment, and communicate effectively with a team. Mastering these skills is critical for anyone looking to excel in the healthcare industry and provide quality care during emergencies.
Throughout this guide, we’ll explore the key areas tested during the assessment process and offer valuable tips on how to prepare. By understanding what to expect, you can approach the challenge with confidence and increase your chances of success.
EMT Basic Practical Exam Overview
The evaluation for emergency medical personnel focuses on testing real-world skills that are essential for effective care. This process involves demonstrating competency in various critical techniques and procedures needed to manage patients in urgent situations. It’s a comprehensive assessment where candidates must apply their knowledge in simulated emergencies to ensure they can handle high-pressure scenarios.
Key Areas of Evaluation
The assessment covers several key skills that are vital in the field. Candidates are required to show proficiency in areas such as patient assessment, airway management, trauma care, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Each skill is evaluated on its accuracy, speed, and ability to adapt to the given scenario.
| Skill Area | Description | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Assessment | Initial evaluation of the patient’s condition | Rapid evaluation, history taking, vital signs |
| Airway Management | Ensuring an open airway for breathing | Head-tilt-chin-lift, suctioning, oxygen administration |
| Trauma Care | Assessing and stabilizing injuries | Spinal immobilization, bandaging, wound care |
| CPR and Resuscitation | Performing life-saving techniques | Chest compressions, defibrillation, ventilation |
Evaluation Process
During the assessment, candidates perform a series of tasks under observation. Each procedure is timed and scored, with emphasis placed on correct technique, communication, and decision-making. These evaluations are designed not only to test technical proficiency but also to assess how individuals remain calm and collected under pressure.
Key Skills Tested in the Exam

The evaluation process for emergency medical professionals requires candidates to demonstrate proficiency in a variety of critical skills that are essential for providing effective care in high-pressure situations. These abilities encompass both the technical aspects of patient care and the interpersonal skills needed to work efficiently in a team environment. The focus is on real-world scenarios where swift, accurate actions can save lives.
One of the most important areas assessed is patient assessment, which involves quickly identifying the patient’s condition and prioritizing care. This includes taking vital signs, performing a thorough medical history, and assessing physical injuries or symptoms. Another crucial skill is airway management, ensuring the patient’s airway remains open and unobstructed for proper breathing.
Trauma care is also tested, requiring candidates to handle injuries such as fractures, bleeding, and spinal issues with the appropriate techniques. Additionally, life-saving procedures like CPR and defibrillation are evaluated to determine the candidate’s ability to stabilize a patient during cardiac emergencies.
These essential skills are combined with the ability to remain composed under pressure, think critically, and communicate effectively with other team members. Each skill is carefully assessed to ensure candidates are ready to handle the complexities of emergency medical situations.
Understanding the Exam Format
The evaluation process for emergency medical personnel is structured to assess practical skills through a series of hands-on scenarios. During this assessment, candidates are required to perform a set of tasks that simulate real-life emergencies. These scenarios are designed to test not only technical knowledge but also the ability to think and act quickly under pressure.
The format typically includes several stations, each focused on a different aspect of patient care. At each station, candidates are presented with a simulated medical situation in which they must apply their skills to manage the patient’s condition. The evaluation is timed, and performance is closely observed by instructors who assess both accuracy and efficiency.
Throughout the process, candidates are expected to demonstrate a clear understanding of protocols, maintain a calm demeanor, and effectively communicate with any team members or simulated patients. The exam is designed to replicate the challenges faced in the field, ensuring that only those with the necessary skills and composure are certified for real-world emergency care.
Preparing Your Equipment for the Exam
One of the most important aspects of your assessment is ensuring that all necessary tools and equipment are prepared and in proper working order. The right materials not only help you perform efficiently but also demonstrate your preparedness and professionalism during the evaluation. Being familiar with your gear ensures that you can complete each task smoothly and confidently.
Before the assessment, it’s essential to check and organize all the equipment you will need. This includes items like airway management tools, bandages, and defibrillators. You should also make sure that your medical kit is fully stocked and that you are comfortable using each item. Proper organization will save time and reduce stress during the evaluation.
Ensure that each piece of equipment is in working condition and accessible within your kit. Practice using the tools until you feel confident in your ability to deploy them quickly when needed. Being well-prepared with your gear will allow you to focus on your clinical skills without worrying about missing or malfunctioning equipment during the process.
Common Challenges During the Practical Test
During the evaluation, candidates often face several challenges that can make performing tasks under pressure difficult. These challenges not only test technical proficiency but also the ability to remain composed in stressful situations. Understanding these obstacles and preparing for them can help you perform at your best during the assessment.
Time Management
One of the most common difficulties is managing time effectively during the tasks. Each scenario has a time limit, and candidates must complete the required procedures quickly and accurately. Rushing can lead to mistakes, while taking too long can result in failure to complete all steps.
- Prioritize tasks based on urgency.
- Stay focused and avoid unnecessary steps.
- Practice under timed conditions to build speed and efficiency.
Remaining Calm Under Pressure
Staying calm during high-pressure situations is another common challenge. The ability to think clearly and make decisions in real time is critical in an emergency setting. Nervousness can impair performance, making it important to practice mental resilience as well as physical skills.
- Practice deep breathing techniques to stay focused.
- Visualize success before starting each task.
- Stay positive and remind yourself that you are prepared.
By preparing for these challenges and honing both technical and mental skills, candidates can increase their chances of success and perform confidently during the evaluation process.
How to Stay Calm Under Pressure
Remaining composed during high-pressure situations is crucial for effective performance in emergency care assessments. The ability to stay calm helps you think clearly, make better decisions, and execute tasks with precision. Training your mind to handle stress is just as important as mastering clinical skills, as it enables you to perform at your best when every second counts.
Mindfulness and Focus
One effective way to manage stress is by practicing mindfulness. Being fully present and focused on the task at hand allows you to block out distractions and remain in control. When you feel overwhelmed, take a moment to pause and refocus your thoughts. Concentrate on the immediate steps you need to take and avoid thinking too far ahead.
- Take deep, steady breaths to calm your mind.
- Focus on one task at a time to prevent feeling overwhelmed.
- Use positive self-talk to remind yourself that you are capable.
Visualization Techniques
Visualization is another powerful tool to reduce anxiety. Before your assessment, mentally rehearse each step of the process. Imagine yourself succeeding in each scenario, performing tasks with confidence and ease. This mental preparation can help you feel more confident and relaxed when the real test begins.
- Visualize yourself handling high-pressure situations calmly.
- Picture your actions being deliberate and precise.
- Use visualization to reinforce your confidence in your abilities.
By incorporating these techniques into your preparation, you can maintain a clear and focused mindset, even in the most challenging situations.
What to Expect on Test Day
On the day of your assessment, it’s important to be well-prepared both mentally and physically. The process is designed to evaluate your ability to perform key procedures in a realistic, high-pressure setting. Expect to undergo a series of tasks where you will need to demonstrate your knowledge and skills, often with limited time and resources. Understanding the format and being prepared for the environment will help you approach the test with confidence.
Arrival and Setup
When you arrive, you’ll typically check in and be given instructions on where the assessment will take place. Be sure to arrive early to avoid any unnecessary stress. You may be asked to organize your equipment and prepare your gear before the test begins. This is also a good time to double-check that all necessary tools are in working order.
- Arrive early to familiarize yourself with the testing area.
- Check that all required tools and materials are ready for use.
- Ensure that you have any personal items, such as identification, if needed.
During the Test
Once the test begins, you will rotate through various stations where different skills are assessed. Each station will have a set of specific tasks that you need to complete within a set time frame. It’s important to stay focused and maintain a steady pace throughout the process. Instructors will observe and score your performance based on accuracy, technique, and efficiency.
- Perform each task with focus and attention to detail.
- Manage your time effectively to complete all steps within the time limit.
- Stay calm and composed, even when working under pressure.
By being mentally prepared for the structure and pacing of the assessment, you can maximize your chances of performing well on the day of the test.
Time Management Tips for Success
Effective time management is crucial when performing tasks in an assessment, especially when each scenario has a strict time limit. Balancing speed with accuracy can be challenging, but with proper planning and focus, you can complete each task efficiently while maintaining high standards. Being mindful of how you allocate your time during each step can make the difference between success and failure.
Here are some practical tips to help you manage your time effectively during the assessment:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Prioritize Critical Tasks | Identify which actions are most urgent and need to be completed first, ensuring the patient’s immediate needs are met before moving on to less critical tasks. |
| Stay Focused | Concentrate on one task at a time. Avoid distractions or the temptation to rush through multiple steps at once, which can lead to errors and wasted time. |
| Use Time Checks | Periodically glance at the clock to ensure you are on track to finish within the allotted time. Adjust your pace if necessary without sacrificing quality. |
| Practice Under Timed Conditions | Before the assessment, rehearse each skill under timed conditions to get comfortable with completing tasks quickly and efficiently while staying focused. |
By using these strategies, you can enhance your ability to manage time effectively and improve your performance during the assessment process. Practicing these techniques ahead of time will help you stay calm and work more efficiently under pressure.
Practical Exam Evaluation Criteria
During the assessment, evaluators observe and score your performance based on specific criteria designed to measure your competency and ability to apply learned skills in real-life scenarios. These standards ensure that you can safely and effectively handle emergency situations. Understanding the key areas that are evaluated will help you focus your preparation and perform to the best of your ability.
The evaluation process typically focuses on several key aspects of your performance:
- Knowledge and Accuracy: How well you understand the procedures and execute each step according to established guidelines.
- Skill Execution: The precision and correctness with which you perform each task, including the proper use of equipment.
- Time Management: The ability to perform tasks efficiently within the given time limits, without sacrificing quality.
- Safety and Protocol Adherence: Whether you follow all safety protocols, ensuring the well-being of both the patient and yourself throughout the process.
- Communication and Teamwork: Your ability to communicate effectively with the patient, fellow team members, and evaluators, and demonstrate leadership or cooperation when needed.
Evaluators will also assess your ability to stay calm under pressure, make quick decisions, and adapt to changing circumstances in emergency situations. The final score reflects how well you meet these standards in each scenario.
How to Ace Patient Assessment Skills
Mastering patient assessment is a critical component of providing effective emergency care. The ability to quickly and accurately assess a patient’s condition allows you to make informed decisions and prioritize treatment. A thorough assessment ensures that nothing is overlooked, which is vital when time is of the essence.
To excel in patient evaluation, it’s important to focus on a systematic approach, paying attention to every detail. Developing a structured method will help you remain organized and ensure you don’t miss any crucial signs or symptoms. Here are a few strategies to help you succeed in this essential skill:
- Start with a Primary Survey: Always begin with the ABCs (Airway, Breathing, Circulation) to identify life-threatening conditions first. This will guide your immediate actions and help you prioritize care.
- Conduct a Thorough Secondary Survey: After stabilizing the patient, perform a more detailed assessment. Check for signs of trauma, take a complete history, and evaluate the patient’s overall condition.
- Be Methodical: Consistently follow your steps to avoid missing important details. A structured approach will keep you focused and ensure you assess all areas of the patient’s condition.
- Stay Calm and Communicate: Establish rapport with the patient, providing clear instructions and explaining your actions. Effective communication can help calm the patient and provide you with more accurate information.
Regular practice, simulation training, and self-reflection are all vital to refining your assessment abilities. With these techniques, you can build confidence and become proficient in gathering the essential information needed to provide the best care possible.
Mastering Airway Management Techniques
Effectively managing a patient’s airway is one of the most critical skills in emergency care. Ensuring that the airway is clear and open allows for proper ventilation and oxygenation, which are essential for survival. A skilled practitioner must be able to quickly assess and intervene in situations where the airway is compromised, preventing further complications and stabilizing the patient.
Mastering airway management techniques requires both knowledge and hands-on experience. Different situations will demand different approaches, and having the flexibility to adapt to each case is key. Here are some important techniques to focus on:
Basic Airway Maneuvers

In many cases, simple maneuvers can help open the airway and allow air to flow freely. These are the first steps in addressing airway obstruction:
- Head-Tilt, Chin-Lift: This technique is used to clear the airway by lifting the chin and tilting the head back to prevent the tongue from obstructing the throat.
- Jaw-Thrust Maneuver: This is especially useful when dealing with suspected spinal injuries, as it opens the airway without moving the neck.
- Recovery Position: For patients who are unconscious but breathing, placing them in the recovery position can help keep the airway open and prevent choking.
Advanced Techniques
In more complex situations, advanced airway management techniques may be required to ensure that the airway is properly secured:
- Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Airways: These devices help to maintain airway patency in patients who cannot maintain their own airway.
- Endotracheal Intubation: In critical situations, intubating the patient and securing the airway with a tube may be necessary to ensure adequate ventilation.
- Supraglottic Airway Devices: These devices, such as the Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA), provide an alternative to intubation when intubation is not feasible.
Becoming proficient in airway management takes practice and attention to detail. Regular training, simulation exercises, and an understanding of the anatomical and physiological aspects of the airway will help you develop the expertise needed to manage even the most challenging cases effectively.
Effective CPR and Resuscitation Practices
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and resuscitation practices are life-saving techniques that are essential in cases of cardiac arrest and other respiratory emergencies. When a patient’s heart stops beating, or they stop breathing, every second counts. Proper execution of these techniques can dramatically improve the chances of survival and reduce the risk of long-term damage. Mastery of these skills is critical for anyone involved in emergency care, as it can be the difference between life and death.
To perform CPR and resuscitation effectively, it is essential to understand the correct procedures and remain calm under pressure. These techniques rely on precise actions, proper timing, and effective communication with other team members. Here are the key practices to focus on:
Chest Compressions and Ventilations
The foundation of CPR consists of chest compressions and rescue breathing. The ratio of compressions to breaths, the depth and rate of compressions, and proper ventilation are all crucial for successful resuscitation:
- Chest Compressions: Perform compressions at a depth of at least two inches, at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. Ensure that the chest fully recoils between compressions to allow the heart to refill with blood.
- Rescue Breaths: Deliver two rescue breaths after every 30 chest compressions. Each breath should last about one second and should make the chest rise visibly, ensuring that air is reaching the lungs.
- Compression-to-Ventilation Ratio: In adult patients, the recommended ratio is 30:2 (30 compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths). In children or infants, the ratio may change, and adjustments should be made according to guidelines.
Advanced Resuscitation Techniques
In more advanced resuscitation scenarios, additional techniques and tools may be necessary to support the patient’s recovery:
- Defibrillation: When a patient experiences certain types of cardiac arrest, such as ventricular fibrillation, delivering a shock via an automated external defibrillator (AED) can restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Advanced Airway Management: In some cases, securing an advanced airway, such as intubation, may be necessary to ensure proper ventilation and oxygenation during resuscitation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as epinephrine, may be administered during advanced resuscitation to stimulate the heart and improve circulation.
Consistent practice, along with knowledge of the latest CPR guidelines, is essential for maintaining proficiency. Regular training and simulations can help improve speed, accuracy, and effectiveness in real-life situations.
Critical Thinking During the Exam

During an evaluation that tests emergency response skills, critical thinking plays a crucial role in decision-making and problem-solving. The ability to think quickly and adapt to changing situations can significantly impact the outcome of a case. Rather than simply following a set of instructions, candidates must assess the situation, prioritize actions, and apply their knowledge effectively. This skill is essential for success, as it allows you to manage multiple tasks under pressure and make informed decisions in real-time.
Analyzing the Situation

The first step in critical thinking is evaluating the scenario in front of you. Gathering key information about the patient’s condition, surroundings, and available resources is vital. A clear mental picture of the situation will help you prioritize immediate actions and avoid errors. Key considerations include:
- Patient Assessment: Begin with a systematic assessment to identify life-threatening conditions. Determine airway, breathing, and circulation (ABC) status to guide your next steps.
- Environmental Factors: Be mindful of hazards such as traffic, unstable terrain, or exposure to toxins. Ensure that the environment is safe before proceeding with care.
- Team Communication: Effective communication with your team is essential. Relay information clearly and delegate tasks based on the situation at hand.
Making Informed Decisions
Once the situation is analyzed, the next step is to make decisions that will lead to the best possible outcome. In high-pressure scenarios, the ability to remain calm and focus on evidence-based practices is key. It’s important to:
- Prioritize Actions: Address the most urgent needs first, such as ensuring the patient’s airway is clear or initiating CPR. Less critical issues can be handled later.
- Adapt as Needed: Be prepared to modify your approach as new information emerges or conditions change. Flexibility is vital in dynamic environments.
- Stay Confident: Trust in your training and abilities. Confidence, along with critical thinking, can help you remain composed and make effective decisions under pressure.
Mastering critical thinking enhances your ability to respond effectively, ensuring that you provide the best care possible while under evaluation.
Post-Exam Reflection and Feedback
After completing a skills assessment, it’s essential to take time for reflection and to seek constructive feedback. This stage is critical for personal growth, as it helps you identify areas of strength and improvement. Reflecting on your performance allows you to evaluate your decision-making, time management, and overall approach to each task. Feedback from evaluators or peers provides valuable insights that can enhance your future performance.
Reflecting on Your Performance

Taking time to think about how you handled each part of the assessment can provide a clearer understanding of your abilities. Consider the following points during your reflection:
- Decision-Making: Did you prioritize tasks effectively? Did your actions align with the patient’s needs and urgency?
- Skill Execution: Were your technical skills, such as airway management or patient assessment, executed with precision and confidence?
- Communication: How well did you communicate with others, including your team or the patient? Were you clear, calm, and concise?
- Time Management: Did you stay on track and manage your time effectively? Were you able to complete each task within the allotted time frame?
Seeking Constructive Feedback
Feedback from instructors, examiners, or peers is crucial for improvement. Constructive feedback helps you recognize what worked well and what could be improved. Consider the following approaches for obtaining and utilizing feedback:
- Ask Specific Questions: Inquire about particular aspects of your performance, such as how you managed a certain skill or handled a particular situation.
- Listen Actively: Pay close attention to both positive and constructive comments. Keep an open mind, and avoid becoming defensive.
- Request Actionable Advice: Ask for tips on how to improve in specific areas. This can help guide your study or practice in preparation for future assessments.
- Use Feedback for Growth: Incorporate the feedback into your training routine, focusing on areas that need refinement or further practice.
Engaging in reflection and actively seeking feedback creates a continuous learning cycle, fostering both personal and professional development.
How to Handle Unexpected Scenarios
In any hands-on assessment, it’s common to encounter situations that are unpredictable or outside of your usual preparation. Being able to stay composed and think critically when faced with these unexpected challenges is essential. The ability to adapt quickly while maintaining a clear and logical approach will not only help you perform better but also demonstrate your readiness to handle real-world situations. Here are strategies for managing these types of situations effectively.
Stay Calm and Focused

The first step when confronted with an unforeseen event is to remain calm. Panicking will only make the situation more difficult. Take a deep breath and assess the situation methodically:
- Pause and Assess: Take a moment to quickly analyze the issue. What has changed? What new information is available? Understanding the problem fully is the first step in finding a solution.
- Stay Focused: Keep your mind clear of distractions. Focus on the task at hand and avoid thinking about any past mistakes or what might have gone wrong earlier.
- Prioritize Tasks: In unexpected scenarios, it’s vital to quickly identify the most urgent needs. Focus on critical tasks first and address less pressing matters later.
Adapt and Problem-Solve
Once you’ve assessed the situation and collected relevant information, adapt your approach. Problem-solving is key to navigating unpredictable scenarios:
- Think Creatively: If a typical solution is not available, be resourceful. Consider alternative methods and think outside the box to find a viable solution.
- Use Available Resources: Leverage any tools, equipment, or team members that can assist in resolving the issue. Don’t hesitate to ask for help or consult resources if needed.
- Communicate Effectively: If the situation requires assistance from others, communicate clearly and calmly. This ensures everyone is on the same page and can contribute to the resolution.
- Stay Flexible: Unexpected situations often require adjustments to your plan. Stay flexible and be willing to change your approach as the situation evolves.
By maintaining a calm demeanor and using problem-solving skills, you can manage unforeseen challenges with confidence. These abilities will not only enhance your performance during the assessment but also prepare you for real-life emergencies.
EMT Exam Myths and Misconceptions
There are many misconceptions and myths that surround hands-on assessments in the medical field. These misunderstandings can cause unnecessary stress or confusion for individuals preparing for these evaluations. It’s essential to separate fact from fiction to approach the process with the right mindset and be better prepared for success. Below, we’ll address some of the most common myths and clear up the confusion surrounding them.
Common Myths About the Assessment
Many people believe certain things about these evaluations that simply aren’t true. Here are some myths that need to be dispelled:
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| You need to memorize everything perfectly. | While knowing key procedures and protocols is important, it’s not about memorizing every detail. Understanding the fundamentals and being able to apply them in different scenarios is what matters most. |
| There’s no room for error. | Minor mistakes can happen. What’s important is how you recover and handle the situation. Demonstrating problem-solving skills and resilience is often more valuable than perfect execution. |
| Only experienced individuals pass the test. | People at various levels of experience can succeed. The key is preparation, practice, and the ability to remain calm under pressure. Experience helps, but even beginners can perform well with enough dedication. |
| The test is about speed, not accuracy. | While efficiency is important, precision and safety are paramount. Rushing through tasks may lead to mistakes. A balanced approach that emphasizes both speed and accuracy is the best strategy. |
Clearing Up Misconceptions About Preparation
Preparation for a hands-on evaluation is often misunderstood. Below are some common misconceptions and the truth behind them:
- Myth: You can study the night before and still do well. Reality: Consistent study and practice over time are key. Cramming will not provide lasting results.
- Myth: The test is all about technical knowledge. Reality: Critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving are just as important as technical skills.
- Myth: You’ll be evaluated in isolation. Reality: Teamwork and collaboration often play a role in the assessment, so working well with others is essential.
By understanding the realities behind these myths, you can approach the process with confidence and clarity, knowing what to expect and how to prepare effectively.
Steps to Take After Passing the Exam
Successfully completing a hands-on evaluation is a significant achievement, but it is just the beginning of your journey in the medical field. There are several important steps to take following this milestone that will help you transition smoothly into your professional role. Below, we outline the key actions to take after achieving this important goal.
Celebrate Your Achievement
It’s essential to acknowledge and celebrate the effort you’ve put into reaching this point. Completing the assessment demonstrates that you’ve acquired the necessary skills and knowledge, so take a moment to recognize your success. However, it’s also time to look ahead toward further professional development.
Next Steps for Certification and Employment
Once you’ve passed the assessment, there are a few steps you need to take to become fully certified and start your career:
- Submit Your Documentation: After passing the evaluation, ensure all required documentation, including test results, is submitted to the relevant certification or licensing body.
- Complete Any Additional Requirements: Depending on your region, there may be additional steps required to finalize your certification, such as background checks, physical exams, or continuing education.
- Search for Job Opportunities: Once certified, start looking for job openings that align with your new qualifications. Networking with industry professionals can also help in discovering potential opportunities.
Focus on Continuing Education

Your learning doesn’t end after the evaluation. The medical field is constantly evolving, so it’s crucial to stay up to date with the latest techniques and procedures. Continuing education is essential for your growth, and it can often be a requirement to maintain your certification.
- Enroll in Advanced Courses: Consider taking advanced courses or workshops to expand your skills and specialize in areas that interest you.
- Join Professional Associations: Becoming a member of professional organizations can provide access to educational resources, events, and a supportive community.
- Seek Mentorship: Find a mentor or experienced colleagues who can offer guidance and help you refine your skills further.
By following these steps after passing the assessment, you will be well-equipped to begin your career and continue advancing within your field. Keep focused on ongoing professional development, and embrace opportunities for growth and improvement.