
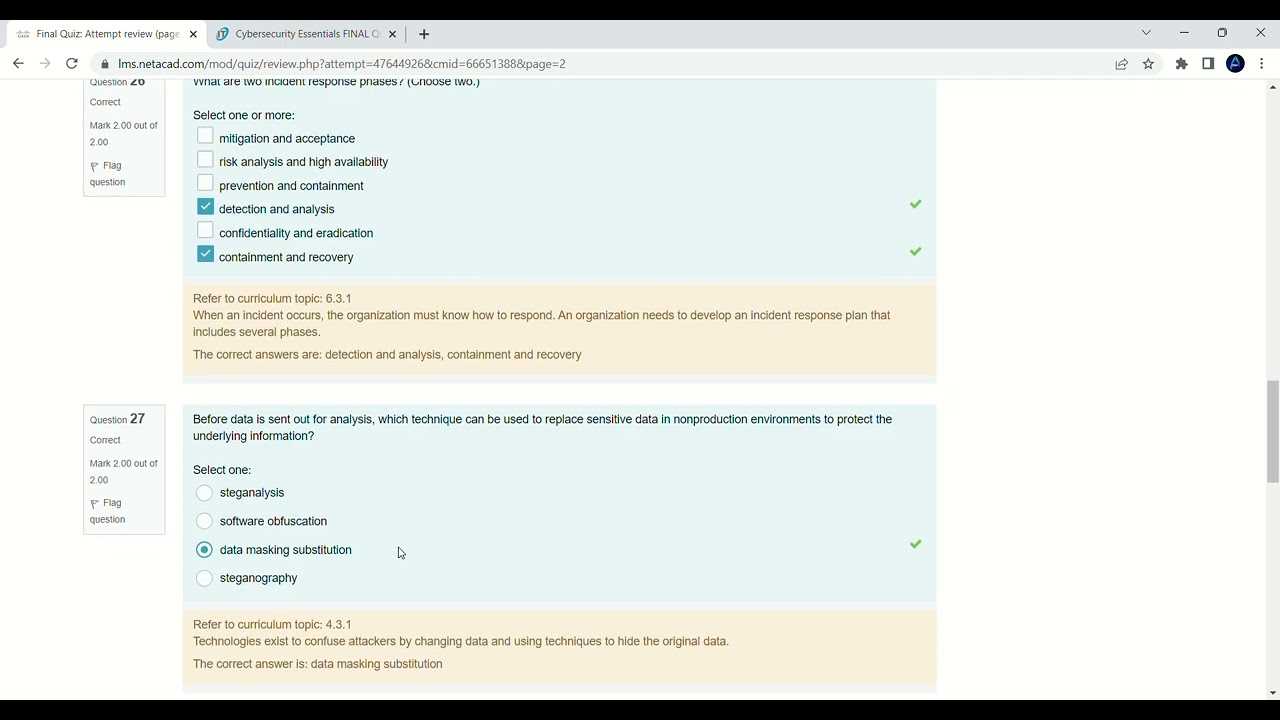
In today’s digital world, protecting sensitive data and systems from potential threats is a critical concern. With a variety of techniques and strategies available, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles that form the backbone of a well-structured defense plan. This section aims to guide learners through key topics that help develop the knowledge necessary for safeguarding critical information.
Through focused study, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of risk management, access control, and defensive measures designed to prevent unauthorized access or damage. It is important to grasp the underlying concepts that empower professionals to make informed decisions about how to tackle various challenges in the realm of system protection.
Whether you are preparing for a certification or aiming to sharpen your expertise, mastering these core ideas will provide the foundation you need to excel in any related field. The questions and scenarios presented are designed to test your grasp of vital concepts and ensure you are well-prepared to apply this knowledge in real-world situations.
Cyber Protection Fundamentals: Key Insights

When preparing for an assessment in the field of information defense, it is crucial to understand a wide array of principles and techniques that govern how systems and data are protected. This section highlights the core concepts that are typically explored, testing both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Familiarizing yourself with these key elements will help ensure a solid grasp of fundamental ideas in this area.
Core Topics You Need to Understand
- Identifying potential threats and weaknesses in digital infrastructures.
- Methods for controlling access to sensitive information and systems.
- Understanding the role of encryption in safeguarding data.
- Best practices for securing networks and applications from attacks.
- Developing risk management strategies to address emerging vulnerabilities.
Approaching Practice Questions
To succeed in any knowledge-based evaluation, it’s essential to engage with a variety of practice scenarios. Here are some tips to approach them effectively:
- Understand the Context: Read each question carefully, ensuring you fully grasp the scenario before responding.
- Focus on Key Concepts: Identify the core principle being tested and connect it with practical solutions or strategies.
- Apply Real-World Scenarios: Think about how the theoretical knowledge you have learned can be applied in a real-world setting.
Overview of Key Concepts in Information Protection
Protecting digital systems and sensitive data requires a comprehensive understanding of various fundamental principles. This area of study focuses on the methods, tools, and techniques necessary to prevent unauthorized access, mitigate risks, and ensure the safe operation of information systems. Mastering these core concepts is crucial for anyone seeking to safeguard networks, applications, and personal data from a wide range of potential threats.
In this section, we will explore the primary topics that lay the foundation for effective defense strategies. Gaining knowledge of these principles equips individuals with the skills needed to address challenges in the ever-evolving landscape of digital protection.
Core Topics You Will Encounter
- Understanding different types of risks and how to assess vulnerabilities in systems.
- Key techniques for safeguarding confidential information from unauthorized access.
- The importance of developing robust strategies for managing potential threats.
- Implementing controls to restrict access to sensitive data and systems.
- Strategies for monitoring and responding to security incidents or breaches.
Applying Knowledge in Real-World Scenarios
Once you have a solid understanding of the concepts, it’s essential to apply them in practical situations. Here are a few areas where you can test and refine your knowledge:
- Simulating Threat Scenarios: Engage in mock scenarios to identify and address vulnerabilities in a controlled environment.
- Risk Assessment Exercises: Conduct assessments to evaluate potential risks and create mitigation plans.
- Tools and Techniques: Explore and apply tools designed to monitor, detect, and respond to threats.
Key Concepts Covered in the Assessment
In any assessment focused on information protection, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the fundamental ideas that underpin this field. The questions typically cover a wide range of topics, each designed to test your knowledge of how to defend digital systems, manage risks, and apply defensive strategies. These core concepts are central to building a comprehensive understanding of how to safeguard data and resources effectively.
The following table outlines some of the primary topics that you will encounter, each highlighting a key area of study that is critical for anyone working in the field of information defense.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Management | Identifying and mitigating potential threats and vulnerabilities in systems and networks. |
| Access Control | Implementing methods to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive information or systems. |
| Encryption | Using cryptographic techniques to protect data during storage or transmission. |
| Network Defense | Applying strategies to safeguard networks from attacks and breaches. |
| Incident Response | Developing procedures for detecting, analyzing, and responding to potential breaches or attacks. |
Understanding Threats and Vulnerabilities
In the field of information protection, it is crucial to recognize and understand the various risks and weaknesses that can compromise digital systems. Identifying these threats and vulnerabilities allows professionals to create effective strategies for preventing or mitigating potential damage. Understanding the nature of these dangers is the first step in safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of networks and applications.
There are several types of threats and vulnerabilities that organizations must be aware of. These range from external attacks to internal misconfigurations, all of which can expose systems to potential breaches or exploitation. Below are some of the most common threats and vulnerabilities found in the digital environment.
Common Threats
- Malware: Malicious software designed to infiltrate and damage systems, often used to steal data or disrupt operations.
- Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to acquire sensitive information through deceptive communications, often appearing as legitimate requests.
- Ransomware: A form of malware that locks or encrypts files and demands payment for access restoration.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Overloading a system or network to make it unavailable to users, often causing business disruptions.
- Insider Threats: Risks posed by individuals within the organization who intentionally or unintentionally compromise security.
Common Vulnerabilities
- Weak Passwords: Using easily guessable or reused passwords that can be exploited by attackers.
- Unpatched Software: Failure to update systems and software can leave them open to exploitation through known vulnerabilities.
- Improper Configuration: Misconfigured systems or networks that expose sensitive data or resources to unauthorized access.
- Lack of Encryption: Unencrypted data is vulnerable to interception and theft, especially during transmission.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into revealing confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
By understanding these threats and vulnerabilities, individuals and organizations can take the necessary steps to prevent attacks and improve overall protection strategies.
Protecting Networks and Information Systems
Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of digital networks and the data they carry is vital for maintaining a secure environment. Protecting these infrastructures requires a combination of technological solutions and strategic practices that work together to prevent unauthorized access and potential damage. From firewalls to encryption, various tools and methodologies help safeguard critical systems and sensitive information.
Proper protection begins with a solid understanding of the potential risks and how they can be mitigated through proactive measures. This involves not only using the right tools but also implementing policies and procedures that reduce vulnerabilities and enhance the overall defense mechanisms.
Key Protection Techniques

- Firewalls: Devices or software that control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, acting as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Tools designed to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential threats.
- Encryption: The process of encoding information so that only authorized individuals can access or read it, ensuring data confidentiality during storage and transmission.
- Access Control: Mechanisms that restrict access to systems or data based on user credentials and permissions, ensuring that only authorized individuals can perform specific actions.
Best Practices for Maintaining Protection
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping systems and applications up to date ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched, reducing the chances of exploitation.
- Security Audits: Conducting regular audits and assessments to identify potential weaknesses and areas for improvement in the network and system defenses.
- Employee Training: Educating staff about potential risks such as phishing, social engineering, and safe online practices helps prevent human error from becoming a vulnerability.
- Backups: Regularly backing up important data ensures that, in the event of an attack or failure, critical information can be restored without significant loss.
Common Attacks and Defense Methods
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, various types of malicious activities are constantly emerging, each designed to exploit weaknesses in systems and networks. Understanding the common types of attacks is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate risks and protect valuable information. This section explores the most frequent forms of threats and the defense methods that can be implemented to counteract them.
These attacks often aim to disrupt, damage, or steal sensitive data. However, with the right defensive measures in place, organizations can significantly reduce the impact of these threats and maintain the integrity of their systems.
Types of Attacks
- Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to trick individuals into disclosing personal information, often through deceptive emails or websites.
- Malware: Malicious software designed to damage or gain unauthorized access to systems, including viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Denial of Service (DoS): Overloading a network or server with traffic to disrupt its normal operation and make it unavailable to users.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and altering communication between two parties to steal or manipulate sensitive data.
- SQL Injection: Injecting malicious SQL queries into a database to gain unauthorized access to information stored within it.
Defense Methods
- Firewalls: Implementing firewalls to filter and monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, preventing unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encrypting data ensures that even if it is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Using IDS to detect unusual network activity and alert administrators to potential attacks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of verification to enhance access control and prevent unauthorized login attempts.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
Security Tools and Techniques Explained
To protect valuable data and ensure the integrity of information systems, various tools and methods are employed. These instruments help identify vulnerabilities, prevent unauthorized access, and provide mechanisms for recovery in case of breaches. Understanding how these tools work and how they complement each other is crucial for building a robust defense system. This section explores the most commonly used tools and techniques for safeguarding digital environments.
From firewalls to advanced monitoring systems, the right combination of techniques can help prevent the most common threats. These tools are essential for both detecting and mitigating risks before they escalate into serious incidents.
Common Security Tools

| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Firewall | Monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, acting as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external sources. |
| Antivirus Software | Detects, prevents, and removes malicious software such as viruses, worms, and ransomware that can compromise a system’s integrity. |
| Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | Monitors network or system activities for malicious activities or policy violations and provides alerts to administrators when potential threats are detected. |
| Encryption Tools | Encrypts data to protect it from unauthorized access during storage or transmission, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. |
| Virtual Private Network (VPN) | Secures internet connections by creating a private network over a public one, helping protect sensitive data during transmission. |
Techniques for Data Protection
- Access Control: Restricting access to systems or data based on user roles and responsibilities to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a fingerprint scan, to verify user identity before granting access.
- Regular Patching: Updating software and systems regularly to fix known vulnerabilities and ensure systems remain protected against emerging threats.
- Data Backups: Regularly backing up critical data to ensure recovery in case of data loss or system compromise.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into segments to limit access to sensitive data and reduce the scope of potential attacks.
Importance of Risk Management in Cybersecurity
Effective risk management plays a crucial role in protecting digital systems and sensitive data from potential threats. It involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to minimize their impact and likelihood. Without a structured approach to managing risks, organizations leave themselves vulnerable to attacks, data breaches, and other forms of disruption. This section highlights the importance of a solid risk management strategy and how it contributes to maintaining a secure and resilient digital environment.
By understanding potential risks and implementing mitigation strategies, businesses can better prepare for unforeseen events and reduce the likelihood of significant damage. Risk management not only helps protect valuable assets but also ensures that organizations can continue to operate effectively even in the face of challenges.
How to Prepare for the Final Assessment
Preparing effectively for any comprehensive assessment requires a focused approach and a solid understanding of the subject matter. Success depends on familiarizing yourself with key concepts, identifying areas that need improvement, and practicing problem-solving skills. This section provides practical tips and strategies for preparing thoroughly, ensuring you feel confident and ready for the challenges that lie ahead.
Start by reviewing all relevant material, focusing on the most critical topics. Make sure to allocate sufficient time for each subject, and seek out additional resources if necessary. By staying organized and proactive in your studies, you can enhance your readiness and improve your performance during the assessment.
Top Study Tips for Cybersecurity Exams
Successfully preparing for an assessment in the field of digital protection requires strategic planning and focused effort. It’s important to approach your study sessions in a way that maximizes understanding and retention of key topics. This section will offer practical tips to help you organize your study time effectively and ensure you cover all the necessary material before your assessment.
Start Early: Begin your revision well in advance to avoid last-minute cramming. Spacing out your study sessions allows for better long-term retention and reduces stress.
Focus on Core Concepts: Identify the most critical topics within the subject and dedicate more time to understanding these concepts. A strong grasp of the fundamentals will help you tackle more complex questions during the assessment.
Practice with Sample Questions: Working through practice questions and previous assessments is an excellent way to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions that may appear. It also helps you identify areas where you need more focus.
Use Visual Aids: Diagrams, flowcharts, and mind maps can help simplify complex information and make it easier to recall. Visualizing concepts can enhance your understanding and retention.
Study in Groups: Collaborating with peers can provide new insights and help reinforce your knowledge. Group study encourages discussion and allows you to explain concepts to others, which further strengthens your own understanding.
Stay Organized: Keep track of all your notes, resources, and study materials in an organized manner. Creating a study schedule and breaking down tasks into manageable sections can prevent overwhelm and ensure efficient preparation.
Cyber Security Laws and Ethical Considerations
In the field of digital protection, legal and ethical aspects are just as important as technical skills. Professionals must navigate a complex landscape of laws and regulations while ensuring that their actions align with ethical standards. Understanding the legal requirements and ethical implications helps organizations avoid legal pitfalls and promotes responsible practices in safeguarding digital assets.
Regulations governing the use of technology and the protection of data have become increasingly important as digital threats evolve. These laws are designed to maintain privacy, protect user data, and ensure that digital systems are used in a fair and responsible manner. Ethical considerations, on the other hand, focus on the moral obligations of those working with sensitive information and technologies.
Key Legal Aspects
- Data Protection Laws: Laws that govern how personal and sensitive data is collected, stored, and shared. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a prime example of such legislation.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Protects the rights of creators and organizations regarding software, patents, and proprietary information.
- Computer Fraud and Abuse Laws: Legal frameworks that address activities such as hacking, unauthorized access to systems, and fraud committed using technology.
- Compliance Standards: Regulations like PCI-DSS and HIPAA that set mandatory requirements for industries dealing with sensitive financial or health data.
Ethical Considerations
- Privacy: The right of individuals to control their personal information and how it is used by organizations.
- Transparency: Ensuring that practices are open and that stakeholders are informed about how their data is being protected.
- Responsibility: Professionals must take accountability for the actions they take in relation to digital systems and data.
- Fairness: Ensuring that all individuals are treated equally and without bias, especially when it comes to data usage and access rights.
By understanding both legal requirements and ethical responsibilities, professionals can help create a safer, more trustworthy digital environment while staying compliant with the law.
Impact of Data Protection on Businesses
Effective management of data protection plays a vital role in the success and reputation of businesses. It not only ensures the safety and privacy of sensitive information but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders. As organizations increasingly rely on digital systems to store and process data, safeguarding that information has become a core component of business operations. In this section, we will explore how data protection impacts various aspects of a business, from legal compliance to customer loyalty.
When businesses implement strong data protection practices, they reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, which can result in significant financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage. On the other hand, a lack of proper protection can lead to serious consequences, affecting both the organization and its clients.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with data protection laws is mandatory for businesses that handle sensitive information. Failure to adhere to regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) can result in hefty fines and legal challenges. Ensuring compliance not only prevents legal repercussions but also demonstrates a commitment to privacy and transparency.
Customer Trust and Reputation
When customers know that their personal data is being handled with care, they are more likely to trust the organization and engage in long-term business relationships. A strong data protection strategy can thus be a competitive advantage, helping businesses attract and retain customers. Conversely, a data breach can erode customer confidence and lead to loss of business.
Operational Efficiency

Implementing data protection measures often involves streamlining processes, improving data management practices, and adopting security technologies. These steps can enhance the overall efficiency of business operations by reducing errors, ensuring better data integrity, and preventing downtime caused by data-related issues.
In conclusion, businesses that prioritize data protection not only safeguard sensitive information but also position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly digital and regulated world.
Critical Security Principles for Organizations
In today’s digital landscape, organizations must adopt key principles to protect their information systems, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their data. By following a set of fundamental guidelines, businesses can reduce the risk of breaches and maintain the trust of their customers and partners. This section explores the core principles that every organization should embrace to strengthen its defenses and improve overall resilience.
Key Principles to Follow

- Least Privilege: Granting access only to the data and systems that are necessary for an individual’s role. This minimizes potential exposure and limits the scope of damage if credentials are compromised.
- Defense in Depth: Implementing multiple layers of security measures across the organization. This strategy ensures that if one layer is bypassed, additional layers will still provide protection.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This protects information from being accessed by unauthorized parties, even if it is intercepted.
- Regular Audits: Conducting frequent reviews of systems, policies, and access controls. Audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Incident Response Plan: Having a structured approach for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents. This helps minimize the impact of breaches and ensures quick recovery.
Building a Culture of Awareness
A crucial element in maintaining strong defenses is fostering a culture of awareness within the organization. Employees should be regularly trained on best practices, potential risks, and how to recognize security threats. Engaging staff in proactive learning and raising awareness of potential threats, such as phishing or social engineering attacks, can significantly reduce the likelihood of human error compromising an organization’s safety.
By adhering to these principles, organizations not only protect their own interests but also contribute to a safer and more resilient digital ecosystem. Ensuring robust defenses requires a commitment to continuous improvement and vigilance.
Exam Questions Related to Cryptography

Understanding the principles and techniques of encryption is crucial in safeguarding data. Cryptography plays an essential role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. This section covers common topics and types of questions related to cryptographic methods, offering insights into the core concepts and practices you should be familiar with for assessment purposes.
Key Areas in Cryptography
When preparing for questions related to cryptography, it is important to focus on the following areas:
- Symmetric Encryption: Algorithms where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. Understand their strengths, weaknesses, and use cases.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Public and private keys work together to encrypt and decrypt messages. Be familiar with how this technique is implemented in various protocols.
- Hash Functions: These one-way functions are used to verify data integrity. Understand how hashes are applied in digital signatures and password storage.
- Digital Signatures: Learn how they ensure the authenticity and integrity of messages or documents.
- Cryptographic Protocols: Familiarize yourself with the various protocols that leverage cryptographic techniques, such as SSL/TLS, and their role in secure communications.
Example Questions
| Question | Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption? | Encryption Techniques | Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys (public and private). |
| Explain the role of a hash function in digital security. | Hash Functions | Hash functions generate a fixed-length output from an input of any size, providing a unique identifier for data to ensure integrity. |
| How does a digital signature work? | Digital Signatures | A digital signature verifies the authenticity of a message or document by using asymmetric encryption, ensuring that the sender is legitimate. |
| What is the purpose of public-key infrastructure (PKI)? | Public-Key Cryptography | PKI is a framework for managing public and private keys, enabling secure communications and verifying identities using digital certificates. |
Being familiar with these topics and understanding how to apply cryptographic principles will ensure that you are well-prepared for any questions related to encryption methods. Focus on both theoretical knowledge and practical applications for a comprehensive understanding.
Access Control Methods and Best Practices
In any organization, controlling who has access to what information is vital for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of data. Proper access management ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive systems, applications, and data, while also preventing unauthorized use. This section covers the primary methods for regulating access to critical resources and outlines best practices for implementing these strategies effectively.
Access control mechanisms typically fall into a few categories, each designed to protect systems in different ways. These methods are designed to enforce restrictions, monitor activity, and mitigate the risk of data breaches or other malicious actions. Whether it’s granting permission based on user identity, role, or even specific needs, having the right structure is key to safeguarding organizational assets.
Common Access Control Models
The following models represent the most commonly used approaches to restricting access to sensitive resources:
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): In this model, owners of the resources have the discretion to decide who can access their data or systems. It’s flexible but can be prone to human error.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): This model enforces strict access controls based on classification levels. Permissions are assigned by the system, not individual users.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Access is granted based on a user’s role within the organization. Permissions are tied to roles rather than individuals, making this model more efficient for large organizations.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Access decisions are made based on attributes, such as a user’s job position, location, or security clearance, providing fine-grained access control.
Best Practices for Access Control
To ensure access control mechanisms are implemented effectively and reduce the risk of unauthorized access, follow these best practices:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Users should only have access to the resources they need to perform their job functions, nothing more. This minimizes the risk of accidental or malicious misuse.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic reviews of access permissions to ensure that users have the appropriate level of access. Remove unnecessary permissions to reduce vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance access control by requiring multiple forms of verification. This adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Segregation of Duties: Ensure that no single individual has control over all aspects of a critical process. This helps prevent fraud and other malicious actions.
- Logging and Monitoring: Keep detailed logs of user access to sensitive data and systems. Regularly monitor these logs to detect and respond to potential security threats.
By adopting these methods and following best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data leaks, and other malicious activities. Effective access control is an essential aspect of any robust data protection strategy.
Role of Security Policies in Cyber Defense

In the modern digital landscape, organizations face numerous threats that can jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information systems. To combat these challenges, a well-structured framework is necessary, one that establishes clear guidelines for protecting sensitive resources. Policies play a central role in this framework by providing the foundational rules and procedures that govern how information should be handled, accessed, and safeguarded.
Security policies act as the blueprint for an organization’s approach to safeguarding its digital assets. They outline the measures, responsibilities, and protocols that employees and systems must follow to mitigate risks and defend against potential breaches. Without these policies, organizations would be left without clear direction, increasing the vulnerability to attacks and unintentional mistakes.
Key Aspects of Effective Security Policies

For security policies to be effective, they must cover several crucial aspects:
- Access Control: Policies should clearly define who can access specific resources, under what circumstances, and what actions they are allowed to perform.
- Data Protection: Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data through encryption, secure storage, and controlled sharing.
- Incident Response: Procedures for how the organization will respond to and recover from security incidents, ensuring minimal damage and swift recovery.
- Compliance: Security policies should align with industry regulations and legal requirements, ensuring the organization adheres to necessary standards and laws.
Benefits of Strong Security Policies
Establishing comprehensive security policies offers numerous benefits for an organization:
- Risk Reduction: Clear policies help minimize the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security incidents by setting preventive measures in place.
- Consistency: Policies ensure that every individual within the organization follows the same guidelines, creating a uniform approach to safeguarding resources.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to industry regulations and standards through security policies helps organizations avoid legal penalties and fines.
- Employee Awareness: Well-defined policies educate employees on the importance of safe digital practices and their role in maintaining a secure environment.
In conclusion, security policies are not merely formal documents but essential tools for creating a culture of vigilance and proactive defense. They provide organizations with the framework necessary to safeguard valuable digital assets, reduce risks, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
How to Interpret Cyber Security Scenarios
When faced with complex situations in the realm of information protection, it is essential to understand how to accurately analyze and interpret various scenarios. Each situation typically involves assessing risks, identifying vulnerabilities, and applying best practices to mitigate potential threats. The ability to break down these scenarios methodically ensures an informed response, whether in a theoretical context or a real-world application.
Understanding how to interpret security scenarios requires a structured approach that focuses on key factors such as the type of threat, the systems involved, and the response strategies. By analyzing the context and key elements of a situation, individuals can formulate appropriate strategies to protect systems and data.
Key Steps in Interpreting Scenarios
To effectively interpret scenarios, it’s important to follow a systematic process. Here are the steps involved:
- Identify the Type of Threat: Determine whether the scenario involves internal or external threats, and assess the scope of the potential risk.
- Analyze the Affected Systems: Evaluate which systems or components are vulnerable, and consider the consequences of an attack or breach.
- Determine the Impact: Assess the potential damage or disruption caused by the incident, focusing on data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
- Identify Mitigation Strategies: Develop appropriate strategies to defend against or resolve the issue, based on the severity of the situation.
Common Scenarios and Responses

Here are some typical scenarios you might encounter, along with suggested actions:
| Scenario | Possible Response |
|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access Attempt | Implement stronger access control measures, such as multi-factor authentication, and monitor logs for suspicious activity. |
| Phishing Attack | Educate users about phishing tactics, enhance email filtering, and conduct regular security awareness training. |
| Data Breach | Investigate the breach, contain the situation, notify affected parties, and review security measures to prevent future incidents. |
| Malware Infection | Run comprehensive antivirus scans, isolate infected systems, and apply patches to vulnerabilities exploited by the malware. |
By following a structured approach and utilizing a wide range of tools, professionals can interpret and respond to scenarios effectively. This process helps ensure the protection of valuable information assets and reduces the risk of serious consequences in the event of a breach or attack.
Key Takeaways from Cyber Security Essentials
Understanding the fundamental concepts behind protecting information and systems is crucial for anyone involved in managing technology. Key takeaways from foundational courses or practices in this area provide valuable insights into the best approaches for safeguarding critical data, responding to potential threats, and maintaining a secure environment. This knowledge lays the groundwork for a solid defense strategy in both professional and personal contexts.
Core Principles of Information Protection

The first takeaway revolves around core principles that form the foundation of any protective strategy:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized individuals, thereby preventing unauthorized access or leakage.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle, preventing alterations or tampering.
- Availability: Ensuring that systems and data are accessible and functional when needed, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
Best Practices for Effective Defense
Another important takeaway is the application of best practices, which serve as guidelines for creating a robust defense system. Some key practices include:
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping software and systems up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Employee Training: Educating staff members about potential risks, including phishing, social engineering, and safe internet usage to reduce human error.
- Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to minimize the impact of potential breaches or disruptions.
By understanding these foundational principles and best practices, individuals can better prepare for and respond to potential threats, ensuring that their systems and information remain secure.