
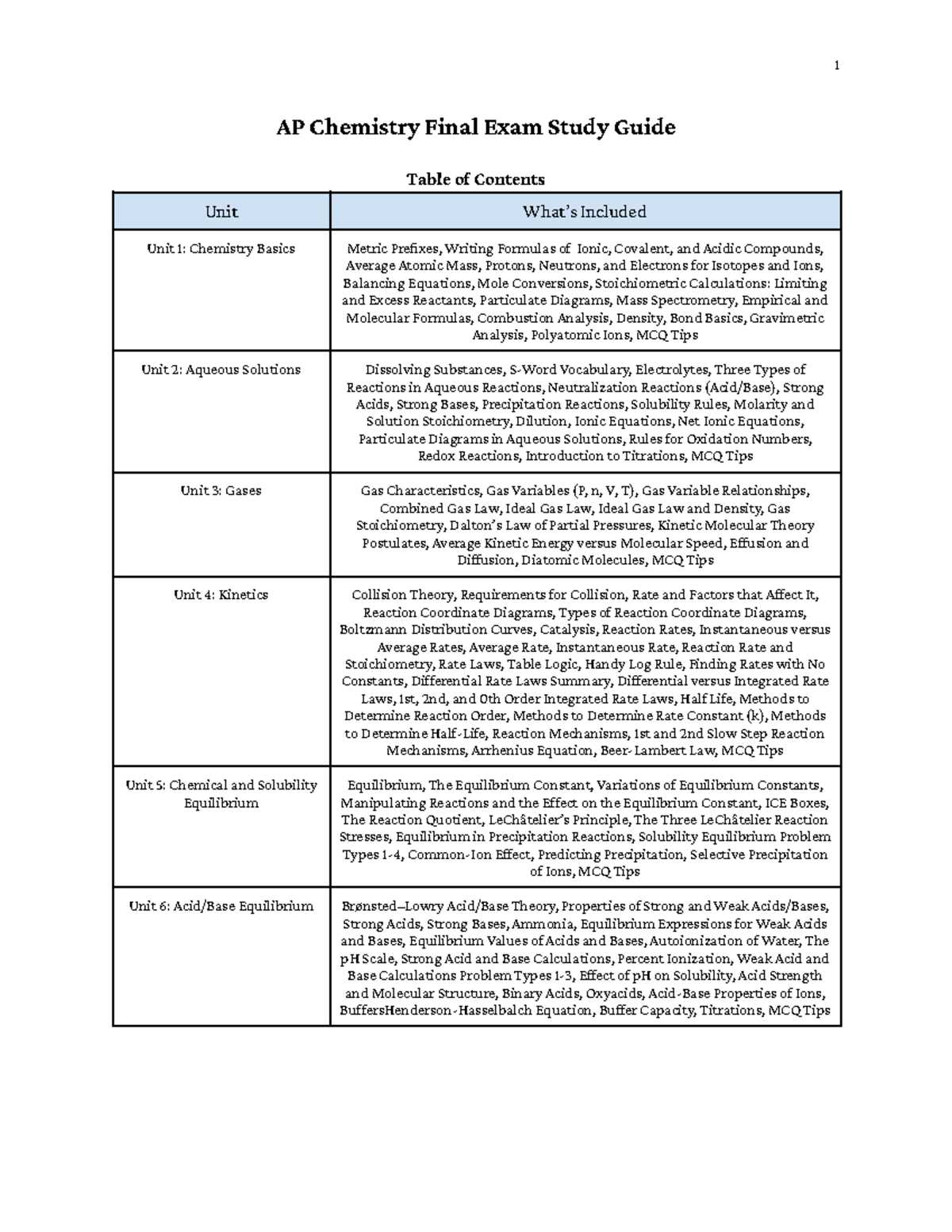
Preparing for an important assessment requires a clear understanding of the topics covered. It’s essential to focus on the core principles that will help you succeed, ensuring that you are well-equipped to tackle a variety of questions. By revisiting fundamental ideas and practicing problem-solving techniques, you can boost your confidence and performance.
Strengthening your knowledge involves reviewing major themes, learning essential formulas, and mastering key strategies. An organized study approach can help you focus on what truly matters, from basic concepts to complex calculations. It’s important to identify areas that need extra attention, allowing you to optimize your preparation time.
Success lies in understanding the material deeply rather than memorizing isolated facts. With a solid foundation, you’ll approach each challenge with clarity and precision. The goal is to confidently apply your understanding when it counts most, ensuring you’re fully prepared for any question that comes your way.
Preparation for the Upcoming Test
Success in any important assessment depends on mastering essential topics and understanding how to apply knowledge to various questions. Focusing on the key principles and methods will not only help you answer questions with confidence but also ensure a strong performance when it matters most. By organizing your study plan and identifying areas that need additional focus, you can sharpen your skills and strengthen your grasp of the material.
To perform well, it’s important to practice applying concepts, whether it’s solving equations, balancing reactions, or understanding scientific principles. Repetition and active engagement with different problem types can help reinforce your understanding and improve your ability to recall information under pressure.
In this section, we will break down the most important topics and provide guidance on how to approach the questions you’re likely to encounter. By reviewing these key areas, you can increase your familiarity with the material and better manage your time during the assessment. Understanding how to approach complex problems and recognizing the connections between different concepts is critical to excelling.
Key Concepts to Focus On
In preparation for any significant assessment, it’s essential to understand the most crucial areas of study. Focusing on the fundamental principles that underpin the material will help you approach the test with confidence. Concentrating on the core concepts allows you to apply your knowledge effectively, ensuring you’re prepared for a wide range of possible questions.
Understanding Atomic Structure

One of the foundational topics to master is the structure of the atom. Understanding the role of protons, neutrons, and electrons, along with their arrangement, is essential for grasping various concepts in other areas. Pay special attention to the periodic table, as it provides a clear layout of elements based on their atomic number and properties.
Mastering Chemical Reactions
Another key area to focus on is chemical reactions. Understanding how substances interact to form new compounds is critical for solving problems. Familiarize yourself with different types of reactions, such as synthesis, decomposition, and combustion, as well as how to balance chemical equations. This knowledge forms the basis for more complex topics, such as stoichiometry and reaction kinetics.
Essential Formulas for the Test
Knowing key mathematical relationships and formulas is crucial for tackling problems efficiently. These formulas serve as tools to solve various types of questions, from calculating molecular weight to determining reaction rates. Familiarizing yourself with these essential equations will enable you to approach complex problems with ease and precision.
Stoichiometry and Molar Relationships
Stoichiometry is the backbone of many problem-solving scenarios. The most important formula in this area is the relationship between moles, mass, and molar mass. Remember the equation:
moles = mass / molar mass. This simple formula helps convert between grams and moles, which is essential for solving a variety of questions related to chemical reactions and compound amounts.
Gas Law Equations
Gas laws are another important topic that requires understanding specific formulas. The ideal gas law is a key equation used to relate the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas. The formula is:
PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature. This formula is fundamental in understanding the behavior of gases under various conditions.
Understanding Chemical Reactions
Grasping the process of how substances interact to form new products is vital for success in solving related problems. Chemical transformations are at the heart of many scientific phenomena and understanding the principles that govern these changes can make it easier to predict and explain outcomes. From simple synthesis to complex combustion processes, mastering reaction types is essential for efficient problem-solving.
Types of Chemical Reactions

There are several types of reactions that you need to be familiar with. Some of the most common include synthesis, decomposition, and displacement reactions. In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a more complex product. Conversely, a decomposition reaction involves the breakdown of a single compound into simpler substances. Understanding these basic types can help you recognize patterns and predict products more effectively.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing equations is a fundamental skill for accurately representing chemical reactions. Every reaction must satisfy the law of conservation of mass, meaning the number of atoms on both sides of the equation must be equal. To balance an equation, adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products until both sides contain the same number of atoms of each element. This process ensures that mass is conserved throughout the reaction.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When preparing for an important assessment, it’s easy to overlook certain details or make avoidable errors that can impact your performance. Recognizing and correcting these common mistakes ahead of time can help you approach the test with greater confidence and accuracy. By understanding the typical pitfalls, you can ensure that you’re applying your knowledge effectively throughout the process.
Misunderstanding Key Concepts
One of the most frequent mistakes is not fully understanding the foundational principles behind the topics. Whether it’s confusion between different types of reactions or incorrect interpretation of formulas, a lack of clarity can lead to errors in problem-solving. Ensure that you have a deep grasp of each concept and can apply it to various scenarios before moving on to more complex problems.
Rushing Through Calculations
Another common mistake is rushing through mathematical calculations. In the pressure of the moment, it’s easy to make simple errors such as misplacing decimal points or miscalculating unit conversions. Always double-check your work and take the time to carefully follow each step. Mistakes often arise when students skip over basic steps or fail to review their calculations before finalizing answers.
Effective Study Strategies for Success
Achieving the best possible results requires not only understanding the material but also using the right approach to studying. Implementing efficient techniques can help you retain information more effectively and apply it when needed. The key is to structure your preparation in a way that minimizes stress while maximizing retention and comprehension.
Active Learning Techniques
Active learning involves engaging with the material in a way that promotes deeper understanding. Rather than simply reading or memorizing, try to actively apply what you’ve learned through problem-solving, teaching the concepts to someone else, or creating mind maps to visualize connections. This approach helps reinforce key ideas and makes it easier to recall information when required.
Time Management and Organization
One of the most effective strategies for success is mastering time management. By organizing your study sessions and sticking to a structured schedule, you can avoid cramming and reduce last-minute stress. Below is a sample study plan to help you organize your time effectively:
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 9:00 AM – 10:30 AM | Review Key Concepts and Formulas |
| 10:45 AM – 12:00 PM | Practice Problem Solving |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Break / Lunch |
| 1:00 PM – 2:30 PM | Work on Past Problems or Quizzes |
| 2:45 PM – 4:00 PM | Review Mistakes and Clarify Concepts |
By following a structured timetable and taking regular breaks, you can stay focused and retain information more effectively throughout your study sessions.
Tips for Time Management During the Test

Managing your time effectively during an assessment is just as important as knowing the material. Proper time allocation allows you to complete all sections while minimizing stress. The key to success is having a clear strategy to tackle each question efficiently without rushing or wasting time on difficult items.
Prioritize the Easy Questions
Start with the questions you find easiest, as this will help you build confidence and gain quick points. This approach also allows you to manage your time better by not spending too long on any single question.
- Quickly scan through the entire test to identify the easiest questions first.
- Answer all questions you’re confident about before moving on to harder ones.
- Ensure you don’t spend too much time on questions you’re uncertain about–mark them and move on.
Allocate Time for Review
It’s important to reserve some time at the end of the test to go back and review your answers. If you finish early, use this extra time to check for simple mistakes, such as calculation errors or misread questions.
- Set a specific time limit for each section of the test.
- Leave 10-15 minutes at the end for a quick review of all your responses.
- Double-check your answers for accuracy, especially for complex calculations or multi-step problems.
With these strategies, you can ensure that you stay on track and manage your time effectively during the entire assessment. The goal is to complete the test with confidence, knowing that you allocated time wisely to maximize your performance.
How to Tackle Multiple Choice Questions

Multiple choice questions often present a challenge due to the variety of potential answers, but they can be managed effectively with the right approach. The key is to read each question carefully, eliminate obviously incorrect options, and use reasoning to select the best possible answer. Following a structured method will increase your chances of selecting the correct response even when you’re unsure.
Step-by-Step Approach
Adopting a systematic method for each multiple choice question ensures that you don’t miss key details. Here’s a simple strategy to follow:
- Read the question thoroughly before looking at the answer choices. Make sure you understand what is being asked.
- Eliminate incorrect options by identifying answers that are clearly wrong or irrelevant. This increases your odds if you need to make a guess.
- Consider all the choices even if one option looks right. Sometimes, multiple choices seem correct, but one will be more precise than the others.
- Double-check your answer before moving on. Ensure that your selected option actually answers the question in full, not just partially.
Handling Uncertainty
If you’re unsure about a question, don’t panic. Follow these strategies to make an educated guess:
- If you know certain details from your study, use them to eliminate the least likely answers.
- Look for patterns in the choices, like similar wording or repeated concepts, which may give clues.
- If you’re completely unsure, choose the most logical or “safe” answer based on general knowledge, and move on.
By using this approach, you can tackle multiple choice questions with greater confidence and increase your accuracy under time pressure. Effective elimination and logical reasoning will allow you to maximize your chances of success.
Breaking Down Chemical Bonding
Understanding the interaction between atoms is essential for mastering many concepts in science. Chemical bonding explains how atoms combine to form compounds, and recognizing the different types of bonds allows for a deeper understanding of molecular behavior and properties. In this section, we will break down the key types of bonding and explore their fundamental differences and significance.
Ionic Bonds
An ionic bond forms when one atom donates an electron to another, resulting in the attraction between positively and negatively charged ions. This type of bond usually occurs between metals and nonmetals. The strong electrostatic force holds the ions together, giving rise to substances that often have high melting points and conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons to achieve stability. This type of bonding typically occurs between nonmetal atoms. Depending on the number of electron pairs shared, covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple. Molecules formed by covalent bonds can vary greatly in their physical properties, from gases to solids, depending on the nature of the atoms involved.
By understanding the differences between these types of bonds, you can predict the properties of substances and explain various reactions. Recognizing when atoms are likely to bond in specific ways allows for better comprehension of molecular structures and their behavior in different environments.
Reviewing Acid-Base Reactions
Understanding how acids and bases interact is a fundamental concept in many scientific fields. Acid-base reactions play a crucial role in various processes, from neutralizing substances to influencing the pH of solutions. In this section, we will explore the basic principles behind these reactions and their importance in both theory and practice.
Key Concepts of Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H+) between substances. Acids donate protons, while bases accept them. This simple concept leads to a wide range of reactions that are essential for everything from digestion to industrial applications.
- Acids are substances that can donate a proton (H+).
- Bases are substances that accept a proton (H+).
- Neutralization occurs when an acid and a base react to form water and a salt.
- pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic), with 7 being neutral.
Types of Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions can vary depending on the substances involved and the environment. Here are some common types:
- Strong Acid-Strong Base Reaction: Both reactants dissociate completely in solution, leading to a quick and complete neutralization.
- Weak Acid-Weak Base Reaction: Neither reactant dissociates completely, often resulting in an equilibrium where the reaction does not fully complete.
- Buffering Reactions: Substances that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acids or bases are added, helping to maintain stability in biological systems.
By grasping the fundamentals of acid-base reactions, you can better understand the behavior of substances in various chemical processes. This knowledge is crucial not only in laboratory settings but also in real-world applications, such as environmental science and medicine.
Mastering Stoichiometry Problems
Solving stoichiometry problems is an essential skill in understanding the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. This process involves converting between different units, using balanced equations, and applying the mole concept to determine the amounts of substances involved. Mastery of stoichiometry will allow you to make accurate predictions about chemical processes and is key to excelling in both theoretical and practical applications.
To tackle stoichiometry problems effectively, you need to follow a step-by-step approach that ensures you are using the correct conversion factors and calculations. With practice, you can quickly move from identifying the information given to solving for the unknown, whether it be moles, masses, or volumes of substances.
Here are some important steps to consider when working through stoichiometry problems:
- Step 1: Begin by balancing the chemical equation to ensure that the law of conservation of mass is satisfied.
- Step 2: Convert any given quantities (such as mass or volume) into moles using the appropriate molar mass or molar volume.
- Step 3: Use the mole ratio from the balanced equation to relate the moles of one substance to the moles of another.
- Step 4: Convert from moles back into the desired units (mass, volume, etc.), if needed.
With these steps, you can systematically solve stoichiometry problems and deepen your understanding of the quantitative nature of chemical reactions. This skill is indispensable for many aspects of science and is an invaluable tool for analyzing chemical processes.
Strategies for Balancing Equations
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill that ensures the law of conservation of mass is upheld in chemical reactions. In every reaction, the number of atoms for each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. This section will provide you with effective strategies for balancing equations and help you apply these techniques with confidence.
The process of balancing equations can seem challenging at first, but with the right approach, it becomes a systematic task. By following certain steps, you can achieve a balanced equation quickly and accurately. Below are some of the key strategies to consider when balancing chemical reactions:
| Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Start with complex molecules | Begin by balancing elements in more complex molecules, such as those with multiple atoms of a given element, before moving on to simpler ones. |
| Balance atoms one at a time | Focus on balancing one element at a time, adjusting the coefficients to ensure that the number of atoms on both sides matches. |
| Balance hydrogen and oxygen last | Since hydrogen and oxygen are often involved in many compounds, it is easiest to balance them at the end of the process. |
| Use fractional coefficients (if necessary) | In some cases, using fractional coefficients can help balance the equation before multiplying through by the least common denominator to eliminate fractions. |
By employing these strategies, you can develop a systematic approach to balancing equations that will save time and improve your accuracy. With practice, balancing chemical reactions will become a straightforward and intuitive process.
Critical Lab Concepts to Remember

Understanding key laboratory concepts is essential for conducting safe and effective experiments. The ability to apply these concepts allows you to interpret results accurately and follow correct procedures, ensuring both safety and precision in your work. Whether you are preparing for hands-on experiments or analyzing theoretical outcomes, keeping track of these critical ideas will greatly enhance your scientific skills.
Several core concepts are integral to any scientific investigation. From proper measurement techniques to understanding the importance of controlling variables, these ideas provide the foundation for conducting successful experiments. Below are some important concepts to always remember:
- Accuracy vs. Precision: Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true value, while precision indicates how consistently results can be reproduced. Both are crucial for reliable data interpretation.
- Safety Protocols: Always follow laboratory safety procedures, including wearing protective gear and handling chemicals carefully to prevent accidents and exposure to hazardous materials.
- Controlled Variables: In any experiment, it is essential to control other variables that could affect the outcome. This ensures that the results are due to the changes in the variable being tested.
- Proper Measurements: Accurate measurements are fundamental to experiment success. Always use the appropriate instruments and follow proper techniques to ensure reliable results.
- Experimental Design: Design experiments with clear objectives, a hypothesis, and reproducible steps. This helps avoid errors and ensures that results are meaningful.
By keeping these critical concepts in mind, you will be able to conduct experiments more effectively, analyze data with confidence, and draw accurate conclusions. Mastering these principles is essential for advancing in any scientific field.
Approaching Thermochemistry Questions
Understanding the flow of energy within chemical reactions is essential for tackling questions related to heat and energy changes. Thermochemistry focuses on the relationship between chemical reactions and the energy released or absorbed. Grasping key principles in this area can help you answer questions more accurately and efficiently, whether you’re calculating heat transfers or interpreting energy diagrams.
When approaching questions about energy changes in reactions, it is important to consider both the system and the surroundings. Pay close attention to whether energy is being absorbed or released, as this will influence the type of reaction and the methods you use to solve the problem. Below are some key strategies for approaching thermochemistry-related questions:
Understanding Heat Transfer
Thermochemistry problems often involve calculating heat transfer, either through specific heat or enthalpy. Familiarize yourself with the formulas and how to apply them in various scenarios, such as using q = mc?T for specific heat or ?H = H(products) – H(reactants) for enthalpy changes.
Recognizing Exothermic vs. Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions release energy, often in the form of heat, while endothermic reactions absorb energy. Identifying the type of reaction in a question will help guide your approach. For example, in an exothermic reaction, the products will have less energy than the reactants, whereas in an endothermic reaction, the products will have more energy.
By focusing on energy conservation and applying appropriate equations, you can effectively approach thermochemistry questions. The key is to methodically analyze the reaction’s energy flow and use the correct formulas to calculate the heat involved. With practice, these types of questions will become more intuitive and manageable.
Important Properties of Elements
Understanding the fundamental characteristics of elements is crucial for mastering topics related to atomic structure and behavior. These properties dictate how elements interact with each other, form compounds, and participate in chemical reactions. Key attributes such as electronegativity, atomic radius, and ionization energy provide insight into the nature of different elements and help predict their reactivity and bonding patterns.
Elements possess distinct properties that influence their behavior in various conditions. For example, the tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond is referred to as electronegativity. This property plays a significant role in determining how elements bond with others, especially in polar and nonpolar bonds.
Trends in the Periodic Table
The periodic table arranges elements based on their atomic number, but it also reflects periodic trends. For instance, as you move across a period (left to right), elements generally exhibit an increase in electronegativity and ionization energy. On the other hand, as you move down a group (top to bottom), these values tend to decrease, while the atomic radius increases. Recognizing these trends can help predict the chemical behavior of elements in reactions.
Electronegativity and Atomic Radius
Electronegativity and atomic radius are essential concepts in understanding chemical bonding. Electronegativity refers to an element’s ability to attract electrons when forming bonds, while atomic radius describes the size of an atom. These two properties are inversely related–elements with larger atomic radii tend to have lower electronegativity values, and vice versa. Understanding these relationships is key to predicting the stability and reactivity of compounds formed by various elements.
By familiarizing yourself with these important properties, you can gain a deeper understanding of how elements interact in chemical reactions and their roles in different compounds. Mastering these concepts is essential for success in studying atomic behavior and molecular formation.
Explaining Gas Laws Clearly

Gas laws describe the behavior of gases under various conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature. These principles are essential for understanding how gases react to changes in their environment. By analyzing these relationships, we can predict how gas particles behave and how different variables influence each other in chemical reactions. The key to mastering these concepts is recognizing how pressure, volume, and temperature interact with one another.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation that links pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of gas molecules. It is often expressed as:
- PV = nRT, where:
- P = pressure
- V = volume
- n = number of moles
- R = ideal gas constant
- T = temperature (in Kelvin)
This equation allows you to solve for any one of the variables if the others are known, providing a clear understanding of gas behavior under specific conditions.
Boyle’s Law and Charles’s Law

Two key gas laws that are often used to explain how gases react to changes in pressure and temperature are Boyle’s Law and Charles’s Law:
- Boyle’s Law: States that for a given amount of gas at constant temperature, the volume is inversely proportional to the pressure. This means that as pressure increases, volume decreases, and vice versa. Mathematically, it is expressed as P?V? = P?V?.
- Charles’s Law: States that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature. This means that as temperature increases, volume also increases. The equation for this relationship is V?/T? = V?/T?.
Both laws are useful when studying gases in different environments and conditions. They help predict how gases will respond when changes are made to their surroundings, making them fundamental tools for understanding the physical properties of gases.
Understanding the Periodic Table Trends
The periodic table is more than just a list of elements; it provides a detailed map of how elements behave and interact based on their properties. By examining patterns across rows and columns, we can identify trends that help explain the chemical behavior of the elements. These trends allow us to predict how elements will react in different situations and form the basis for understanding more complex chemical phenomena.
Trends Across Periods and Groups
Elements in the same group (vertical column) often share similar properties, while elements in the same period (horizontal row) show varying properties. Here are some important trends to note:
- Atomic Radius: As you move from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases because electrons are added to the same energy level, but the effective nuclear charge increases, pulling electrons closer to the nucleus. Conversely, as you move down a group, the atomic radius increases due to the addition of energy levels.
- Ionization Energy: Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. This energy increases as you move across a period (left to right), as the attraction between the electrons and the nucleus becomes stronger. Moving down a group decreases ionization energy because electrons are farther from the nucleus and more shielded by inner electron shells.
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity refers to an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group. Elements in the upper right corner, such as fluorine, are the most electronegative.
Exceptions and Special Cases
While the trends provide a general understanding of elemental properties, there are certain exceptions or nuances that are important to consider:
- Transition Metals: The trends in ionization energy and atomic radius do not always follow the same pattern in transition metals, as these elements have more complex electron configurations.
- Lanthanides and Actinides: These elements often exhibit irregular trends due to the presence of f-block electrons, which have different shielding and energy levels than s- and p-block elements.
By understanding these trends and exceptions, we can make more accurate predictions about the properties and behavior of elements, which is crucial for mastering concepts in chemistry.
Final Tips for Exam Day
On the day of the assessment, being well-prepared can make all the difference. Success depends not only on your understanding of the material but also on how you manage your time, stay focused, and maintain a calm and confident mindset. These last-minute tips are designed to help you optimize your performance when it matters most.
Preparation Before the Day

Ensure that you are physically and mentally prepared before the test. A few key actions can set you up for success:
- Rest Well: A good night’s sleep is essential. Aim for 7-8 hours of rest to ensure you’re alert and focused.
- Eat a Balanced Meal: Fuel your body with a healthy breakfast to provide sustained energy. Avoid heavy or sugary foods that could lead to an energy crash.
- Arrive Early: Get to the location ahead of time so you can settle in and avoid unnecessary stress.
Strategies for the Test
Once you’re in the assessment setting, managing your time and staying calm are essential. Here’s how you can approach the process:
| Tip | Why It Matters | How to Implement |
|---|---|---|
| Read Instructions Carefully | Misunderstanding the directions can lead to avoidable mistakes. | Take a few extra seconds to read each question or section carefully before answering. |
| Manage Your Time | Time is limited, so balancing speed and accuracy is crucial. | Spend more time on questions that carry more points and leave the ones you’re unsure about for later. |
| Stay Calm | Stress can hinder your ability to think clearly and logically. | Take deep breaths if you feel anxious. If you get stuck, move on and return to difficult questions later. |
| Double-Check Your Work | Small mistakes are easy to overlook when you’re in a rush. | If time allows, review your answers, especially calculations and complex questions. |
By following these strategies and staying organized, you can maximize your performance and approach the assessment with confidence. Remember that preparation and a positive mindset go hand-in-hand when striving for success.