
As cyber threats evolve, it becomes increasingly important to adopt structured approaches that help organizations respond effectively to security incidents. One such methodology is focused on providing a systematic way to identify, analyze, and address potential vulnerabilities. By understanding how to implement these frameworks in real-world scenarios, professionals can better defend against a wide range of attacks.
Building the necessary skills to work with these frameworks allows experts to leverage comprehensive data to enhance security operations. This involves familiarizing oneself with the principles behind the models and how they translate into actionable strategies. Successful integration requires attention to detail, practical experience, and a deep understanding of threat detection and response mechanisms.
For cybersecurity practitioners, achieving mastery over such frameworks means more than memorizing theoretical concepts–it’s about developing the ability to adapt, implement, and troubleshoot in dynamic environments. The journey involves continuous learning and hands-on experience, preparing experts to tackle complex security challenges effectively.
Foundations of Operationalizing MITRE ATT&CK Final Exam Answers
To effectively secure systems, cybersecurity professionals must understand the structure and methodology behind identifying and addressing various types of cyber threats. Developing the ability to interpret threat data and implement corresponding countermeasures is key. With a comprehensive framework, experts can map out security gaps and strategically improve their defense mechanisms. This process is essential for tackling modern-day cyber risks.
Practical Application of Security Frameworks
The application of these security structures in real-world situations requires a thorough understanding of attack patterns, threat vectors, and available defense strategies. Professionals must be able to translate theoretical knowledge into actionable steps. This includes identifying threats, analyzing vulnerabilities, and then employing specific countermeasures that align with the framework’s guidelines. The ultimate goal is to strengthen the organization’s security posture.
Continuous Improvement and Skill Development
Staying ahead of cyber threats requires a commitment to ongoing learning and adaptation. By continuously refining one’s approach to security, experts can improve response times and mitigate evolving risks. Mastery over these frameworks ensures that individuals can remain effective in detecting and preventing sophisticated cyber-attacks. Building this expertise is crucial for long-term success in the field of cybersecurity.
Understanding the MITRE ATT&CK Framework
To effectively defend against cyber threats, it’s essential to understand how attackers operate and what techniques they employ at various stages of an attack. A comprehensive model provides a structured approach to classify and understand these tactics, helping security teams detect, respond to, and mitigate threats more efficiently. By breaking down attack methodologies into clear and actionable steps, organizations can anticipate potential risks and enhance their defense strategies.
The Core Components of the Framework
The framework is organized into categories that represent different phases of an attack lifecycle. Each stage contains specific techniques that attackers might use. These techniques are then mapped to their corresponding actions and tools, giving security teams a detailed view of attack patterns. The primary components include:
- Tactics – The high-level objectives of an attacker, such as gaining initial access or maintaining persistence.
- Techniques – Specific methods used by attackers to achieve their tactics, like exploiting vulnerabilities or using social engineering.
- Sub-techniques – More granular methods that describe how a particular technique can be implemented.
- Mitigations – Recommended actions to prevent or reduce the impact of specific attack techniques.
- Detections – Methods for identifying when an attack technique has been used.
Benefits of Using This Approach
By leveraging such a framework, security teams can:
- Better identify and categorize potential threats based on known attack patterns.
- Improve incident response times by providing a common language and understanding for security operations.
- Enhance threat hunting capabilities by proactively searching for indicators of compromise.
- Map and align existing security tools and procedures with a comprehensive model, identifying potential gaps in coverage.
Key Concepts for Operationalization
Successfully applying a security framework within an organization requires more than just theoretical knowledge. It involves translating complex concepts into practical, actionable steps that can be implemented across various security operations. This process ensures that the strategies developed are both effective and sustainable in the long term. By understanding the core principles and their application, security teams can better prepare for and respond to emerging threats.
Adapting the Framework to Organizational Needs
One of the first challenges in implementing any security framework is adapting it to the specific requirements of an organization. Each environment has unique risks, resources, and capabilities, meaning a one-size-fits-all approach is rarely effective. To achieve successful integration, security teams must:
- Assess the organization’s existing security posture and identify gaps.
- Tailor detection strategies and mitigation actions to fit specific risk profiles.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for team members based on the framework’s recommendations.
- Ensure that all security tools and systems are aligned with the chosen approach.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Effective implementation also requires a focus on ongoing monitoring and adaptation. As cyber threats continuously evolve, so must security measures. A dynamic, iterative process ensures that defense strategies stay relevant and resilient over time. Key actions in this process include:
- Regularly reviewing and updating security protocols based on new threat intelligence.
- Conducting continuous assessments to detect new vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Incorporating feedback from incidents and lessons learned to improve future responses.
Preparing for the Final Exam
Achieving proficiency in cybersecurity frameworks requires both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Preparing for an assessment of these skills involves not only studying the material but also practicing real-world scenarios. The key to success lies in understanding the core concepts, being able to apply them in different contexts, and mastering the techniques that will be tested.
Focus on Key Concepts and Techniques
To effectively prepare, it’s essential to focus on the most critical aspects of the framework. This includes:
- Understanding the structure and components of the security framework.
- Familiarizing oneself with various attack vectors and defensive strategies.
- Learning how to map attack techniques to defensive actions.
- Practicing with tools and resources commonly used in real-world cybersecurity scenarios.
Simulating Real-World Scenarios
In addition to theoretical knowledge, applying the concepts in practical settings is crucial. Simulated scenarios can help reinforce the material and build confidence. Key strategies include:
- Engaging in hands-on exercises that mirror real-world security challenges.
- Participating in labs or virtual environments that mimic attack and defense situations.
- Reviewing case studies and understanding how frameworks were implemented in different organizations.
Common Pitfalls in ATT&CK Implementation
When applying a security framework to detect and mitigate cyber threats, organizations often encounter challenges that can hinder successful integration. These obstacles can arise from various factors, including insufficient knowledge, lack of resources, or misaligned strategies. Identifying and avoiding common mistakes during the implementation process is crucial for achieving a robust defense posture.
One of the primary challenges is the improper alignment between the framework and the organization’s unique security needs. This can lead to ineffective defenses or gaps in coverage. Another common pitfall is the failure to continuously update and adapt the system to evolving threats. Without regular reviews and adjustments, security measures may become outdated, leaving systems vulnerable. Additionally, overcomplicating the process or underestimating the importance of user training can also result in ineffective deployment and poor utilization of available tools.
Building Effective Detection Strategies

In the modern cybersecurity landscape, detecting potential threats in real time is essential for protecting systems and data. An effective detection strategy involves not only identifying known attack patterns but also anticipating emerging risks. By designing a comprehensive and proactive approach, organizations can better monitor their infrastructure, detect suspicious activities, and respond swiftly to security incidents.
The first step in building a strong detection strategy is understanding the types of threats an organization faces. From there, security teams must focus on creating robust monitoring systems that can track a wide range of behaviors, from common vulnerabilities to advanced persistent threats. Key components of an effective strategy include:
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Using up-to-date intelligence feeds to inform detection systems and anticipate new attack techniques.
- Behavioral Analysis: Identifying anomalies by analyzing deviations from normal system and user behavior.
- Correlation of Events: Combining data from multiple sources, such as logs and network traffic, to identify patterns that may indicate malicious activity.
- Alert Tuning: Fine-tuning alert thresholds to reduce false positives while ensuring real threats are not missed.
- Automated Response Mechanisms: Implementing systems that can trigger automated actions in response to certain detected threats, minimizing human intervention time.
Additionally, regular testing and refining of detection methods are necessary to ensure their effectiveness over time. This includes simulating real-world attacks and performing vulnerability assessments to identify gaps in coverage. With a well-structured and continually evolving detection strategy, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential cyber threats.
Aligning Threat Intelligence with ATT&CK
Integrating threat intelligence into a cybersecurity strategy is a critical step in identifying and mitigating advanced threats. By aligning threat intelligence with structured security frameworks, organizations can enhance their ability to detect, understand, and respond to emerging risks. This alignment allows security teams to leverage real-time data, identify trends, and anticipate potential attack vectors, ensuring that defensive measures are as proactive as possible.
Key Elements of Threat Intelligence Integration
To align threat intelligence effectively, security teams must focus on mapping intelligence data to specific attack techniques and tactics. This alignment helps teams correlate real-world threat data with known adversary behaviors and predict their next moves. Key elements in this integration process include:
- Contextual Information: Understanding the motivations, tools, and methods used by attackers.
- Real-Time Data: Using updated intelligence to detect current threats.
- Automation: Automating the integration process to reduce manual efforts and enhance response times.
- Customization: Tailoring threat feeds to focus on relevant risks specific to the organization’s industry or threat landscape.
Mapping Threat Intelligence to Security Frameworks
By aligning threat intelligence with a security framework, organizations can create a more robust defense strategy. The following table outlines how different types of threat intelligence map to various elements of a security framework:
| Threat Intelligence Type | Mapped Framework Element | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Indicator of Compromise (IOC) | Detection Techniques | Malicious IP addresses, URLs |
| Adversary Tactics and Techniques | Attack Phases | Initial Access, Lateral Movement |
| Behavioral Patterns | Threat Detection | Unusual login times, data exfiltration |
| Tools and Malware | Response Actions | Ransomware, Remote Access Tools (RATs) |
This process ensures that threat intelligence is not only used for detection but also for active defense and incident response. When effectively aligned, threat intelligence becomes an integral part of an organization’s broader security strategy, enabling them to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Hands-On Techniques for Exam Success
Successfully applying theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios is essential for mastering any cybersecurity assessment. While understanding the concepts is important, hands-on practice plays a crucial role in building the skills required to excel. Engaging directly with the tools and techniques used in real-world security environments can help reinforce key principles and boost confidence before the test.
Simulating Real-World Scenarios
One of the most effective ways to prepare is by simulating real-world attacks and defensive measures. This allows you to apply your knowledge to dynamic situations, much like what you would face in a professional setting. Focus on the following methods:
- Practice in Virtual Labs: Use virtual machines or lab environments to conduct penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and attack simulations.
- Analyze Case Studies: Study previous incidents and try to recreate the attack methods and defensive strategies used to respond to them.
- Participate in Capture the Flag (CTF) Events: These competitions allow you to solve security challenges, providing practical experience in identifying vulnerabilities and exploiting them.
Leveraging Tools and Resources
Another hands-on strategy is getting comfortable with the tools used to detect, analyze, and mitigate cyber threats. By mastering the tools, you can increase your ability to respond to incidents efficiently. Some important actions include:
- Familiarize Yourself with Security Tools: Spend time using SIEM platforms, forensic analysis tools, and network monitoring systems to get a feel for their functionalities.
- Review Threat Intelligence Feeds: Incorporate real-time data to enhance your understanding of current attack trends and tactics.
- Test and Tweak Detection Rules: Create and adjust detection rules based on hypothetical scenarios to improve alert accuracy and reduce false positives.
By applying these hands-on techniques, you not only solidify your theoretical knowledge but also develop the practical skills needed to handle complex security situations, preparing you for success in any cybersecurity challenge.
Leveraging ATT&CK for Incident Response
In incident response, understanding the techniques and tactics used by attackers is essential for detecting, mitigating, and recovering from cyber threats. By aligning response efforts with a structured framework, organizations can systematically track and analyze adversary behaviors, allowing for a more effective and rapid response. Leveraging such frameworks helps security teams to identify attack patterns, predict the next move, and deploy appropriate defensive actions in real time.
Using a structured approach to attack mapping during an incident enables responders to quickly determine which systems are affected and how they were compromised. By applying this knowledge, teams can minimize damage, contain the breach, and start the recovery process as soon as possible. Key elements in leveraging a framework for incident response include:
- Identification of Adversary Tactics: Understanding the specific goals and phases of the attack helps to prioritize response actions.
- Tracking Attack Techniques: Mapping the attacker’s methods to known patterns enables faster detection and containment.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Detection: Continuously monitoring systems for indicators of compromise and unusual behaviors to identify and stop the attack early.
- Contextualizing Attack Data: Correlating data from different sources, such as network logs and endpoint data, helps to build a complete picture of the attack.
By leveraging the insights provided by structured frameworks, incident response teams can act swiftly and with more precision. The following steps outline a common approach to aligning response actions with known attack patterns:
- Step 1: Identify indicators of compromise (IOCs) and correlate them with known attack techniques.
- Step 2: Prioritize response actions based on the severity of the techniques used and the impact on systems.
- Step 3: Implement containment strategies to limit the spread of the attack while conducting a thorough investigation.
- Step 4: Remediate affected systems, apply patches, and strengthen security measures to prevent future occurrences.
- Step 5: Document the incident thoroughly to improve future responses and refine security policies.
By embedding such frameworks into their incident response procedures, organizations can significantly improve their ability to quickly and effectively respond to security incidents, reducing the time to recovery and minimizing the potential damage from cyber threats.
Best Practices for Threat Hunting
Effective threat hunting is essential for identifying and mitigating potential cyber risks before they can cause significant harm. Unlike traditional defense mechanisms that respond to known threats, threat hunting focuses on proactively searching for hidden or advanced threats within the network. By adopting the right methodologies and leveraging advanced tools, security teams can uncover hidden vulnerabilities, detect subtle attack patterns, and take swift action to protect their systems.
One of the core principles of successful threat hunting is maintaining a systematic approach. Security teams should have a clear understanding of their environment, an organized process to investigate suspicious activities, and the right set of tools to support their efforts. Some key best practices include:
- Establish a Clear Hypothesis: Begin by formulating a hypothesis based on known threat patterns, historical data, or emerging trends. This can guide the hunting process and focus attention on specific areas of concern.
- Leverage Threat Intelligence: Use up-to-date threat intelligence feeds to identify new attack vectors, tools, or tactics being used by adversaries. Correlate this data with your internal logs to detect early indicators of compromise.
- Use Behavioral Analysis: Focus on identifying abnormal behavior rather than relying solely on signature-based detection. This helps identify threats that have evaded traditional detection methods.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Threat hunting should be a collaborative effort. Engage with other departments, such as incident response and network operations, to share findings and gather insights that may not be immediately apparent.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Automate repetitive or time-consuming tasks, such as data collection and log aggregation, to free up valuable time for deeper analysis and investigation.
In addition to these practices, threat hunters should regularly refine their methods based on lessons learned from previous hunts and continually improve their strategies. Continuous training, engagement with the broader cybersecurity community, and active participation in threat intelligence sharing groups also play an important role in staying ahead of emerging threats.
By following these best practices, security teams can develop a proactive and dynamic approach to threat hunting, enabling them to detect and address potential risks before they escalate into full-blown incidents.
Exploring the ATT&CK Matrix
The ATT&CK Matrix provides a comprehensive and structured framework for understanding and categorizing the various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cyber adversaries. It offers security teams a clear map of how attacks unfold, enabling them to analyze and respond effectively to intrusions. This tool allows for the identification of adversary behaviors, making it possible to anticipate their next moves and create tailored defense strategies.
The matrix itself is organized into rows representing distinct phases of an attack, from initial access to impact. Each row corresponds to a specific tactic, and within each tactic, there are multiple techniques that attackers may use to achieve their objective. This categorization helps defenders recognize patterns in adversary activity and correlate them with known attack methods. Key areas covered in the matrix include:
- Initial Access: Techniques used to gain a foothold in the target system, such as phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Execution: Methods used to run malicious code within the environment, like scripting or exploiting software flaws.
- Persistence: Techniques that allow attackers to maintain access to a compromised system over time, even after a reboot or system reset.
- Privilege Escalation: Methods to gain higher-level permissions, allowing attackers to escalate their access within the network.
- Defense Evasion: Techniques used to avoid detection by security systems and evade active defense mechanisms.
By aligning threat detection and response efforts with the matrix, security teams can identify gaps in their defenses and improve their ability to detect and block sophisticated attacks. The ATT&CK Matrix also supports incident response teams by providing them with a set of well-defined techniques that can be used to investigate and mitigate the effects of an ongoing attack.
Exploring this matrix and incorporating it into security operations can provide a systematic approach to threat hunting, detection, and mitigation, making it an essential tool for any organization aiming to bolster its cybersecurity posture.
Integrating ATT&CK with SIEM Systems
Integrating threat frameworks with security information and event management (SIEM) systems enhances an organization’s ability to detect, analyze, and respond to cyber threats in real-time. By leveraging a structured approach to understanding adversary tactics and techniques, security teams can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of their monitoring systems. This integration allows SIEM tools to correlate security events with known attack behaviors, creating a more comprehensive and proactive defense strategy.
Enhancing Detection Capabilities
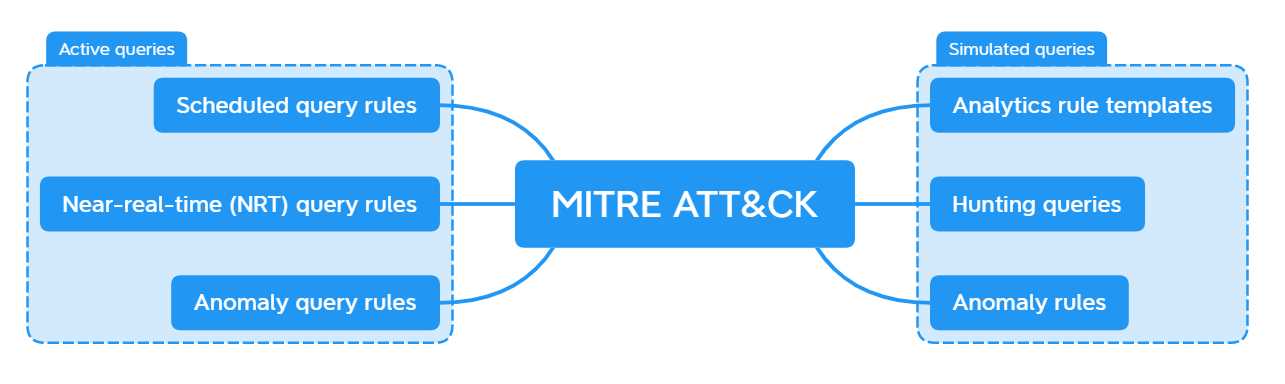
One of the key benefits of integrating a threat framework with SIEM is the enhanced detection capability. A well-integrated SIEM can automatically recognize attack patterns by mapping incoming security events to specific adversary tactics and techniques. This process improves the visibility of security operations, enabling teams to identify suspicious activities faster and more accurately. For example, if a SIEM detects a suspicious login attempt followed by unusual system access, it can automatically link these events to a known attack pattern, signaling a potential threat.
Streamlining Incident Response
Integrating threat frameworks into SIEM systems also streamlines incident response efforts. By using a common set of tactics and techniques, security teams can more quickly correlate events across different systems and create a unified response. This reduces the time spent investigating individual alerts and accelerates the decision-making process during a security incident. Additionally, integration ensures that relevant context is provided with each alert, allowing responders to prioritize actions based on the severity of the threat.
Overall, combining a structured threat framework with SIEM systems offers a significant improvement in threat detection and response. It enables organizations to shift from a reactive to a proactive security posture, providing better protection against evolving cyber threats.
Improving Defensive Posture Using ATT&CK
Enhancing a security strategy requires a clear understanding of how adversaries operate and the tactics they employ. By adopting a comprehensive framework for identifying and defending against cyber threats, organizations can create a more robust security posture. This approach allows for better preparedness, response times, and the ability to detect threats at various stages of an attack. Leveraging structured intelligence not only strengthens the defense but also ensures that security measures align with real-world adversary techniques.
Identifying Gaps in Existing Defenses
A significant advantage of using a structured threat framework is the ability to identify weaknesses in an organization’s current security setup. By mapping known attack tactics to existing security measures, teams can pinpoint gaps in defenses and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited. This proactive approach helps to ensure that defensive strategies are up to date and capable of handling evolving threats.
Prioritizing Defensive Measures
With an understanding of how different tactics are employed by adversaries, security teams can prioritize their defense efforts. Focusing on the most common or most critical techniques allows organizations to allocate resources where they are needed most. This prioritization ensures that defensive measures are not only comprehensive but also efficient, addressing high-risk areas that could have the greatest impact on organizational security.
| Tactic | Defense Measure |
|---|---|
| Initial Access | Phishing detection, firewall configuration |
| Privilege Escalation | Access controls, monitoring for abnormal behavior |
| Exfiltration | Data loss prevention, network traffic analysis |
By integrating this methodical approach to defense, organizations can improve their ability to predict and prevent cyberattacks, ensuring that their security measures are aligned with real-world threat scenarios. This leads to a more resilient and adaptive security posture, better equipped to handle a wide range of attack vectors.
Case Studies in Operationalizing ATT&CK
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how organizations can effectively apply structured threat frameworks to enhance their security posture. By studying how different entities have implemented these approaches, security teams can learn practical strategies, identify potential pitfalls, and refine their own defense strategies. These case studies demonstrate the value of adapting theoretical frameworks into actionable, real-time security measures, ultimately improving incident detection and response capabilities.
Case Study 1: Financial Sector Implementation
One prominent case comes from the financial industry, where a large institution used a threat framework to bolster its defense against increasingly sophisticated phishing attacks. By mapping known adversary techniques to its security infrastructure, the organization identified vulnerabilities in its email filtering system. With the help of structured intelligence, the financial institution was able to implement more advanced detection measures, such as AI-driven phishing recognition and improved email filtering rules, resulting in a significant reduction in successful phishing attempts.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Industry Response
Another example can be found in the healthcare sector, where a hospital network faced a surge in ransomware attacks targeting sensitive patient data. By leveraging threat intelligence frameworks, the hospital was able to assess its current defenses and improve endpoint detection. The hospital integrated network monitoring tools with real-time behavioral analysis to spot malicious activity more quickly. As a result, the hospital’s incident response team reduced the average time to contain attacks, preventing major data breaches.
These examples showcase the importance of adapting threat intelligence frameworks to an organization’s specific context. By doing so, security teams can build more resilient defense strategies tailored to their unique risk profile and operational requirements.
Mapping Real-World Attacks to ATT&CK
Understanding how real-world cyberattacks align with structured frameworks is essential for improving detection and response efforts. By mapping observed attack techniques to a predefined framework, security teams can better understand the tactics, tools, and procedures (TTPs) used by threat actors. This process helps identify common attack patterns, highlight vulnerabilities, and enhance an organization’s ability to anticipate future threats.
When mapping an attack to a framework, the first step is to capture key data from the attack, such as the attack vector, methods of escalation, and persistence mechanisms. Once these details are collected, they are compared to the known techniques in the framework to identify similarities. This process reveals not only the tactics used by the attackers but also the effectiveness of existing security controls in detecting and mitigating these methods.
Case Example: Ransomware Attack
In a recent ransomware attack targeting a large enterprise, the threat actors employed a variety of techniques to gain access and propagate across the network. By mapping these activities to the framework, the security team identified several key tactics, such as initial access via phishing, privilege escalation through exploiting vulnerable systems, and lateral movement through compromised credentials. By aligning these steps with the framework, the team could focus on enhancing detection capabilities for phishing attempts and better secure vulnerable endpoints.
Case Example: APT Group Activity
Another example comes from a well-known advanced persistent threat (APT) group that used a complex multi-stage attack to breach a government agency. By examining the attack, analysts mapped the group’s activities to the framework, identifying tactics like credential dumping, command-and-control channels, and data exfiltration techniques. This mapping allowed the organization to identify gaps in its security posture, particularly around detecting unauthorized data transfers and identifying compromised accounts early in the attack cycle.
By mapping real-world attacks to a framework, organizations can refine their defensive measures, ensuring they are prepared for the tactics and techniques that adversaries are most likely to use. This proactive approach not only strengthens incident response but also improves overall security resilience.
Advanced Topics in ATT&CK Framework
As organizations become more proficient in using threat detection frameworks, they move beyond basic implementation to explore advanced techniques and concepts. These advanced topics enhance the framework’s value by providing deeper insights into threat actor behaviors, improving detection efficacy, and refining defensive strategies. By delving into these complex areas, security teams can optimize their security posture and stay ahead of evolving threats.
1. Threat Intelligence Integration
Integrating external threat intelligence into the framework allows for a more proactive defense strategy. By leveraging indicators of compromise (IOCs) and tactics from threat intelligence feeds, teams can align observed behaviors with known adversary patterns. This integration enriches the framework by providing additional context and allowing organizations to recognize and respond to threats more effectively.
- External Threat Feeds: Using data from reputable sources, such as government advisories or commercial intelligence providers, to update the framework with the latest adversary tactics and techniques.
- Threat Actor Profiles: Creating detailed profiles for known threat groups and mapping their typical behaviors to strengthen defenses against specific adversaries.
- Contextual Awareness: Gaining a deeper understanding of threats by analyzing geographic, sectoral, and organizational data to identify relevant attack patterns.
2. Automation and Machine Learning
Incorporating automation and machine learning into threat detection systems enhances the capability to quickly identify and respond to suspicious activities. By automating the mapping of observed incidents to the framework, security tools can streamline the detection and investigation process. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can detect subtle deviations from normal behavior, improving the accuracy of threat identification.
- Automated Mapping: Using automated systems to match incoming events with known tactics and techniques, reducing the manual effort required for analysis.
- Behavioral Analysis: Leveraging machine learning to identify patterns of activity that deviate from the baseline, indicating potential security incidents.
- Dynamic Updates: Automating the integration of new techniques and tactics into detection systems as adversaries evolve their methods.
Exploring these advanced topics not only enhances the effectiveness of threat detection but also improves incident response times and helps organizations stay ahead of the increasingly sophisticated tactics used by cyber adversaries. By adopting a holistic and dynamic approach, security teams can better anticipate emerging threats and reinforce their defenses against future attacks.
Collaboration Between Teams Using ATT&CK
Effective cybersecurity relies heavily on cross-team collaboration, especially when it comes to detecting, analyzing, and mitigating threats. By using a standardized framework, different teams within an organization can work more cohesively, sharing knowledge, insights, and techniques. This collaboration not only improves the response time to incidents but also strengthens the overall defense posture. A shared understanding of tactics and techniques enables security, IT, and incident response teams to align their efforts in a more synchronized and strategic way.
1. Shared Knowledge and Common Language
One of the key advantages of using a structured approach is the ability to create a common language among different teams. By referring to the same set of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), security operations, network defense, and threat hunting teams can easily communicate and share findings. This common framework facilitates the interpretation of security events and makes cross-team collaboration more efficient.
- Common Terminology: Ensuring all teams understand and use the same definitions for threats, tactics, and techniques streamlines communication and reduces misunderstandings.
- Centralized Knowledge Base: Documenting incidents, lessons learned, and threat actor behaviors in a shared repository allows teams to quickly reference information during an incident.
- Collaborative Tools: Utilizing platforms that support collaborative workflows, such as ticketing systems and chat platforms, ensures that knowledge and actions are aligned across teams.
2. Coordinated Threat Response
When an incident occurs, the ability to quickly bring together the right expertise from different teams is crucial for effective response. By mapping the observed attack techniques to the framework, teams can identify the best course of action based on previously established tactics. The framework helps guide the collaboration by clearly showing which defensive measures and countermeasures to prioritize during each stage of an incident.
- Incident Response and Forensics: By referring to the framework, response teams can determine whether an attack is part of a known threat actor’s methodology, allowing them to adjust their response accordingly.
- Threat Hunting Coordination: Collaboration between incident response and threat hunting teams allows for deeper investigation into unusual patterns and possible vulnerabilities.
- Rapid Information Sharing: Using a common framework enables faster information sharing between teams, allowing them to work in real-time and improve incident detection and mitigation efforts.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, collaboration is the key to staying ahead of adversaries. By using a standardized approach, teams can synchronize their efforts, reduce response times, and enhance overall effectiveness in defending against complex and sophisticated attacks.
Continuing Education After the Exam
Once you’ve completed your certification or training, the journey doesn’t stop there. In the dynamic field of cybersecurity, the landscape is constantly evolving with new threats, tools, and techniques emerging regularly. To maintain and enhance your expertise, continuous learning is essential. This section explores ways to stay up-to-date and keep your skills sharp long after the initial certification process.
1. Participating in Ongoing Training and Certifications
One of the most effective ways to stay current in your field is by engaging in additional training and earning new certifications. Many organizations and institutions offer advanced courses that delve deeper into specialized areas of cybersecurity. These programs are designed to build on the foundational knowledge you’ve already acquired and help you stay ahead of the curve.
- Advanced Security Certifications: Pursue advanced certifications that focus on specific areas, such as cloud security, penetration testing, or incident response.
- Vendor-Specific Training: Participate in vendor-provided training for tools and platforms you use regularly, as they often update their offerings with new features and best practices.
- Workshops and Bootcamps: Attend hands-on training workshops or immersive bootcamps to refine your skills and gain practical experience.
2. Engaging in Professional Communities and Networks
Engaging with like-minded professionals in cybersecurity communities provides valuable insights and keeps you informed about the latest developments. By participating in forums, attending conferences, or joining local meetups, you can expand your knowledge and network with industry leaders. Active involvement in these communities can offer real-world perspectives on how to apply learned concepts in new and evolving contexts.
- Industry Conferences: Attend leading conferences to learn from experts, participate in discussions, and stay informed about the latest trends.
- Online Communities and Forums: Join online platforms where cybersecurity professionals discuss challenges, share solutions, and learn from each other.
- Mentorship Programs: Seek out a mentor in the field or offer to mentor others, as teaching is often a great way to deepen your understanding.
Cybersecurity is a field that demands constant vigilance and adaptability. By pursuing continuous education and staying involved in the community, you can ensure your skills remain relevant and continue to grow throughout your career.