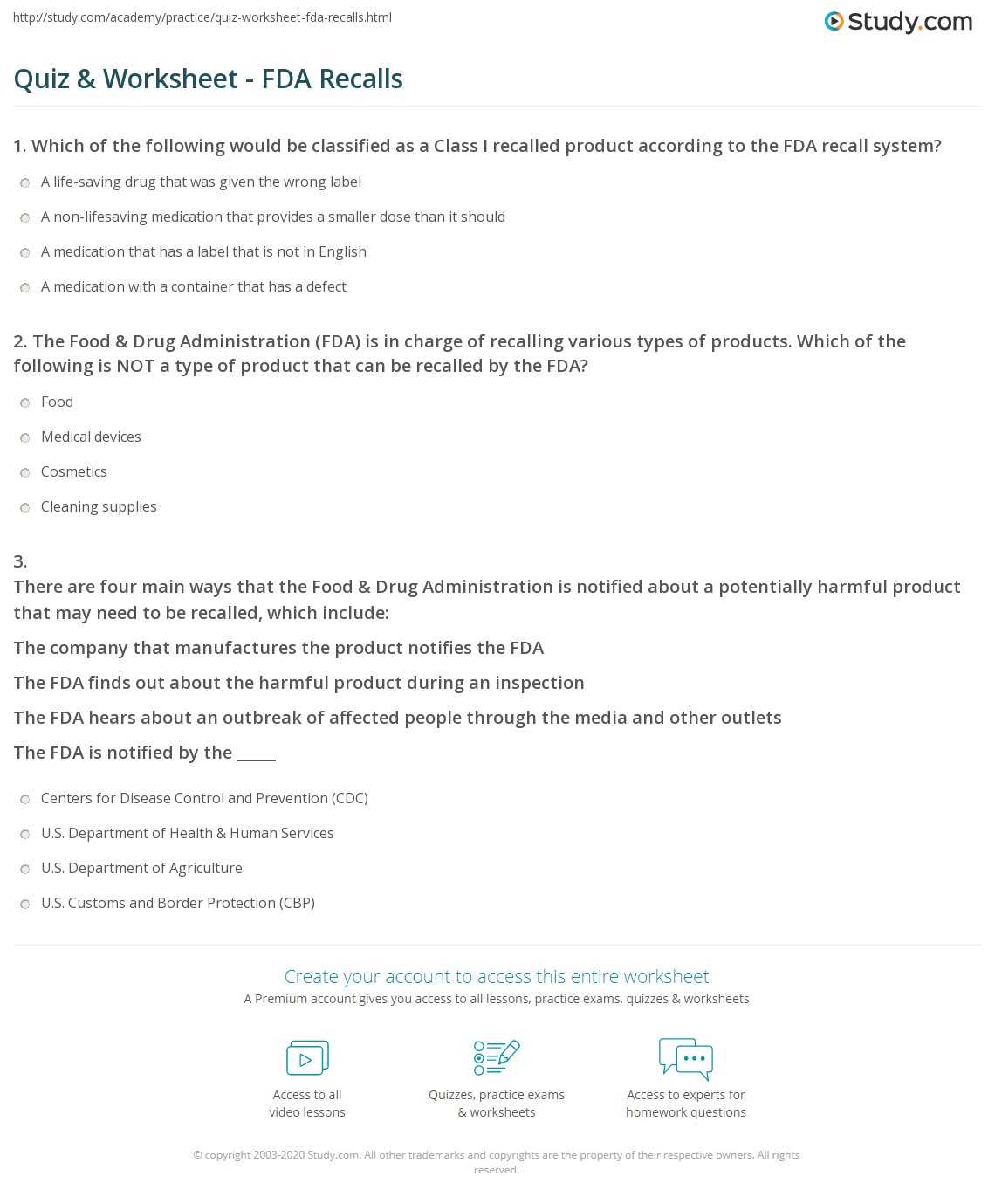
In any testing situation, being able to retrieve information quickly and accurately is crucial for success. The ability to tap into your knowledge base when needed can significantly impact your performance, especially when faced with challenging questions. Effective memory strategies can help ensure that you are able to access the right facts at the right time, even under pressure.
Various methods exist to strengthen mental recall, each focusing on different aspects of memory, from enhancing focus to organizing information in a way that’s easier to retrieve. By improving your cognitive processes, you can approach tests with greater confidence and reduce the stress that often accompanies moments of uncertainty.
Developing a strong recall system involves more than just cramming information. It requires consistent practice, a proper mindset, and a variety of tools that can be tailored to your unique learning style. By incorporating these techniques into your study routine, you can improve your ability to access stored knowledge whenever it’s required.
How to Recall Answers in Exam

During a testing session, being able to access previously learned information efficiently is essential for achieving good results. This skill is largely influenced by how well you have organized and stored the material in your memory. With the right strategies, it’s possible to bring to mind the necessary facts, formulas, or concepts when they are most needed, even in high-pressure situations.
One effective approach is to focus on active engagement with the material rather than passive review. Techniques like spaced repetition, where you review content at increasing intervals, can reinforce memory retention over time. The more actively you interact with the information, the stronger your ability to retrieve it during critical moments.
Visualization is another powerful tool for improving mental recall. By picturing the material in a structured way, such as creating a mental map or associating concepts with vivid images, you can make connections that are easier to access when you need them. Additionally, reducing anxiety and staying calm can enhance cognitive performance, helping you focus on the task at hand and find the information you need more efficiently.
Understanding Memory Techniques for Exams

Improving the ability to access and apply learned information during a test requires effective strategies that optimize how the brain stores and retrieves data. These methods are not about simply cramming facts but about reinforcing long-term retention and enhancing mental clarity under pressure. By utilizing specific memory techniques, individuals can better organize knowledge, making it easier to recall during critical moments.
One popular technique is the use of mnemonics, which involves associating complex information with simpler, memorable cues. Another effective method is spaced repetition, which enhances retention by reviewing material at gradually increasing intervals. This approach helps solidify knowledge in the long-term memory, reducing the likelihood of forgetting important details.
Additionally, creating mental maps or diagrams allows for the visualization of interconnected ideas, aiding in the quick retrieval of related concepts. Consistency in applying these techniques, coupled with a well-structured study routine, significantly boosts memory recall and improves overall performance during testing scenarios.
Importance of Active Recall in Studying
Engaging actively with the material you are learning is a crucial step in enhancing memory retention. Simply reviewing notes or re-reading textbooks is not enough to solidify information in your mind. To truly internalize knowledge, it’s essential to test your ability to retrieve and apply the information without external prompts. This method strengthens neural connections, making it easier to bring information to the forefront when needed.
One of the most effective ways to incorporate active learning is through self-testing. Instead of passively reviewing notes, actively challenge yourself by attempting to recall key points or concepts from memory. This process helps identify gaps in understanding, enabling you to focus your efforts on areas that need improvement. Over time, this approach improves both long-term retention and the speed at which information can be accessed during testing situations.
Moreover, using spaced intervals between review sessions while actively trying to retrieve learned material boosts the likelihood of retaining that knowledge for the long term. The more often you test yourself, the more effective the process becomes, allowing you to perform at your best when it matters most.
How Sleep Affects Exam Performance
The quality of sleep plays a significant role in cognitive function, particularly when it comes to processing and retrieving learned information. Adequate rest is essential for consolidating memories, allowing the brain to organize and store knowledge more effectively. Without proper sleep, even the most well-studied material can become difficult to access, leading to subpar performance when it’s time to apply that knowledge.
Lack of sleep can impair several cognitive processes, including:
- Memory consolidation: Sleep helps transfer information from short-term to long-term memory.
- Focus: Insufficient rest can lead to difficulty concentrating and staying on task.
- Problem-solving: Sleep deprivation can reduce creativity and the ability to think critically.
- Decision-making: Lack of sleep affects your ability to make quick, accurate judgments during a test.
Studies have shown that getting a full night’s sleep before a test can improve performance by enhancing memory retrieval and processing speed. On the other hand, staying up late to cram can do more harm than good, leading to fatigue and reduced mental clarity. Therefore, prioritizing rest in the days leading up to an assessment is just as important as studying the material itself.
Using Visualization to Boost Memory
Visualization is a powerful technique that enhances the brain’s ability to remember and organize information by creating vivid mental images. This approach taps into the brain’s natural ability to store visual cues, making it easier to retrieve complex ideas and concepts when needed. By associating abstract information with clear, memorable images, the material becomes more accessible and easier to recall during high-pressure situations.
To use visualization effectively, start by picturing key ideas in your mind as detailed images or scenarios. For example, if you’re studying historical events, imagine the scenes unfolding as if they were happening in front of you. This technique helps create strong mental associations that are easier to access when trying to connect different pieces of information. You can also use mind mapping or color coding to organize concepts visually, which further aids memory retention.
Incorporating movement and emotion into these visualizations can further enhance their effectiveness. The more engaging and detailed the mental image, the more likely it is to stick in your memory. With practice, visualization can become an invaluable tool for boosting your ability to retain and quickly access learned material when it matters most.
How to Manage Exam Anxiety Effectively
Stress and nervousness are natural responses before a significant test, but managing these emotions effectively can improve performance and help maintain mental clarity. Anxiety can cloud judgment, reduce focus, and even interfere with the ability to access information that has been studied. Learning how to stay calm and composed under pressure is a skill that can be developed through consistent practice and the use of specific relaxation techniques.
Breathing and Relaxation Techniques

Deep breathing exercises are one of the simplest and most effective ways to combat stress. By focusing on slow, controlled breaths, you can activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety. Techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation also help ease tension in the body, promoting a sense of calm.
Positive Mindset and Visualization
Adopting a positive mindset can significantly reduce anxiety levels. Instead of focusing on potential failure, try visualizing yourself succeeding and calmly navigating through the test. Positive affirmations and visualization exercises can help shift your focus away from fear and onto your abilities.
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Reduces physical symptoms of stress |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | Eases tension and promotes calm |
| Visualization | Improves confidence and focus |
By integrating these strategies into your routine, you can maintain a calm and focused mindset, allowing you to perform at your best when it counts most.
Developing a Study Routine for Better Recall
Creating a structured approach to learning can significantly improve your ability to retain and apply knowledge. A well-planned study schedule helps in organizing material, ensuring consistent engagement, and allowing time for regular review. By establishing a routine, you can enhance your mental organization, which in turn supports your capacity to retrieve key information when needed.
Consistency plays a vital role in the learning process. A daily or weekly schedule helps reinforce information over time, allowing your brain to process and retain details more effectively. Spacing out study sessions, rather than cramming, aids in long-term retention, ensuring that knowledge is not just temporary but firmly embedded in memory.
Incorporating active learning techniques into your routine, such as self-testing or summarizing concepts, can strengthen neural connections and deepen understanding. Mixing different subjects or topics during each study session–known as interleaving–can also improve the flexibility and depth of your knowledge, making it easier to recall when needed.
Additionally, breaks are essential. They prevent cognitive overload and allow your brain to consolidate information. By alternating between study sessions and short rest periods, you give yourself the best chance to stay focused and retain key material in the long run.
The Role of Diet in Cognitive Function

A balanced and nutritious diet plays a crucial role in enhancing brain performance. The foods we consume provide the essential nutrients that support mental processes such as concentration, memory, and problem-solving. Proper nutrition fuels the brain, ensuring it has the energy needed to function at its best, especially during mentally demanding tasks.
Certain nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins, are particularly beneficial for cognitive health. Omega-3s, found in fatty fish and seeds, support brain cell structure and function. Antioxidants, present in colorful fruits and vegetables, protect the brain from oxidative stress and enhance memory. B-vitamins and other micronutrients are also integral to maintaining cognitive sharpness and clarity.
In addition to specific nutrients, maintaining overall hydration is vital for mental performance. Dehydration can lead to decreased attention and slower cognitive processing. Regularly consuming water and nutrient-rich beverages helps sustain focus and clarity during long study or work sessions.
Lastly, moderating the intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats is equally important. These can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, leading to energy crashes and impaired cognitive function. A diet focused on whole, nutrient-dense foods contributes to sustained mental energy and better decision-making abilities throughout the day.
How to Use Mnemonics for Memory
Using creative techniques to enhance memory can make information easier to retrieve when needed. Mnemonics are strategies that simplify complex data into more manageable forms, aiding in quicker recall. These techniques rely on associating difficult-to-remember material with familiar concepts, patterns, or visual images.
One popular mnemonic method is the use of acronyms. By creating a word or phrase from the initial letters of a list of items, you can make large sets of information more memorable. For example, to remember the order of operations in mathematics, you might use the acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction).
Another effective technique is visualization. Associating information with vivid mental images or stories can help solidify it in your mind. For instance, when learning about historical events, imagine them unfolding like scenes in a movie, with each key detail represented by an image or a character.
Additionally, the method of loci, also known as the memory palace technique, involves associating information with specific locations in a familiar space. As you mentally walk through this space, you can “place” pieces of information in different spots, which makes them easier to retrieve later.
Other strategies include:
- Chunking: Breaking down information into smaller, more manageable pieces.
- Rhyming: Creating short rhymes or phrases to remember facts or lists.
- Association: Linking new information to something already known.
These techniques can be used individually or in combination, depending on the nature of the material and your learning preferences. With practice, mnemonics can greatly improve your ability to process and recall important details with ease.
Taking Breaks to Improve Focus
Maintaining consistent attention during long study sessions can be challenging, and without regular rest, mental fatigue can set in quickly. Taking periodic breaks allows the brain to recharge, improving concentration and efficiency when returning to tasks. By integrating short pauses into your routine, you can sustain high levels of focus and avoid burnout.
Benefits of Regular Breaks
Breaks help prevent cognitive overload and provide an opportunity for your brain to process and consolidate information. When you step away from your studies, your mind is able to relax and reset, which ultimately enhances your ability to focus when you return. Studies show that frequent short breaks lead to improved retention and better problem-solving skills, as they keep the brain engaged without causing exhaustion.
Effective Strategies for Breaks
Timing your breaks is key to maintaining productivity. One popular method is the Pomodoro Technique, which involves working for 25 minutes followed by a 5-minute break. After four sessions, you take a longer break of 15-30 minutes. This method helps keep your energy levels consistent and maximizes focus during work intervals.
During your break, it’s important to step away from your study material completely. Engage in activities that allow your mind to rest, such as taking a walk, stretching, or practicing deep breathing. Avoid distractions like checking social media or emails, as these can diminish the benefits of your break. By returning to your studies feeling refreshed, you’ll be able to focus more effectively and process information more efficiently.
Using Mind Maps for Organizing Information
Mind maps are a powerful tool for visually organizing thoughts and concepts, helping to structure information in a way that enhances understanding and memory. By mapping out key ideas and connecting them through branches, you create a visual representation of the relationships between different pieces of information, making it easier to see patterns and connections.
One of the main advantages of mind maps is their ability to break down complex material into manageable chunks. Rather than focusing on linear notes or paragraphs, mind maps allow you to view information in a non-linear way, which can lead to deeper comprehension. This approach also makes it easier to identify gaps in knowledge and areas that require further study.
To create an effective mind map, start with a central idea or topic at the center of the page. From there, draw branches outward to represent subtopics or key points related to the main concept. Each branch can further divide into smaller details, creating a network of connected information. You can use colors, symbols, and images to make the map more engaging and memorable.
Mind maps are especially useful when preparing for tasks that require synthesizing a large amount of information. They help organize key concepts in a way that makes it easier to review and mentally process them. Whether you’re studying for a test, planning a project, or learning a new skill, mind maps can significantly improve your ability to organize and access information when needed.
The Power of Repetition in Learning
Repeated exposure to information is one of the most effective strategies for strengthening memory and enhancing the ability to process and use new knowledge. By reviewing material at spaced intervals, you reinforce neural connections, making it easier to retain and access details over time. This process helps convert short-term understanding into long-term memory, improving overall learning efficiency.
Repetition works by creating stronger pathways in the brain, allowing information to be stored more securely. The more often you revisit a topic, the more familiar it becomes, leading to quicker retrieval and better comprehension. This is why reviewing material multiple times, rather than cramming all at once, produces better results in mastering complex concepts.
There are different ways to incorporate repetition into a study routine. For instance, spaced repetition involves reviewing information at increasing intervals, ensuring that material is revisited just as it begins to fade from memory. This method maximizes retention while minimizing the time spent on each review session.
Another effective technique is active recall, which encourages you to actively retrieve information from memory instead of passively reviewing notes. This strengthens memory pathways and enhances the ability to quickly retrieve relevant details when needed. By regularly applying these techniques, you can boost retention and improve performance in tasks requiring deep knowledge.
How to Improve Focus During the Exam
Maintaining concentration under pressure is essential for optimal performance during high-stakes situations. Being able to stay focused ensures that you can manage time effectively, process questions accurately, and avoid distractions that might interfere with your results. There are various strategies to help you stay mentally sharp and fully engaged throughout the duration of the test.
Techniques to Stay Engaged

Several practices can help keep your mind alert and clear. Deep breathing exercises, for example, can reduce anxiety and boost your ability to concentrate. Taking a few seconds between questions to inhale deeply and exhale slowly can calm the mind and improve focus. Additionally, ensuring adequate hydration and maintaining stable energy levels through small, healthy snacks can make a significant difference in staying sharp.
Time Management Strategies
Effective time management is key to reducing stress and maintaining focus. Setting clear time limits for each section or question helps avoid the tendency to dwell too long on any one part. Using a mental or physical timer can serve as a reminder to pace yourself and prevent feelings of being overwhelmed.
| Strategy | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Reduces stress and anxiety, enhances mental clarity | Take a 3-second inhale, hold for 3 seconds, then exhale for 3 seconds |
| Healthy Snacks | Maintains energy levels and focus | Eat a handful of nuts or fruit before the test |
| Time Blocking | Prevents overthinking and ensures efficient use of time | Allocate 5 minutes to each multiple-choice question, 10 minutes to essay questions |
By applying these strategies, you can increase your focus, reduce distractions, and approach the test with greater confidence and clarity. Staying present in the moment allows you to perform at your best, ensuring that each piece of information is processed and used effectively.
Techniques for Retaining Complex Information

Managing intricate or detailed material can be challenging, but there are several effective techniques that can help make this information more accessible and easier to retain. By breaking down complex content into smaller, digestible parts and using strategic methods, you can enhance your understanding and memory of difficult topics.
One useful approach is chunking, where large amounts of information are divided into smaller, more manageable groups. This method reduces cognitive overload by organizing data into patterns or categories that are easier to remember. For instance, when studying for a subject that involves memorizing long lists or formulas, grouping similar items together can simplify the process and aid in faster retrieval.
Another technique is spaced repetition, which involves revisiting material at increasing intervals over time. This method takes advantage of the brain’s natural ability to retain information when it’s reviewed periodically. Rather than cramming all at once, spacing out review sessions ensures that the material is reinforced in long-term memory, making it more accessible when needed.
Visualization is also a powerful tool when trying to retain complex information. Creating mental images or diagrams to represent abstract concepts can provide a visual anchor that aids in memory retention. Whether it’s mapping out processes or drawing connections between ideas, associating material with vivid visuals makes it easier to recall later on.
Lastly, teaching or explaining the material to someone else can reinforce your own understanding. By verbalizing what you’ve learned, you force yourself to organize your thoughts and clarify any areas of confusion. This active approach to learning can significantly strengthen your grasp of complex concepts and ensure that the information sticks for the long term.
Strategies for Managing Time in Exams

Effective time management during a high-pressure situation is essential for maximizing performance. By planning ahead and allocating appropriate time to each section or question, you can ensure that every part of the task receives the attention it deserves. Properly managing your time allows you to approach the test with a clear mind and ensures that you are not rushed or overwhelmed.
Prioritize and Organize
Before diving into the questions, take a moment to scan through the entire test and determine which sections or questions are more time-consuming or challenging. Prioritize the easier tasks first, as they will take less time and boost your confidence. Allocate more time to the sections that require deeper thought or more detailed answers. This approach helps in maintaining a steady pace throughout the duration.
Use Time Limits for Each Section
Setting a specific time limit for each section or question can help you stay focused and prevent spending too much time on any single part. If a question is particularly difficult, move on and come back to it later if time permits. This ensures that you make progress on all parts of the task and reduces the risk of running out of time before completing everything.
Using a timer or watch can be a helpful tool to track your progress. For example, if the test is two hours long and consists of five sections, you can aim to complete each section in 24 minutes. Keeping an eye on the clock throughout the process helps to pace yourself, making sure that you stay on track without feeling rushed.
How to Review Notes Effectively
Effective note review is crucial for retaining important information and preparing for any demanding task. The process involves more than just reading through your notes; it requires an active approach to reinforce key concepts and identify areas that need further attention. By using structured methods, you can improve comprehension and increase retention.
Active Reading Techniques
Start by actively engaging with your notes instead of passively skimming them. Here are some techniques to enhance the review process:
- Highlight Key Information: Mark important points, definitions, and concepts. This will make them easier to find during later reviews.
- Summarize in Your Own Words: After reading a section, try to summarize the material without looking at your notes. This reinforces your understanding and helps identify areas that need more focus.
- Ask Questions: Turn headings and key points into questions. Challenge yourself to answer them based on what you’ve learned. This can improve memory retention and comprehension.
Spaced Repetition and Review Intervals

Rather than reviewing all your notes in one sitting, it’s more effective to break up the material and spread your review sessions over time. This is known as spaced repetition. By revisiting your notes at increasing intervals, you reinforce the information in your long-term memory.
- First Review: Immediately after taking notes, review them within 24 hours to solidify your understanding.
- Subsequent Reviews: Review the material again after a few days, then after a week, and so on. Each review session helps strengthen memory retention.
Combining these strategies creates a more efficient and effective approach to note review, ensuring that important details are retained and easily accessible when needed. By consistently revisiting and engaging with your material, you set yourself up for success in processing and utilizing the information effectively.