
In today’s educational and professional environments, ensuring fairness and security during assessments has become a top priority. With advancements in technology, various methods have been developed to monitor individuals while they complete their tests, guaranteeing the authenticity of their performance. These techniques are especially important when participants are not physically present in a traditional setting.
Secure assessments are now widely used to prevent dishonest behavior, providing a more reliable way to verify a test-taker’s identity and monitor their actions. With a combination of physical and digital monitoring tools, these measures aim to create a controlled environment that discourages cheating.
As education and certification processes evolve, understanding the different types of monitoring methods becomes essential. Whether conducted remotely or in-person, these assessments play a crucial role in maintaining the credibility of academic achievements and professional qualifications.
Proctored Exam Definition
In educational and professional settings, ensuring that individuals complete assessments under fair and controlled conditions is essential. This process involves monitoring participants throughout the testing process to maintain the integrity of the results. Such supervision can take various forms, combining both in-person and digital methods to guarantee security and prevent cheating.
Monitoring Methods Used During Assessments
During these supervised tests, technology plays a vital role in monitoring the participant’s environment. Whether through webcams, screen recording software, or real-time surveillance, the goal is to prevent any unauthorized assistance. These tools work together to create a secure atmosphere where the individual is observed continuously, ensuring their actions align with the rules of the assessment.
Importance of Secure Assessment Methods
With the rise of online learning and remote certification programs, the need for secure testing has become more prominent. By employing monitoring measures, institutions can ensure that the assessments reflect the true abilities of the individual, free from external influences. This process not only safeguards the value of qualifications but also helps uphold fairness in competitive environments.
What Is a Proctored Exam
In various assessment scenarios, it is essential to ensure that individuals complete their tasks honestly and without external help. This type of testing involves supervision during the process, where the participant’s behavior is observed and monitored to ensure that the integrity of the results is maintained. Different methods can be used to oversee the individual, whether in person or through digital tools.
Typically, the monitoring process includes:
- Real-time surveillance through cameras or other recording devices
- Remote monitoring via software that tracks the test-taker’s screen and activity
- Verification of identity to prevent impersonation
These measures ensure that the person taking the test follows all the rules and guidelines, providing a fair and secure environment. Whether in a physical testing center or online, such procedures help to validate that the assessment is completed without interference.
How Proctored Exams Ensure Academic Integrity
In the world of education, maintaining fairness and honesty during assessments is crucial. To achieve this, certain methods are employed to monitor and control the environment in which individuals complete their tasks. By overseeing the testing process, these measures prevent dishonest behaviors such as cheating or unauthorized assistance, ensuring that the results reflect the true abilities of the test-taker.
Monitoring is a key factor in preserving the credibility of academic assessments. By observing the participant’s actions in real-time, institutions can detect any irregularities that may compromise the integrity of the process. These monitoring techniques can be both physical, such as in-person supervision, and digital, using advanced software tools to track activities during the test.
Another important aspect is identity verification. Ensuring that the person taking the test is indeed the registered individual prevents impersonation and guarantees that qualifications are awarded to the correct person. This step reinforces trust in the system, benefiting both educational institutions and employers who rely on the accuracy of the results.
Types of Proctored Exams Explained
There are several methods used to supervise individuals during assessments, each designed to ensure security and integrity. These approaches vary in terms of the level of supervision required and the technology involved. Depending on the nature of the test and the location of the participant, different techniques can be applied to monitor behavior and prevent cheating.
Some common types of monitored assessments include:
- In-person monitoring: A supervisor is physically present during the test, observing the participant’s actions and ensuring they follow the rules.
- Remote monitoring: Tests taken online are monitored using webcam feeds, screen recording, and real-time surveillance software.
- Automated monitoring: Software tools track user activities, such as keystrokes, mouse movements, and browser behavior, to detect any unusual actions.
Each method has its own set of advantages and challenges. The choice of monitoring technique depends on factors such as test format, location, and the level of security required to maintain the integrity of the assessment process.
Difference Between Proctored and Unproctored Tests
Assessments can be divided into two main categories based on the level of supervision during the process: those that involve monitoring and those that do not. While both types aim to evaluate knowledge or skills, the methods used to ensure fairness and prevent cheating can vary significantly. Understanding the key differences between these two types of assessments is essential for both test-takers and administrators.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Monitored Assessments | Unmonitored Assessments |
|---|---|---|
| Supervision | Real-time monitoring by a supervisor or through digital tools | No active supervision, participants are trusted to follow guidelines |
| Security | High security, with measures to prevent cheating | Lower security, more room for dishonesty |
| Identity Verification | Strict identity checks to confirm the test-taker | Often no verification, can be done at home or anonymously |
| Technology | Uses webcams, screen recording, and software to track behavior | Typically no technology involved, or minimal tracking |
Choosing the Right Method
Both types of assessments serve different purposes and are suited to varying testing environments. Monitored assessments are often used for high-stakes certifications or qualifications, where security and integrity are of utmost importance. On the other hand, unmonitored assessments are typically used in less formal situations or where trust in the participant is high. The choice between the two depends on the nature of the test, the need for security, and the resources available.
Why Are Proctored Exams Used
Supervised assessments play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of academic and professional testing. These methods ensure that participants complete their tasks fairly and without external assistance, providing a reliable measure of their skills and knowledge. The use of monitoring techniques helps institutions and organizations uphold the credibility of their certification processes.
Some of the key reasons for utilizing monitored assessments include:
- Preventing cheating: Monitoring participants during testing reduces the risk of dishonest behavior, such as accessing unauthorized materials or receiving external help.
- Ensuring fairness: Supervision creates a level playing field, ensuring that all individuals have the same conditions during the assessment process.
- Maintaining security: Through identity verification and continuous observation, these methods protect against impersonation and other security breaches.
- Validating results: Monitored assessments increase the trustworthiness of the results, making them more valuable for educational institutions, employers, and certifying bodies.
As remote learning and online certification programs become more common, these methods have become essential in guaranteeing that assessments are conducted fairly, regardless of the test-taker’s location. The integration of monitoring tools helps to create an environment where the results are accurate and trustworthy.
Common Proctoring Methods in Exams
Various techniques are used to ensure the security and integrity of assessments, particularly when participants are tested remotely or in unmonitored settings. These methods range from in-person supervision to advanced technological solutions that track and observe the test-taker’s actions. The goal is to maintain a fair testing environment, free from external influence, and ensure the authenticity of the results.
Monitoring Techniques
Some common approaches to overseeing assessments include:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Live Surveillance | Participants are monitored in real-time through cameras or in-person supervision by an invigilator. |
| Screen Monitoring | Test-takers’ computer screens are monitored using software that records activity and tracks potential violations. |
| Identity Verification | Test-takers may be asked to show ID, take a photo, or use biometric data to confirm their identity before and during the assessment. |
| Browser Lockdown | Participants’ devices are restricted from opening unauthorized websites or using external resources during the assessment. |
Technological Solutions

Advances in technology have led to the development of digital tools that enhance the monitoring process, particularly for online assessments. These include:
- AI-Based Monitoring: Artificial intelligence is used to track behaviors, detect suspicious activity, and alert administrators to potential cheating.
- Automated Recording: Continuous video and audio recordings are made during the test, which can later be reviewed for irregularities.
- Real-Time Alerts: Systems may trigger alerts to administrators if abnormal behavior or technical issues arise during the testing process.
Each of these methods serves to enhance security and ensure that the assessment is completed fairly, regardless of the format or location of the test-taker.
The Role of Technology in Proctored Exams
Technology has revolutionized the way assessments are monitored and conducted, making it possible to securely evaluate participants from virtually anywhere in the world. By leveraging advanced tools and software, institutions can ensure the integrity of the testing process while minimizing the risk of cheating or dishonesty. The integration of digital solutions allows for more efficient and scalable monitoring of test-takers, regardless of location.
Key Technological Tools in Monitoring
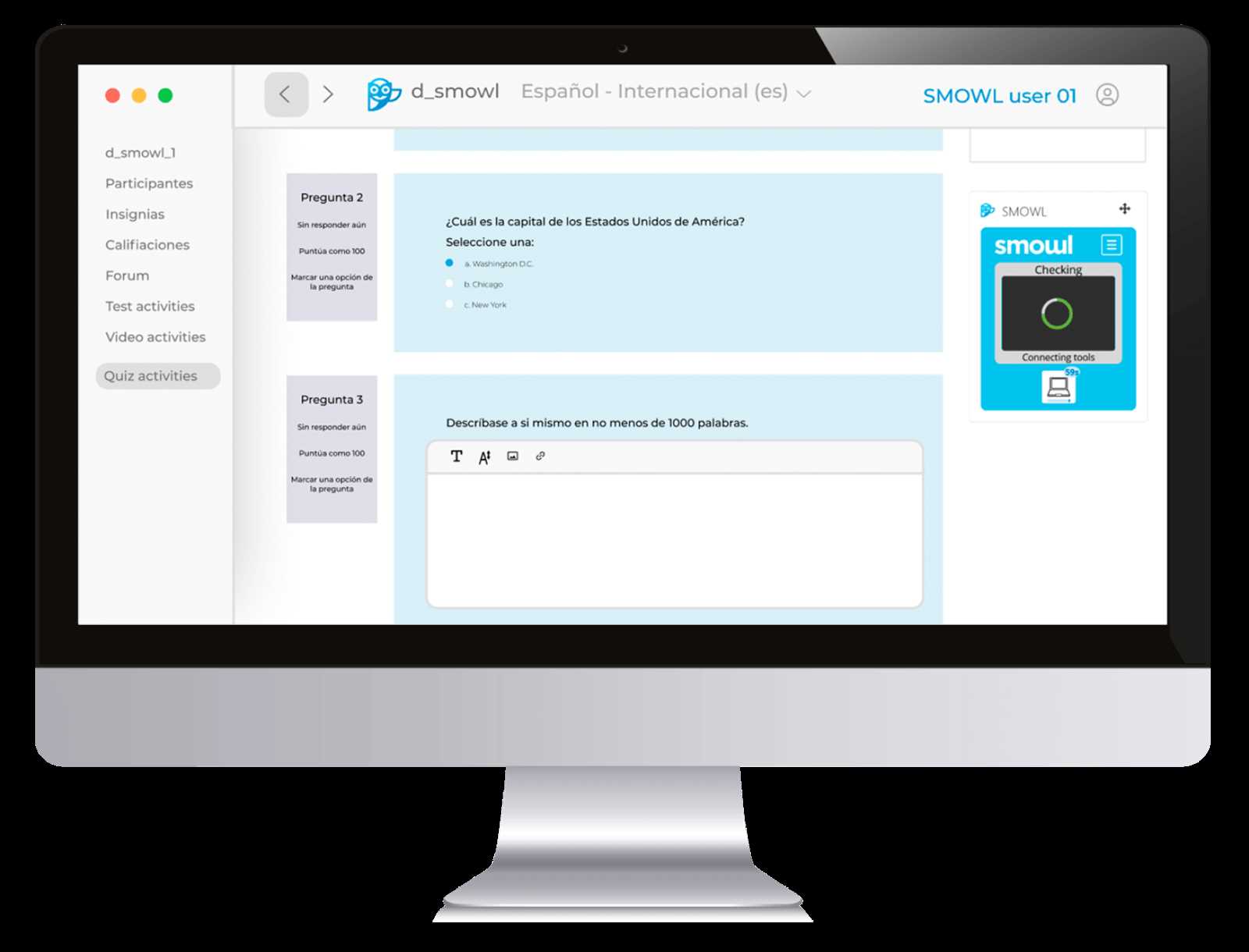
Several technological innovations play a vital role in maintaining fairness and security during assessments:
- Real-Time Video Surveillance: Cameras and webcams allow invigilators to monitor test-takers remotely, ensuring they follow the rules and don’t receive external assistance.
- Screen Recording and Lockdown Software: Specialized programs track participants’ screen activity, prevent access to unauthorized websites, and lock down other computer functions to avoid distractions.
- AI-Based Behavior Analysis: Artificial intelligence can analyze test-takers’ actions, identifying any suspicious patterns or irregularities in their behavior during the assessment.
- Biometric Authentication: Facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, or other biometric methods confirm the identity of participants to prevent impersonation.
Benefits of Technology in Testing
The use of technology not only improves the security of the assessment process but also offers several additional advantages:
- Scalability: Technology enables the secure monitoring of large numbers of test-takers, making it feasible for institutions to manage assessments at a global scale.
- Accessibility: Remote proctoring solutions make it possible for individuals in distant locations or those with mobility issues to take assessments without needing to be physically present at a testing center.
- Efficiency: Automated tools reduce the need for human intervention, streamlining the monitoring process and making it more cost-effective for educational institutions and certification bodies.
In conclusion, technology plays an essential role in ensuring that assessments are both secure and efficient, helping to uphold academic integrity while adapting to the changing needs of modern education and certification systems.
Benefits of Proctored Exams for Institutions
For educational and certification institutions, ensuring the reliability and fairness of assessments is crucial. By employing various monitoring techniques, institutions can maintain the integrity of their testing processes. These methods not only help to prevent cheating but also improve the credibility and recognition of the qualifications they award.
Enhanced Security and Integrity

One of the primary benefits of utilizing supervision during assessments is the increased security it offers. Institutions can rely on:
- Prevention of Academic Dishonesty: With active monitoring, cheating is less likely, ensuring that the results accurately reflect the abilities of the participants.
- Protection Against Impersonation: Supervision, including identity verification techniques, helps to eliminate the risk of someone else taking the test on behalf of the participant.
- Fairness: All participants are held to the same standards, regardless of their location or access to resources, ensuring a level playing field.
Operational Efficiency
For institutions, implementing monitored assessments can lead to operational improvements:
- Scalability: Supervised tests can be conducted on a large scale, accommodating a global student or candidate pool without sacrificing security.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The use of digital tools for monitoring reduces the need for in-person invigilators and physical testing facilities, lowering operational costs.
- Convenience for Participants: Remote monitoring allows institutions to offer flexible testing times and locations, making it easier for participants to complete their assessments.
By adopting these methods, institutions not only protect the integrity of their assessments but also streamline their administrative processes, making testing more accessible and efficient for all parties involved.
Challenges Faced by Proctored Exams
While supervised assessments are essential for ensuring fairness and integrity, they also come with their own set of challenges. These hurdles can impact both the test-takers and the institutions that implement such systems. From technical issues to concerns about privacy, the implementation of monitored testing can sometimes be more complex than anticipated.
One of the key difficulties faced by institutions is the need for sophisticated technology to handle remote monitoring. This often requires reliable software, high-quality cameras, and other digital tools that may not always be accessible to all test-takers. Additionally, the cost of implementing such systems can be prohibitive for smaller institutions.
Test-takers, on the other hand, may encounter issues related to the technology used, such as slow internet connections, device compatibility problems, or difficulties with identity verification. Furthermore, there are concerns about privacy, as participants may feel uncomfortable being constantly watched during their assessment.
Another challenge is ensuring that the integrity of the process is maintained without compromising user experience. For example, the overuse of restrictive measures like browser lockdowns or facial recognition technology might lead to technical difficulties or feelings of distrust among participants.
In conclusion, while monitored assessments provide a necessary safeguard for academic integrity, both institutions and participants must address the challenges related to technology, accessibility, and privacy in order to make these systems more effective and user-friendly.
How to Prepare for a Proctored Exam
Proper preparation is key to succeeding in any monitored assessment. These tests often require a higher level of focus and organization due to the added elements of supervision and technology. By following a few simple steps, you can ensure you are fully ready to take the test under monitored conditions while maintaining your best performance.
1. Understand the Rules and Requirements
Before the test, make sure to familiarize yourself with the specific guidelines and technology requirements set by the institution. This includes:
- System Specifications: Ensure your device meets the necessary technical requirements, such as webcam, microphone, and a stable internet connection.
- Testing Environment: Prepare a quiet, well-lit space free from distractions. You may be required to show your surroundings before the assessment begins.
- Identification Process: Be prepared for identity verification procedures, such as providing a valid ID or having your face scanned.
2. Practice with the Technology
Many institutions provide a trial session or a practice test that simulates the conditions of the actual assessment. Take advantage of this to:
- Test Your Equipment: Make sure your webcam, microphone, and internet connection work properly to avoid technical difficulties during the real test.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Software: Get comfortable with any monitoring or lockdown software used during the assessment, ensuring you know how to navigate through it without issues.
By preparing in advance, you can reduce the chances of technical problems and increase your confidence on test day.
Security Measures in Online Proctored Exams
To ensure the integrity of assessments conducted remotely, a variety of security measures are put in place. These methods help prevent cheating and maintain fairness during the test. With the growing shift to online testing, these strategies are essential in creating a secure testing environment that closely mirrors in-person assessments.
1. Identity Verification
Before participants can begin, their identity must be verified. Common techniques include:
- Facial Recognition: A scan of the participant’s face is compared with the ID provided to ensure it matches the individual sitting for the test.
- Document Upload: Participants may need to upload a government-issued ID for additional verification before starting.
- Live Monitoring: In some cases, a live proctor will conduct a video call to verify the test-taker’s identity and the test environment.
2. Remote Monitoring Tools
Once the test begins, a variety of monitoring tools are used to ensure no dishonest behavior takes place:
- Screen Locking: The software may prevent participants from accessing other applications or websites during the test.
- Browser Monitoring: Certain tools track and block any attempts to open new tabs or windows that might be used for cheating.
- Real-Time Surveillance: Cameras and microphones monitor the test-taker’s actions and environment to detect any suspicious behavior, such as looking off-screen or receiving outside help.
These measures work together to create a secure and fair environment for remote assessments, minimizing the risk of cheating while ensuring that only the individual registered for the test participates.
How Proctored Exams Protect Against Cheating
Maintaining academic integrity is one of the primary goals of any supervised assessment. By employing various monitoring techniques, institutions can ensure that test-takers complete their assessments honestly, without resorting to dishonest practices. These methods help reduce opportunities for cheating and maintain the fairness of the testing process.
1. Surveillance and Monitoring
One of the key ways to prevent cheating is through continuous surveillance during the test. Common strategies include:
- Live Monitoring: A live proctor can observe the test-taker through video feeds, ensuring they are not using unauthorized materials or receiving outside help.
- Recorded Video: In some cases, the entire session is recorded, allowing for review if any suspicious behavior is flagged.
- Behavioral Analysis: Advanced software can track a test-taker’s actions, identifying irregularities such as excessive movements or looking away from the screen.
2. Technology-Driven Restrictions
In addition to monitoring, several technological tools are used to limit cheating opportunities:
- Screen Locking: The testing software may block access to other applications, ensuring the test-taker cannot search for answers or open other programs during the assessment.
- Browser Restrictions: Some systems prevent participants from opening new tabs or using multiple browsers, which limits access to online resources.
- AI Detection: Artificial intelligence can be used to detect suspicious behavior, such as a participant’s voice rising in volume or multiple people being in the room during the test.
By combining human oversight with technological restrictions, these methods significantly reduce the chances of cheating and help ensure a fair testing environment for all participants.
Proctored Exams for Remote Learning
As more educational institutions move towards remote learning, ensuring the integrity of assessments has become increasingly important. Supervised assessments help maintain academic honesty while enabling students to complete their courses from a distance. These controlled testing environments are essential in preventing dishonesty during online evaluations, ensuring that all participants are following the same set of rules, no matter where they are located.
1. Ensuring Fairness in Remote Assessments

Remote learning brings unique challenges when it comes to assessment. To maintain fairness across the board, a variety of measures are used, such as:
- Identity Verification: Students may need to verify their identity before taking the test, using methods like face scans or government-issued IDs to ensure that the right person is taking the test.
- Environment Monitoring: The space in which the student takes the test may be checked to ensure no unauthorized materials are present, such as notes, books, or electronic devices.
- Real-Time Surveillance: Through video feeds, instructors or proctors can observe students while they take their assessments to make sure there are no attempts to cheat or collaborate with others.
2. Overcoming Challenges with Technology
Technology plays a crucial role in supporting remote assessments. Several tools are used to create secure, fair, and efficient testing environments:
- Browser Locking: Many systems restrict students from navigating away from the testing platform, preventing them from accessing the internet or other applications during the assessment.
- Screen Recording: Some platforms record the entire testing session, allowing for review if any suspicious activity is flagged.
- AI and Monitoring Software: Advanced tools use AI to track eye movements, detect unusual behavior, and analyze whether a student is following the exam rules.
These measures ensure that remote assessments are conducted securely, preventing cheating while offering students the flexibility to complete their coursework from anywhere in the world.
Legal and Ethical Aspects of Proctoring
As the use of surveillance and monitoring tools in assessments grows, so does the concern over the legal and ethical implications of such practices. Institutions must balance the need for academic integrity with the rights and privacy of individuals. Ensuring compliance with laws while implementing effective monitoring systems is crucial in maintaining a fair and transparent evaluation process.
Legally, there are several considerations when employing surveillance techniques during online evaluations. These include adherence to data protection regulations, such as GDPR in the EU or similar privacy laws in other regions. These laws ensure that students’ personal information, including video footage or biometric data, is handled with the utmost care and only for legitimate purposes. Educational institutions must obtain consent from students before using monitoring software, making it clear what data will be collected and how it will be used.
Ethically, the primary concern is the potential invasion of privacy. Students are often required to share personal data, be monitored via cameras, or even submit biometric information during assessments. Institutions must ensure that these measures are not excessive or overly intrusive. Clear communication about the purpose of monitoring, coupled with informed consent, helps maintain ethical standards while ensuring the legitimacy of the assessment process.
Additionally, institutions must consider the accessibility of these tools. Not all students have access to high-end technology or stable internet connections, and these disparities can create unfair advantages or disadvantages. Ensuring equitable access to the resources needed for these monitored assessments is essential to uphold fairness and inclusivity in education.
The Future of Proctored Exams
The landscape of online assessments is rapidly evolving, and with it, the systems designed to ensure integrity during these evaluations. As technology advances, so do the methods of monitoring students, leading to greater efficiency, accuracy, and security. The future of these evaluation practices will likely be shaped by innovations in artificial intelligence, biometrics, and data analysis, allowing for even more streamlined and effective solutions for ensuring fair assessments.
One potential development is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to detect anomalies and patterns that suggest academic dishonesty. With the power of AI, surveillance tools could not only monitor students’ actions but also analyze behavior to spot inconsistencies, such as unusual movements or multiple faces in the frame, in real time. This could lead to a more proactive approach to preventing cheating, rather than relying solely on human intervention after the fact.
Moreover, biometric technology is expected to play a larger role in online assessments. Tools such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning could be used to verify the identity of a student before and during an evaluation, minimizing the risk of impersonation. As these technologies become more widely available and affordable, their integration into the assessment process could help increase trust in online evaluations.
| Technology | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| AI Monitoring | Real-time anomaly detection, better fraud prevention | Privacy concerns, potential inaccuracies in detection |
| Biometrics | Improved identity verification, reduced risk of impersonation | Data security, accessibility issues |
| Remote Monitoring Software | Convenient, scalable for large institutions | Potential for intrusive surveillance, technology limitations |
Despite these promising advancements, challenges remain. The privacy of students is a critical concern, and institutions will need to carefully navigate the ethical implications of using these technologies. Additionally, ensuring that all students have access to the required technology will be essential to maintain fairness across diverse populations. Moving forward, the development of new systems will need to strike a balance between security and privacy, ensuring that the benefits of advanced monitoring outweigh the potential drawbacks.