Assessments in advanced science courses are essential for measuring student proficiency and knowledge. These evaluations use a structured approach to quantify performance and provide a clear indication of a student’s understanding of the material. Each test is designed to assess a range of skills, from basic concepts to more complex problem-solving abilities, with varying weight assigned to different sections of the test.
Grading in these assessments follows a specific methodology that translates raw scores into an understandable final result. The process is structured to reflect the difficulty of the questions and the importance of the topics covered. Knowing how your performance is evaluated can help you better prepare and manage expectations as you progress through the course.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the key elements of how these evaluations are scored, highlighting important factors that influence the final outcome. We’ll explore what each score range means and how it can impact your academic standing. Understanding this framework will allow you to approach your study strategies with greater clarity and focus.
ACS Organic Chemistry Exam Grading Scale
The evaluation method used in this field of study is designed to provide a comprehensive measurement of student performance. It considers multiple factors, including accuracy, understanding of key concepts, and problem-solving abilities. The system is structured in a way that helps both instructors and students understand how well the material has been mastered and where further improvement might be needed.
Structure of the Grading System
The scoring system is typically divided into different sections, each contributing to the overall result. Some sections focus on multiple-choice questions, while others may require detailed explanations or calculations. Here are the key components that make up the overall score:
- Multiple-Choice Questions: These assess your ability to recall information and apply concepts to solve problems efficiently.
- Written Problems: These test your ability to demonstrate a deeper understanding of the material by working through complex problems step by step.
- Practical Application: Some assessments may include sections that evaluate your ability to apply learned concepts to real-world scenarios or experiments.
How Scores are Interpreted
Each student’s score is interpreted based on a predefined range. The final score helps determine the level of mastery achieved in the subject matter. The typical ranges are as follows:
- Excellent: A score in this range indicates a strong grasp of the material with minimal errors.
- Good: A score here suggests a solid understanding, but there may be a few areas needing improvement.
- Average: A score within this range reflects a general understanding, but with noticeable gaps in certain areas.
- Needs Improvement: Scores in this range indicate significant gaps in understanding that require further study and practice.
Ultimately, the final score reflects not just the ability to recall facts but the depth of understanding and application. It is crucial for students to understand the different sections of the test and focus on improving both speed and accuracy to achieve the best results.
What is the ACS Grading System
The evaluation process in scientific assessments is designed to measure how well students grasp complex concepts and apply their knowledge to solve problems. This method aims to provide a clear and standardized way to interpret performance, allowing for both individual and group comparisons. The system is built to reflect the varying levels of mastery achieved by students through different types of questions and tasks.
Key Components of the Evaluation Method
The evaluation system is typically divided into distinct parts, each designed to assess different aspects of student learning. These sections test a range of skills, from recalling factual knowledge to demonstrating analytical thinking. Below are the key areas that are evaluated:
- Conceptual Understanding: This portion assesses the ability to recall and explain fundamental ideas and theories.
- Problem-Solving Skills: This section evaluates how well students can apply learned knowledge to solve complex problems, often in novel contexts.
- Application to Real-World Scenarios: Some assessments involve tasks that require students to apply their knowledge in practical or experimental settings.
How Scores are Determined
Scores are assigned based on how well students perform across these various sections. The final result is not solely based on correct answers but also on the quality of reasoning and the application of learned concepts. Here’s how the final performance is typically categorized:
- Outstanding: A high score signifies a strong understanding of all concepts and the ability to apply them effectively.
- Good: A solid performance with minor areas for improvement.
- Fair: This score indicates a general understanding, with room for further development in key areas.
- Needs Improvement: A lower score indicates significant gaps in understanding that must be addressed.
Understanding this system is crucial for students aiming to improve their performance and achieve the best possible results. It helps identify both strengths and areas that need further attention.
Understanding Exam Score Calculation
The process of calculating scores in scientific assessments is a methodical procedure that translates a student’s performance into a measurable result. It takes into account the number of correct answers, the difficulty of questions, and the weight assigned to various sections. The calculation ensures that the final score accurately reflects a student’s understanding and application of the material covered.
Factors Affecting the Final Score
Several factors influence the final score, each contributing to the overall result. The following elements are key in determining the final outcome:
- Correct Answers: The number of correct responses directly impacts the score, with more accurate answers leading to higher results.
- Question Difficulty: Some questions carry more weight than others, particularly those that require deeper understanding or more complex reasoning.
- Time Management: Efficiently completing the assessment within the given time frame can influence the final score, especially in time-sensitive sections.
How Scores Are Tabulated
The raw score is usually calculated by adding up the points earned from correct responses. Each question or task might be assigned a specific point value, with more complex questions potentially offering higher points. After calculating the raw score, it is then adjusted to account for the difficulty level of the test, ensuring fairness across different versions of the assessment.
In some cases, scores are converted into a percentage or placed on a standardized scale, making it easier to compare individual performances. Understanding how this process works can help students focus on key areas for improvement.
How ACS Exam Scores Are Interpreted
Interpreting the results of a scientific assessment goes beyond just looking at the final score. It involves understanding what the score represents in terms of knowledge, skills, and the ability to apply learned concepts in various contexts. The interpretation of results provides valuable insight into a student’s proficiency and identifies areas for improvement.
What Your Score Reflects
Your performance on the test is not simply a reflection of how many correct answers you gave, but also of how well you understand the material. The final result can indicate different levels of mastery, from a basic understanding to a deep grasp of the subject. Below is how the final score is typically interpreted:
- High Score: Indicates strong proficiency in the material, with a solid understanding of complex concepts and the ability to apply them effectively.
- Moderate Score: Reflects a good grasp of the core concepts, but may show some gaps in more advanced areas or the application of knowledge.
- Low Score: Suggests significant areas of misunderstanding or insufficient preparation, requiring additional study and focus on key topics.
Impact on Academic Standing
Depending on the context, the interpretation of the score can have various implications for a student’s academic progress. For example, a high score might lead to advanced placement or eligibility for honors courses, while a lower score may necessitate additional coursework or remedial study. Understanding how your results are interpreted helps set realistic goals for future assessments.
Key Factors Affecting Your Score
Your performance in any assessment is influenced by several important factors. These factors determine how well you are able to demonstrate your understanding and how effectively you can apply the concepts you have learned. Recognizing these key elements can help you focus your efforts in preparation and improve your results.
Accuracy and Precision
One of the most important factors in determining your score is the accuracy of your responses. A high level of precision in answering questions not only shows your knowledge but also reflects your ability to apply concepts correctly. Minor errors can significantly impact your score, especially in complex problem-solving sections where every step counts.
Time Management
How well you manage your time during the test can also affect your performance. Rushed answers often lead to mistakes, while taking too much time on a single question can leave you with insufficient time for others. Being able to balance speed with accuracy is crucial in achieving a high score. Planning your time wisely can help you tackle each section more effectively.
Understanding of Complex Concepts

The depth of your understanding plays a crucial role in how well you perform. Some questions may require you to demonstrate an in-depth comprehension of more advanced topics. A strong grasp of foundational concepts is essential for successfully answering these more challenging questions. Reviewing difficult material and seeking clarity on complex topics can help you perform better.
Application of Knowledge
Tests are often designed to assess how well you can apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. The ability to use what you’ve learned in practical situations demonstrates a higher level of understanding. Students who excel at applying concepts tend to perform better, as this skill is often heavily weighted in the assessment process.
Grading Scale for ACS Organic Chemistry
The way in which scores are interpreted in a scientific assessment can vary significantly depending on the method used. Typically, scores are categorized into different levels that reflect the student’s overall understanding and performance. These levels help both instructors and students gauge the mastery of the material and identify areas of improvement.
Score Ranges and Their Meaning
Each test has a predefined range of scores, which are broken down into categories that represent different levels of achievement. The interpretation of these ranges can help clarify what each student’s score means in terms of their comprehension and application of the subject matter. The most common ranges are:
- Excellent: This range represents a near-perfect understanding of the material, with very few errors. Students scoring in this range have demonstrated a thorough grasp of both basic and advanced concepts.
- Good: A score in this range indicates solid proficiency. While the student has a good understanding of the material, there may be minor gaps or mistakes in their application of the concepts.
- Average: Students in this range have a general understanding of the subject but may struggle with more complex problems or have gaps in knowledge that need addressing.
- Needs Improvement: A lower score indicates that the student faces significant challenges in grasping key concepts and will need to dedicate time to review the material thoroughly.
Impact of Score Interpretation
Understanding how scores are categorized is important because it can impact a student’s academic progression. Higher scores may be required for certain qualifications or advanced courses, while lower scores might signal a need for additional study or tutoring. By interpreting your score within this framework, you can better plan your study approach and seek help where necessary.
Comparison with Other Grading Systems
While each testing system has its own methods for evaluating student performance, it is helpful to compare these approaches to understand their strengths and weaknesses. Different systems may use varying criteria, thresholds, and weightings to determine how well students grasp the material. This comparison allows for a broader understanding of how one method stands in relation to others, providing insight into its effectiveness and fairness.
Traditional Grading Systems
Most educational institutions use a letter-based grading system (A, B, C, etc.), which is relatively straightforward and widely understood. However, this method does not always offer detailed insight into a student’s ability to apply their knowledge in practical contexts. Here’s how this system typically compares:
- Letter Grades: Clear and simple, but often less informative about the depth of understanding or problem-solving skills.
- Percentage-Based: Provides a more precise figure but can fail to account for question difficulty or conceptual mastery.
- Weighted Average: Some systems use weighted averages to reflect the relative importance of each section of the test.
Competency-Based Grading
In some cases, grading is based on demonstrating a specific level of competency in a subject. This approach focuses on assessing how well students perform on particular tasks rather than just a final score. Here’s how competency-based systems compare:
- Focus on Mastery: Students are required to demonstrate full mastery of each concept before moving forward.
- Individualized Approach: This system can provide more personalized feedback, though it may be more time-consuming for instructors.
- Emphasis on Application: Like other systems, competency-based approaches often value the ability to apply knowledge in practical contexts.
By comparing these different systems, it becomes clear that each has its unique benefits and challenges. The system used in scientific assessments can offer a more comprehensive view of a student’s capabilities in comparison to traditional grading methods, helping to more accurately reflect their mastery of the subject.
How to Improve Your Score
Achieving a higher score requires more than just reviewing content; it involves strategic preparation and improving key skills that can help you perform at your best. There are several effective approaches that can enhance your understanding of the material and your ability to apply it effectively in assessments. Below are some practical tips that can help boost your performance.
1. Strengthen Your Fundamentals

Solid foundational knowledge is essential for success in any subject. Make sure you have a strong grasp of the basic concepts before moving on to more complex material. This will make it easier to understand advanced topics and improve your overall score.
- Review Key Topics: Focus on core concepts and frequently tested areas.
- Practice Problem-Solving: Work on applying theory to real-world problems to strengthen your critical thinking skills.
2. Time Management
Being able to manage your time effectively during preparation and on the test itself is crucial for success. Proper time management can ensure that you have enough time to address all questions and complete each section thoroughly.
- Set Study Schedules: Break your study sessions into manageable chunks, focusing on different topics each time.
- Practice Under Time Constraints: Take timed practice tests to get comfortable with the pressure of working within time limits.
3. Practice Regularly
Consistent practice can greatly improve your ability to recall information and apply it effectively. The more you practice, the more familiar you will become with the test format and the types of questions that are typically asked.
- Use Practice Tests: Simulate test conditions to practice answering questions under pressure.
- Identify Weak Areas: Focus on topics where you consistently struggle, and seek additional resources if needed.
4. Seek Feedback and Support
If you’re struggling with certain concepts or techniques, don’t hesitate to ask for help. Getting feedback from peers, tutors, or instructors can help clarify doubts and guide you towards more effective study strategies.
- Study Groups: Collaborate with others to discuss challenging topics and share knowledge.
- Ask for Clarifications: Seek guidance on areas that are unclear or require additional explanation.
By applying these strategies consistently, you can enhance your understanding, improve your performance, and ultimately achieve a higher score. Focused effort and smart preparation will help you make significant progress over time.
What Does Each Score Mean
Understanding the meaning behind your score is crucial for interpreting your performance and identifying areas of strength and weakness. Scores are often categorized into different levels, each representing a particular degree of mastery over the material. These categories help both students and instructors understand how well the student has grasped the subject and where further attention is needed.
A score typically reflects the level of understanding demonstrated on the test, and each range offers insight into a student’s proficiency. Below is an overview of what different score ranges generally indicate:
- High Score: This range reflects a deep understanding of the material, with very few errors. It signifies a strong grasp of both fundamental and complex concepts, indicating that the student has mastered the key topics.
- Above Average: Students who fall into this range have a solid understanding of the material, with minor gaps in their knowledge. They are able to apply most concepts correctly, though they may occasionally struggle with more challenging questions.
- Average: A score in this range indicates a general understanding of the material, but the student may face difficulties in applying certain concepts or solving more complex problems. Some additional study or practice may be necessary to improve performance.
- Needs Improvement: A lower score suggests that the student is having significant difficulty with the material. There are likely gaps in understanding, and further study or support is needed to strengthen their grasp of the key concepts.
By interpreting the score in this way, students can focus their efforts on specific areas of weakness, while also recognizing their strengths. It helps provide a clearer picture of their academic progress and guides them toward a more effective study plan moving forward.
Typical Range of ACS Exam Scores
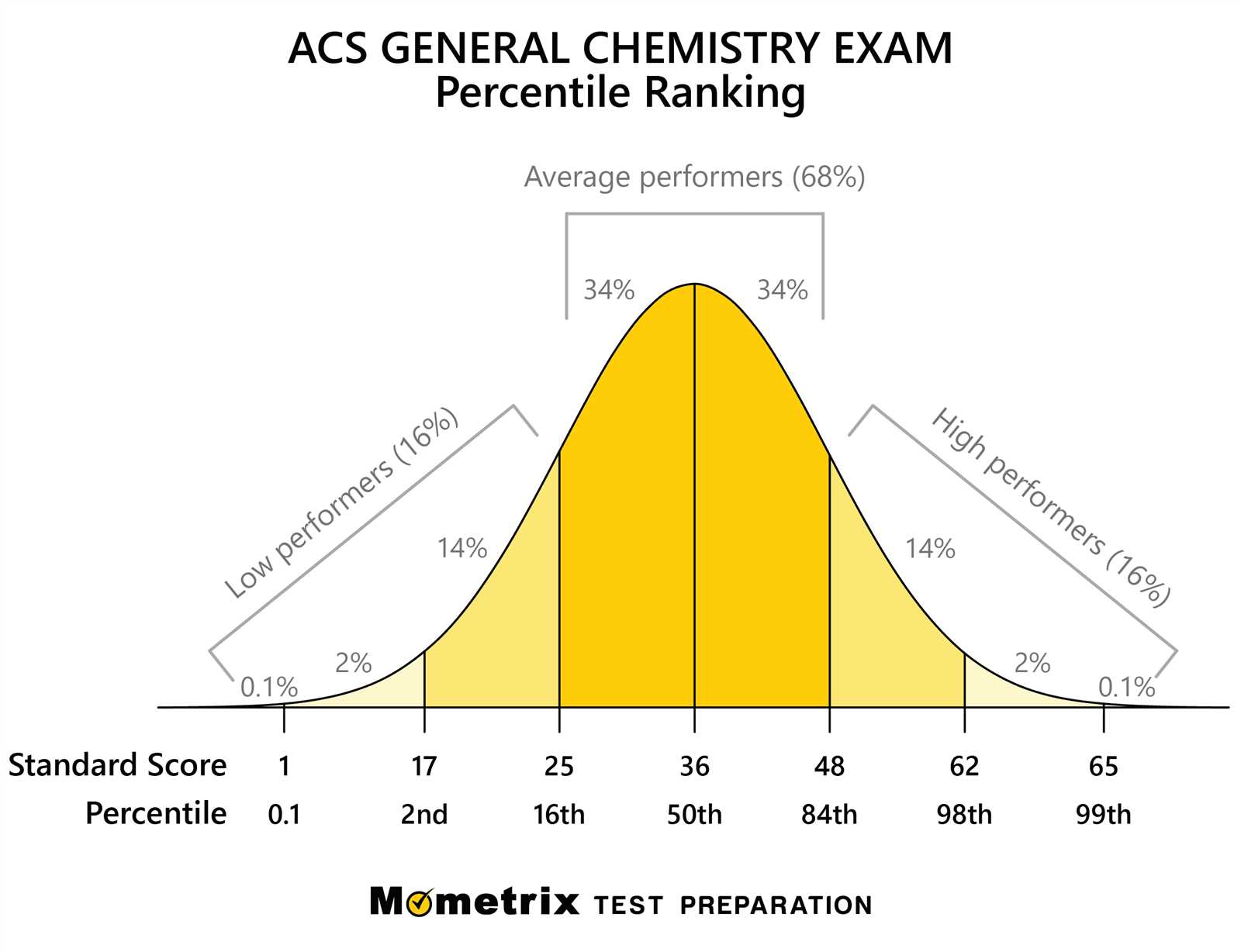
Understanding the typical distribution of scores can help students gauge where they stand in relation to their peers and assess their own progress. Scores are often grouped into categories that reflect different levels of mastery. While there can be some variation depending on the difficulty of the test or the testing group, there is a general range within which most students tend to score.
Below is a general overview of the typical score ranges and their corresponding interpretations:
| Score Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 85% and above | Excellent performance, demonstrating mastery of most concepts and a high level of problem-solving ability. |
| 70% – 84% | Good performance, with solid understanding and only minor mistakes in applying concepts. |
| 50% – 69% | Average performance, indicating a general understanding with several areas needing further study and improvement. |
| Below 50% | Poor performance, indicating significant gaps in understanding and requiring substantial review and further learning. |
These ranges provide a useful reference point for students to assess their performance and identify the areas where they need to focus their efforts for improvement. It is important to note that achieving a higher score may require continued practice, a deeper understanding of key concepts, and strategic study techniques.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in ACS Exams
When taking assessments, certain common errors can negatively impact your performance and lower your final score. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them and maximize your potential. Below are some of the most frequent mistakes students make, along with strategies for preventing them.
1. Misunderstanding the Question
One of the most common mistakes is failing to fully comprehend what the question is asking. This can lead to incorrect answers, even when the student knows the material. It’s crucial to read each question carefully, identify key terms, and ensure that you understand the specifics before attempting to answer.
2. Rushing Through Problems
Another frequent issue is rushing through the questions without taking the necessary time to think critically and check work. This often results in careless mistakes. Take your time to read through each question thoroughly, and make sure to review your answers when you have completed the test.
| Mistake | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Misunderstanding the Question | Read each question slowly and make sure you understand the key points before answering. |
| Rushing Through Problems | Take your time and double-check your work before moving on to the next question. |
| Skipping Over Key Concepts | Review all important topics before the test, and ensure that you don’t skip any critical sections. |
| Not Managing Time Effectively | Allocate specific time for each section and avoid spending too long on difficult questions. |
3. Skipping Over Key Concepts
Students sometimes overlook important topics, especially if they are feeling confident about other areas. This can be a major oversight, as even small gaps in knowledge can affect the outcome. To avoid this, make sure to thoroughly review all key concepts, even those that might seem less relevant.
4. Not Managing Time Effectively
Time management is essential in any assessment. Some students spend too much time on challenging questions, leaving insufficient time for easier ones. To prevent this, practice time management techniques before the test and stick to a planned schedule.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can avoid pitfalls that might lower your score and approach the test with greater confidence and preparation.
How to Prepare for the Exam
Proper preparation is the key to success in any assessment. Effective study strategies, consistent practice, and smart time management can make a significant difference in your performance. The goal is to build a strong understanding of the material, refine your problem-solving skills, and boost your confidence before the test day.
1. Create a Study Schedule
One of the most effective ways to prepare is to create a structured study plan. Break down the topics into manageable chunks and allocate specific times for each. Prioritize areas that you find more challenging and review them regularly. Having a clear plan ensures that you cover all the necessary material and prevents last-minute cramming.
2. Use Practice Problems and Past Papers

Practice is essential for reinforcing your knowledge and improving your test-taking abilities. Work through a variety of problems to familiarize yourself with the question formats and common types of challenges. Past papers can be particularly helpful in understanding the structure of the test and identifying patterns in the types of questions asked.
In addition to practicing problems, try to simulate the exam environment. Set aside a quiet space, use a timer, and try to complete practice tests under real test conditions. This will help you manage time effectively during the actual assessment.
With these preparation strategies, you can enter the assessment with confidence, knowing that you’ve done everything possible to succeed. Proper preparation not only enhances your knowledge but also ensures you’re ready for any challenge the test may present.
The Role of Practice Exams
Practice assessments play a crucial role in preparing for any high-stakes test. They not only help reinforce the material but also provide a valuable opportunity to familiarize yourself with the structure and types of questions you will face. By simulating the actual testing environment, practice tests enable you to refine your time management skills, reduce anxiety, and boost overall confidence.
1. Familiarizing with Question Formats
One of the key benefits of practice tests is getting accustomed to the types of questions that will appear on the actual assessment. This experience can be particularly helpful when it comes to multiple-choice or problem-solving questions. By practicing regularly, you can identify the most common question patterns and develop strategies for approaching them efficiently.
2. Building Test-Taking Strategies
Another advantage of practice exams is the opportunity to experiment with different test-taking techniques. You can assess your ability to manage time, prioritize questions, and handle difficult problems. Regular practice will help you refine your approach, ensuring that you make the best use of your time and focus on areas where you need improvement.
Ultimately, practice tests serve as a bridge between preparation and performance, offering a safe environment to test your skills, identify weaknesses, and prepare for the real assessment day. By incorporating them into your study routine, you can improve both your knowledge and your exam-taking abilities.
Grading Criteria for Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions are a common assessment format used to evaluate knowledge and understanding in various subjects. These questions are designed to test your ability to recall key concepts and apply them in different scenarios. The grading criteria for these types of questions are typically straightforward, focusing on correct answers and sometimes penalizing incorrect responses to encourage careful selection.
1. Correct Answer Weighting
The most direct grading criterion for multiple-choice questions is the accuracy of your answer. Each question typically has four or five answer options, with one correct choice. When you select the correct option, you earn the full point allocated for that question. The emphasis is placed on recognizing the correct response based on your understanding of the material.
2. Negative Marking for Incorrect Answers
Some assessments may implement a system where incorrect answers result in a deduction of points. This is done to discourage guessing and encourage careful consideration before selecting an option. Negative marking typically involves subtracting a fraction of the total points, usually for each incorrect response, while unanswered questions are left unmarked. It’s essential to approach these questions strategically, weighing the risk of incorrect answers before choosing one.
Understanding these grading principles can help you approach multiple-choice questions more effectively. By focusing on accuracy and avoiding careless mistakes, you can maximize your score while minimizing the potential for penalties.
Understanding the Experimental Section Score
The experimental section of an assessment is designed to test practical skills and the application of theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. This part of the evaluation typically involves tasks that require a combination of hands-on technique, problem-solving, and critical thinking. Scoring for this section is often based on how well you demonstrate understanding through experiments, data analysis, and the ability to interpret results accurately.
In this section, the focus is less on memorization and more on how effectively you can apply the concepts you’ve learned to perform tasks or solve problems in a practical context. The assessment may involve interpreting graphs, making observations, conducting calculations, or drawing conclusions based on experimental data.
To score well in this section, it’s essential to not only complete the tasks correctly but also to follow the correct methodology, maintain accuracy throughout the process, and clearly communicate your findings. Practicing these skills can significantly improve your ability to perform well in the experimental part of the assessment.
Impact of Final Scores on Grades
The final performance on an assessment plays a crucial role in determining the overall grade for a course or program. These results often serve as the primary indicator of a student’s understanding and mastery of the subject matter. The way these final scores are integrated into the grading system can significantly influence the final mark you receive, which can, in turn, impact your academic progress and future opportunities.
Typically, the final score is weighted more heavily than individual assignments or quizzes. It may account for a substantial portion of the overall grade, meaning that a strong performance can substantially boost your final result, while a lower score could have a negative impact. In some cases, however, instructors might use a combination of various assessments to calculate the final grade, allowing for more flexibility in how the final result is determined.
Understanding the weight of final results and how they affect your grade can help you prioritize your study efforts and make strategic decisions during your preparation. It is essential to know how much each section or component of the assessment counts towards your final grade to allocate your time and focus accordingly.
Effect on Academic Standing
Final scores are not only important for determining grades in individual courses but also for maintaining your academic standing. High scores may enhance your grade point average (GPA), which could be crucial for scholarships, honors programs, or meeting graduation requirements. On the other hand, consistently low scores can lead to academic challenges or even jeopardize your progression in certain programs.
Strategies to Maximize Impact
To maximize the positive impact of your final scores, focus on consistent preparation and understanding key concepts throughout the course. Utilize practice materials, engage in group study sessions, and seek clarification on any areas of difficulty early on. When the final assessment arrives, you’ll be in a much stronger position to perform well and improve your overall academic results.
Tips for Maximizing Your Exam Performance
Achieving your best possible result on an assessment requires more than just studying the material. It involves effective preparation, smart strategies, and managing your time wisely. By applying the right techniques and approaches, you can improve your performance and feel more confident during the test.
Start Early – One of the most important aspects of successful preparation is starting well in advance. Waiting until the last minute often leads to stress and inadequate retention of key concepts. Begin your review process early, breaking down the material into manageable sections and focusing on mastering each area step by step.
Prioritize Weak Areas – Identify the topics or concepts that you find most challenging and devote extra time to those. It is tempting to focus on what you already know well, but targeting your weaker areas will ensure a more balanced understanding of the entire subject matter. Consider working with study groups or instructors to clarify difficult topics.
Practice Regularly – Regular practice is essential for reinforcing the material. Use practice questions, mock tests, and previous assessments to familiarize yourself with the types of questions and the format of the test. This will help you become more comfortable with the test-taking process and identify any areas that still need attention.
Effective Study Techniques
Using active learning techniques can enhance your retention of information. Try summarizing what you’ve learned in your own words, teaching the material to someone else, or creating flashcards to reinforce key concepts. Additionally, taking breaks during study sessions can help maintain focus and prevent burnout.
Stay Calm and Confident
On the day of the test, maintaining a calm and confident mindset is crucial. Avoid cramming the night before and instead focus on getting a good night’s sleep. During the assessment, carefully read each question, manage your time wisely, and stay focused on the task at hand. Trust in your preparation, and don’t let stress affect your performance.