This section covers fundamental concepts that are crucial for anyone looking to strengthen their skills in system administration and network management. The focus is on essential topics related to managing users, configuring systems, and handling permissions effectively. These concepts are designed to build a strong foundation for those preparing for professional certifications in this field.
In this guide, you will explore vital areas such as managing system users, file access control, network configuration, and basic system maintenance. With a thorough understanding of these topics, you will be equipped to tackle practical tasks and troubleshoot common challenges encountered in the IT industry.
Mastering these skills will not only improve your technical knowledge but also increase your confidence in handling various scenarios. By focusing on these key elements, you can ensure that you are well-prepared to face challenges and succeed in your certification journey. Consistency and practice are the keys to mastering these concepts and applying them effectively in real-world situations.
NDG Linux Essentials Chapter 18 Exam Answers
This section provides a detailed exploration of critical topics that will help you demonstrate proficiency in managing and configuring systems. By focusing on practical skills and key knowledge areas, it prepares you for various challenges related to system administration and network operations. The material covered here is essential for anyone preparing for certification assessments in the IT field.
Key Areas of Focus

The main areas of focus include user management, system configuration, file permissions, and network setup. A thorough understanding of these concepts will ensure that you can confidently navigate and manage different systems. Additionally, you will learn how to troubleshoot common issues, manage resources efficiently, and apply best practices in system administration.
Preparation Tips
To excel in this section, hands-on experience is crucial. Practice configuring and managing system settings, as well as understanding the nuances of file and network management. Study the concepts in-depth and focus on mastering the practical application of these skills, as this will provide a strong foundation for your certification journey.
Overview of Chapter 18 Exam
This section covers a comprehensive set of topics that are essential for demonstrating expertise in system administration and network management. The focus is on understanding core concepts, mastering key skills, and applying knowledge to real-world scenarios. Success in this part relies on a solid grasp of foundational topics related to system configuration, user management, and troubleshooting.
Key Focus Areas
- System configuration and optimization
- Network setup and management
- File permissions and security
- User account creation and management
- Basic troubleshooting techniques
What You Need to Know
To perform well in this section, it is important to review the following skills:
- Understanding how to configure system settings and manage resources effectively
- Familiarity with user and group management commands
- Knowledge of network protocols and configuration tasks
- Ability to secure file access through proper permissions
By focusing on these areas, you will be well-prepared for any practical challenge that may arise during the assessment process. Mastery of these topics is vital for anyone looking to pursue a career in IT system administration.
Key Topics Covered in Chapter 18
This section delves into critical concepts and skills necessary for managing and securing systems, focusing on both theoretical knowledge and practical application. The material presented emphasizes key areas of system administration, networking, and security protocols, providing the foundation for effective management of IT environments.
Core Areas of Focus
- Configuring and managing system settings
- Understanding user access and file permissions
- Network configuration and troubleshooting
- Setting up and managing user accounts
- Maintaining system security and integrity
Practical Applications
Mastering the following areas will be essential for applying your knowledge effectively:
- Performing routine system maintenance and optimizations
- Implementing security measures for system and network protection
- Utilizing commands for managing files and directories
- Configuring network settings to ensure connectivity and security
These topics provide a robust framework for mastering key administrative tasks, ensuring you are well-prepared for handling real-world challenges in IT management.
Important Commands for Chapter 18
This section highlights essential commands that are key to managing and configuring systems effectively. Understanding and mastering these commands will provide you with the tools needed to perform a variety of administrative tasks, from managing user access to configuring network settings and securing files. These commands are vital for anyone seeking to improve their technical proficiency in system administration.
Key System Management Commands
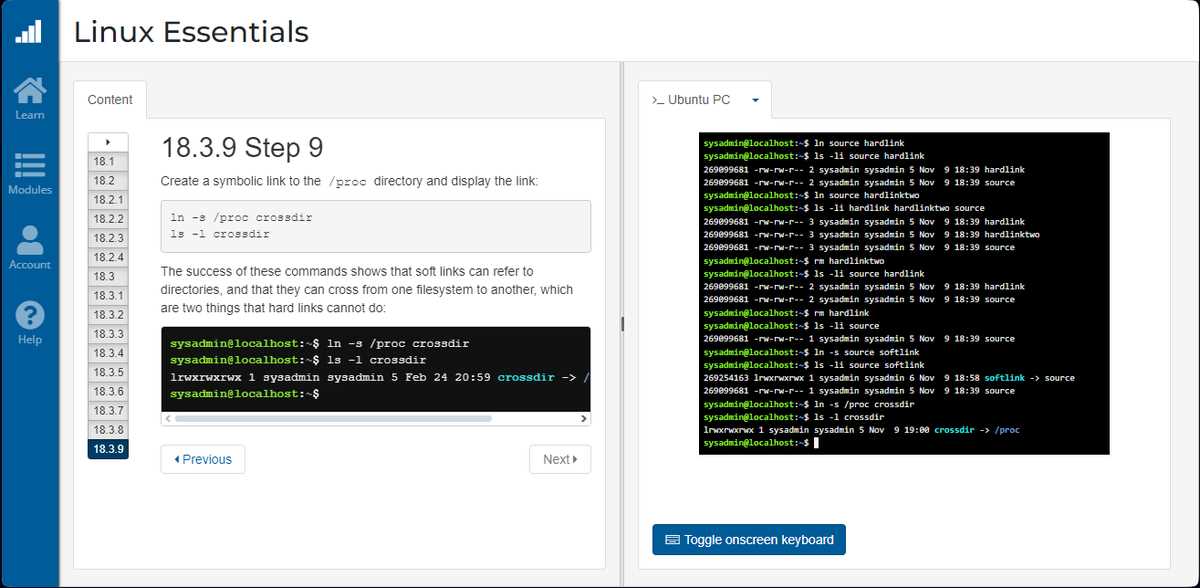
- useradd – Adds a new user to the system
- chmod – Changes file permissions for security management
- chown – Modifies file ownership
- ls – Lists files and directories
- ps – Displays information about running processes
Network Configuration and Troubleshooting
- ifconfig – Configures and displays network interface settings
- ping – Tests network connectivity to a remote host
- netstat – Displays network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics
- route – Manipulates the IP routing table
Mastering these commands will equip you with the necessary skills to manage users, secure files, and configure network settings. Consistent practice with these tools is essential for becoming proficient in system administration.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the Exam
When preparing for an assessment in system administration and networking, it is important to be aware of typical pitfalls that can hinder your performance. Recognizing these common mistakes can help you avoid unnecessary errors and ensure you demonstrate your true capabilities. The following are some frequent mistakes that candidates make, along with tips on how to prevent them.
| Common Mistakes | How to Avoid Them |
|---|---|
| Skipping over important concepts | Review all topics thoroughly to avoid missing crucial areas. Focus on understanding, not just memorizing. |
| Misunderstanding command syntax | Practice using commands in a terminal environment to become familiar with their correct syntax and options. |
| Not testing configurations | Always test configurations after making changes to ensure they work as expected. |
| Neglecting security practices | Pay attention to security settings and follow best practices for file permissions and user management. |
| Not managing time effectively | Allocate time for each section of the assessment and avoid spending too long on any one task. |
By being mindful of these mistakes and focusing on understanding key concepts, you can significantly improve your performance and increase your chances of success in the assessment. Regular practice and attention to detail are essential in mastering the skills required for system administration tasks.
Strategies for Studying Chapter 18
To succeed in mastering the concepts of system administration and network configuration, adopting a structured study approach is crucial. This section provides practical strategies to help you effectively absorb and apply the material. By focusing on key areas, practicing consistently, and testing your knowledge, you will be well-prepared for any assessment in this field.
Effective Study Techniques
Active learning is one of the most powerful strategies. Instead of just reading through the material, engage with it by performing hands-on exercises. This approach allows you to better understand how each concept works in practice and reinforces your learning.
- Work with real systems or virtual machines to apply commands and configurations.
- Use flashcards or notes to test yourself on key concepts and terminology.
- Review each section thoroughly before moving on to the next one.
Maximizing Retention
Regular review is essential to retaining the material long-term. Space out your study sessions over a period of time to strengthen your memory. Also, ensure you actively challenge yourself by trying to explain the concepts in your own words or teaching someone else. This method of self-explanation will deepen your understanding.
- Set up a study schedule that allows you to revisit difficult topics multiple times.
- Join study groups or forums to discuss and clarify challenging areas.
By applying these strategies, you can improve your grasp of complex topics and approach the assessment with confidence.
Understanding File Permissions in Linux
File permissions are a fundamental concept in system administration, crucial for managing access to files and directories. Properly configuring these permissions ensures that only authorized users can read, modify, or execute specific files. Understanding how permissions work helps maintain system security and integrity while preventing unauthorized access or accidental modifications.
Types of File Permissions
There are three main types of file permissions:
- Read (r) – Allows viewing the contents of a file or directory.
- Write (w) – Grants permission to modify the contents of a file or directory.
- Execute (x) – Permits running a file as a program or script.
Understanding User Roles
Permissions are assigned to three distinct user categories:
- Owner – The user who owns the file or directory.
- Group – Users who are part of the same group as the file owner.
- Others – All other users on the system who are neither the owner nor part of the group.
By understanding how to configure and modify these permissions using commands such as chmod and chown, system administrators can ensure that sensitive data is protected and that only authorized users can perform certain actions on files.
Network Configuration Essentials
Proper network configuration is crucial for establishing reliable communication between systems and ensuring data flows smoothly across devices. Whether you’re setting up a local network or configuring connections to external resources, understanding the fundamentals of network setup is essential for any IT professional. This section covers the key elements involved in network configuration, focusing on addressing common tasks like IP addressing, routing, and network troubleshooting.
Configuring Network Interfaces
One of the first steps in network configuration is ensuring that network interfaces are correctly set up. Each device on the network needs a unique IP address, and administrators must configure the appropriate network interface settings. Common commands for managing interfaces include:
- ifconfig – Displays or configures network interface settings.
- ip – Provides more advanced options for managing network interfaces and routes.
Setting Up Routing
Routing is essential for directing traffic between different networks. Properly configured routes ensure that data can be transmitted between local and remote systems. A common command for managing routes is:
- route – Displays or modifies the IP routing table to direct traffic to the correct destination.
Once the network interfaces are configured and routes are set up, testing network connectivity using tools like ping and traceroute can help diagnose issues and confirm that the setup is functioning as expected.
Managing Users and Groups in Linux
Effective user and group management is a fundamental aspect of system administration. By controlling user access and permissions, administrators can ensure that individuals have appropriate access to resources while maintaining system security. This section discusses key concepts and commands for managing users and groups in a multi-user environment.
Creating and Modifying Users
To add a new user to the system, administrators can use the useradd command, which creates a user account with default settings. Once a user is created, modifications can be made to their profile using the usermod command, allowing changes such as group membership or home directory adjustments.
- useradd – Adds a new user to the system.
- usermod – Modifies existing user details such as group membership or login shell.
Managing Groups
Groups allow administrators to manage access permissions for multiple users simultaneously. Creating groups with the groupadd command helps organize users into categories, simplifying the management of file and directory permissions. Users can be added or removed from groups with the gpasswd or usermod commands.
- groupadd – Creates a new group.
- gpasswd – Manages group membership and settings.
By effectively managing user and group configurations, system administrators can ensure that the right individuals have the necessary access to perform their tasks without compromising system security.
Important Exam Resources and Tools
Preparing for any certification assessment requires a strategic approach, including utilizing the right resources and tools. By equipping yourself with comprehensive study materials, practice exams, and relevant software, you can enhance your understanding of the subject and increase your chances of success. This section outlines some essential tools and resources that can help streamline your preparation and improve your performance.
Study Materials
Accessing quality study guides and textbooks is vital to understanding key concepts. Look for materials that offer detailed explanations, examples, and practice questions to test your knowledge. Some of the most useful resources include:
- Official Study Guides – Often written by experts, these guides provide in-depth coverage of the material.
- Online Tutorials and Articles – Websites and blogs can offer insights and practical examples.
- Video Courses – Platforms like YouTube or course websites provide step-by-step demonstrations of concepts.
Practice Exams and Simulations
Taking practice tests is one of the best ways to prepare for an assessment. Simulated exams help familiarize you with the format and timing, while identifying areas that need improvement. Consider using these tools:
- Online Practice Tests – Platforms like Quizlet or exam simulators offer timed mock exams.
- Flashcards – Use them to memorize key terms and concepts quickly.
- Lab Environments – Virtual machines or sandbox environments allow hands-on practice with real-world tasks.
By leveraging these resources and tools, you can approach your assessment with confidence and ensure you’re well-prepared for all topics covered.
Commonly Asked Questions in Chapter 18
During the preparation for technical assessments, certain topics tend to appear more frequently in questions. Understanding these areas can greatly improve your readiness. This section highlights the most commonly asked questions related to key concepts covered in the specific module, helping to identify the areas where focus is essential. Familiarity with these questions can enhance both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Understanding Permissions and User Management
One of the primary concerns in system management is ensuring that users and groups are correctly configured. Questions on permissions and file access are frequently tested, such as:
- How do you modify user permissions for a specific file?
- What is the purpose of user groups, and how do they impact file access?
- Which commands are used to manage user accounts and groups?
Network Configuration and Troubleshooting
Another important area is network setup and troubleshooting. Questions may ask about configuring interfaces, assigning IP addresses, or resolving connectivity issues. Some examples include:
- How do you set up a static IP address on a network interface?
- What command is used to test network connectivity?
- How would you troubleshoot a connection failure in a local network?
Being able to answer these types of questions demonstrates a strong understanding of the underlying principles and commands necessary for managing system resources effectively.
Linux Kernel and System Architecture
Understanding the core components of an operating system is essential for anyone working with system management. At the heart of this system lies the kernel, which serves as the bridge between hardware and software. The kernel’s role is to manage resources and facilitate communication between different parts of the system, ensuring that everything functions seamlessly. This section explores the architecture and fundamental elements that make up a system’s kernel and its interaction with the hardware.
Key Components of the Kernel
The kernel consists of several components that work together to ensure system stability and performance. Some of the core functions include:
- Process Management – The kernel schedules and manages processes, ensuring that each gets appropriate CPU time.
- Memory Management – It allocates memory to processes and handles swapping between physical and virtual memory.
- Device Drivers – These allow the operating system to communicate with hardware devices like hard drives, printers, and network cards.
- System Calls – They are the mechanisms through which applications interact with the kernel, enabling actions like file access and process control.
System Architecture Overview
The architecture of an operating system determines how it organizes its components and how they interact with each other. Key aspects of system architecture include:
- Monolithic Kernel – All services run in kernel space, leading to high performance but potentially less stability due to lack of isolation.
- Microkernel – The core functionality is kept to a minimum, with other services running in user space, offering better security and modularity.
- Hybrid Kernel – A combination of both monolithic and microkernel designs, offering flexibility and balance between performance and stability.
By understanding how the kernel interacts with system architecture, users can better manage system resources, optimize performance, and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Basic Scripting Concepts for Chapter 18

Scripting is a powerful tool for automating repetitive tasks and managing system operations efficiently. In this section, we explore fundamental scripting concepts that are essential for system administrators and users alike. Understanding how to write and execute simple scripts allows you to streamline your workflow and improve productivity. Scripting languages, especially those used in Unix-like systems, offer flexibility and control over system operations.
Key Concepts in Scripting
Before diving into complex scripts, it is crucial to understand some of the basic concepts that form the foundation of scripting. These concepts include:
- Variables – Used to store data such as numbers, strings, or file paths. They allow dynamic input and output in scripts.
- Control Structures – These include conditional statements (if, else) and loops (for, while), which control the flow of the script based on specific conditions.
- Functions – Functions are reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks, making scripts modular and easier to maintain.
- Input and Output – Scripts often interact with the user or the system by taking input and providing output, often through files or the terminal.
Writing Simple Scripts
To get started with scripting, it’s important to understand how to write and execute basic scripts. Here’s an overview of how to create a simple script:
- Shebang (#!) – This is the first line of the script, indicating the interpreter to use (e.g., /bin/bash for Bash scripts).
- Permissions – Scripts must have executable permissions to be run. This is done using the chmod command (e.g., chmod +x script.sh).
- Writing the Script – A script is simply a series of commands written in plain text. It can include any valid commands, variables, control structures, and functions.
- Running the Script – Once the script is written and saved, it can be executed by calling it from the terminal (e.g., ./script.sh).
By mastering these basic scripting concepts, you’ll be able to automate tasks, create more efficient workflows, and solve problems more effectively in a system environment.
Exam Preparation Tips for Chapter 18
Effective preparation is key to success when facing a technical assessment. To ensure you’re fully prepared, it’s essential to focus on understanding core concepts, mastering practical skills, and reviewing key topics. Below are some valuable tips that can help you perform at your best.
Study Strategies
When studying for any technical test, a structured approach is essential. Here’s how to maximize your study time:
- Review Key Concepts: Focus on understanding the main ideas and how they are applied in practice. Knowing the theory behind each topic will make problem-solving much easier.
- Practice Hands-On: Theory is important, but applying it in real scenarios is critical. Set up a test environment where you can practice commands and configurations.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with important terms and definitions. This will help reinforce memory and recall when needed.
- Group Study: Studying with peers allows you to exchange knowledge and clarify any doubts. Collaborative study can also provide different perspectives on complex topics.
Time Management
Time management during preparation is as important as the content you’re studying. Follow these guidelines:
- Set a Study Schedule: Allocate specific time slots for each topic. Stick to the schedule to ensure you cover all important areas.
- Practice Time-Bound Quizzes: Take mock quizzes under timed conditions to improve your ability to think quickly and effectively under pressure.
- Prioritize Weak Areas: Identify and spend extra time on topics you find challenging. Focusing on weak areas will give you the confidence to tackle any question.
Important Resources
There are many resources available that can aid your preparation. Some of the most effective tools include:
| Resource Type | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Practice Exams | Simulate real test conditions and familiarize yourself with question formats. |
| Online Tutorials | Learn step-by-step processes for complex tasks through video tutorials and guides. |
| Official Documentation | Refer to official manuals and documents for accurate, up-to-date information. |
| Study Groups and Forums | Join online communities to discuss and clarify doubts with fellow learners. |
By following these preparation strategies, practicing regularly, and making use of available resources, you will improve your chances of success in the test.
Best Practices for Linux Administration
Effective system management relies on a set of best practices that ensure a stable, secure, and optimized environment. Whether you are managing servers or desktops, following these guidelines can help streamline operations and reduce the risk of errors. Here are some essential practices for anyone involved in system administration.
Regular System Updates
Keeping systems up-to-date is crucial for both performance and security. Regular updates ensure that you have the latest features and fixes available. This includes security patches, kernel upgrades, and software updates. A solid update strategy can minimize vulnerabilities and improve overall system stability.
- Automated Updates: Configure your systems to install security updates automatically whenever possible.
- Manual Checks: Regularly check for updates on important packages that may not be covered by automatic updates.
- Backup Before Updating: Always back up critical data before applying major updates, as they may cause unexpected issues.
System Monitoring and Logs
Effective monitoring is essential to identify problems before they affect system performance. By analyzing logs and tracking system health, administrators can prevent potential failures.
- Centralized Logging: Use tools that centralize logs from various systems, making it easier to spot patterns and identify issues.
- Resource Usage Monitoring: Keep track of CPU, memory, and disk usage to avoid system overloads.
- Alerting Systems: Set up automatic alerts for critical events, such as low disk space or high CPU usage, to take action quickly.
Security Best Practices
Security is a cornerstone of system administration. Implementing robust security practices can protect systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware attacks.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce the use of strong, complex passwords and consider multi-factor authentication for added security.
- Regular Audits: Perform regular security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities in system configurations and software.
- Access Control: Use proper user roles and permissions to limit access to sensitive files and directories, ensuring the principle of least privilege is followed.
Backup and Recovery Strategies
Data loss can happen unexpectedly, so having a reliable backup and recovery strategy is crucial. Regular backups ensure that critical data can be restored if needed.
- Frequent Backups: Schedule regular backups of essential files, databases, and configurations.
- Offsite Backups: Store backup copies in multiple locations, including offsite or in the cloud, to protect against physical disasters.
- Test Restores: Periodically test backup files to ensure that data recovery is possible when needed.
Automation for Efficiency
Automation reduces manual work, speeds up system management tasks, and ensures consistency across systems. It allows administrators to focus on more strategic tasks while handling repetitive jobs automatically.
- Script Automation: Write shell scripts to automate tasks such as backups, updates, and user management.
- Configuration Management Tools: Use tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef to automate system configurations and deployment processes.
- Scheduled Tasks: Use cron jobs to schedule regular tasks, ensuring they run at specified intervals without manual intervention.
By incorporating these best practices into your administration routine, you will enhance the performance, security, and reliability of your systems, making them more efficient and easier to manage.
Real-World Scenarios Covered in the Exam
In preparation for certification assessments, understanding real-world scenarios is essential. These situations are designed to test practical skills that administrators will encounter on the job. By working through these challenges, individuals can better prepare for managing systems effectively and efficiently in production environments.
System Troubleshooting and Issue Resolution
One of the most common tasks faced by system administrators is troubleshooting issues related to system performance, network connectivity, or software malfunctions. In real-world scenarios, exam questions might focus on how to diagnose and resolve these types of problems using the right tools and approaches.
- System Performance Issues: Identifying causes of system slowdowns and applying performance optimization techniques.
- Network Connectivity: Resolving issues related to network settings, DNS resolution, and firewall configurations.
- Application Failures: Diagnosing and correcting issues with software services and ensuring that they restart correctly.
Configuration Management and Automation
Another key area covered in real-world scenarios is the ability to configure and automate systems. As automation is crucial in maintaining consistency across a large number of machines, exam scenarios may require candidates to demonstrate their ability to write scripts, configure services, and use management tools to automate repetitive tasks.
- Automating Routine Tasks: Using scripts to perform tasks such as backups, updates, and log management.
- System Configuration: Configuring user permissions, setting up software packages, and managing network interfaces.
- Managing Configuration Tools: Demonstrating proficiency with tools like Ansible or Puppet for automated configuration management.
By focusing on these types of real-world tasks, candidates can be better prepared to handle the demands of system administration in professional environments. These scenarios test both theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring that individuals are ready for the challenges of the job.