
Preparing for your next test on the body’s structure and functions can feel overwhelming, but with the right approach, you can confidently tackle the material. This guide will help you navigate the key topics and concepts, ensuring you’re well-equipped for success. Understanding how different systems work together is essential, and focusing on critical areas will allow you to perform at your best.
Mastering the fundamentals is crucial when studying complex biological systems. By breaking down each system and its components, you can focus on the details that are most important for your test. Pay attention to terminology, functions, and how each part contributes to the overall function of the body.
Effective preparation involves more than just memorization. Active learning, such as drawing diagrams or quizzing yourself on key terms, can help reinforce your understanding. With the right strategies, you will be able to confidently recall information and apply it under exam conditions.
Study Guide for the Second Test
Successfully preparing for the second assessment on body systems requires a focused strategy and thorough understanding of key concepts. This section will outline the most important areas to review, tips for effective studying, and practical methods to ensure that you’re fully ready. Focus on grasping the core ideas behind each system and how they interact with one another.
Key Areas to Review
- Circulatory system and its components
- Musculoskeletal system structure and functions
- Respiratory system and gas exchange mechanisms
- Digestive processes and organ functions
- Nervous system pathways and responses
- Endocrine system and hormonal regulation
Effective Study Strategies

- Active Recall: Regularly quiz yourself on key terms and definitions to reinforce memory.
- Practice with Diagrams: Drawing and labeling diagrams can help visualize complex systems.
- Group Study: Discussing material with peers can clarify difficult concepts and encourage deeper understanding.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards to test your knowledge on terms and definitions for quick recall.
- Timed Practice: Simulate test conditions by timing yourself during practice tests to improve time management.
Understanding the Body Systems
To succeed in your studies, it’s essential to understand how different systems of the body work and interact. Each system plays a critical role in maintaining health, and learning their functions is key for mastering complex topics. This section will help you grasp the basic principles behind each system and their contribution to overall body function.
Major Body Systems
- Circulatory system: Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products through blood vessels.
- Musculoskeletal system: Provides structure, support, and facilitates movement.
- Respiratory system: Responsible for the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Digestive system: Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients to fuel the body.
- Nervous system: Controls and coordinates body activities through electrical impulses.
- Endocrine system: Regulates body processes via hormones secreted by glands.
How These Systems Work Together
- The circulatory system delivers oxygen from the respiratory system to the muscles, enabling movement.
- Both the digestive and circulatory systems work in tandem to supply the body with nutrients and energy.
- The nervous and endocrine systems communicate to regulate internal processes, ensuring balance and response to changes.
Key Topics to Focus on for Test
When preparing for the upcoming assessment, it’s crucial to prioritize the most important concepts. Focusing on the foundational systems and their key components will give you the best chance of success. Below is a breakdown of the essential topics to review in order to strengthen your understanding and improve performance.
| System | Key Concepts |
|---|---|
| Circulatory | Blood vessels, heart structure, blood flow, oxygen transport |
| Musculoskeletal | Bone structure, joint types, muscle groups, movement patterns |
| Respiratory | Lung anatomy, gas exchange, breathing mechanisms, diaphragm function |
| Digestive | Organs of digestion, nutrient absorption, enzyme function, digestive pathways |
| Nervous | Neurons, central vs. peripheral system, brain regions, sensory pathways |
| Endocrine | Hormone production, gland functions, feedback loops, metabolic regulation |
How to Master Terminology
Mastering the terminology used in the study of body systems is essential for success. Understanding the language allows you to precisely describe structures, functions, and relationships between body parts. This section will provide tips and techniques to help you retain and apply critical terms effectively, making your study process smoother and more efficient.
Break Down Complex Terms

Many terms in this field are derived from Latin and Greek, which can make them intimidating at first. However, breaking them down into smaller parts can make them easier to understand. Focus on common prefixes, suffixes, and roots that appear frequently in terms related to body structures and functions. For example:
- Cardio- refers to the heart.
- -ology means the study of.
- Gastro- refers to the stomach.
Use Visual Aids and Mnemonics
Creating visual associations can help solidify complex terms in your memory. Draw diagrams, label body parts, and connect each label with its term. Mnemonics are also a great tool to remember challenging words or sequences of terms. For instance, using a simple phrase to recall the order of structures or functions can make all the difference.
Common Pitfalls in Assessments
While preparing for assessments on body systems, students often encounter certain challenges that can impact performance. Recognizing these common pitfalls beforehand can help you avoid them and improve your ability to answer questions accurately. This section highlights the most frequent mistakes made during tests and provides strategies for overcoming them.
1. Misunderstanding Terminology
One of the most frequent issues is confusion over complex terms. Many terms are similar in structure but have different meanings. Failing to fully understand the distinction between terms can lead to incorrect answers. Some common examples include:
- Anterior vs. Posterior – confusion between the front and back of the body.
- Medial vs. Lateral – misunderstanding the terms referring to the middle versus the sides.
- Superior vs. Inferior – mixing up the terms for above and below.
2. Ignoring Relationships Between Systems
Body systems are interconnected, and understanding how they work together is crucial. Focusing solely on individual systems without recognizing how they interact can result in incomplete answers. For example:
- The circulatory system relies on the respiratory system for oxygen supply.
- The nervous system coordinates with the musculoskeletal system to control movement.
- The digestive system works with the endocrine system to regulate metabolism.
Effective Study Strategies for Body Systems
Achieving success in studying body systems requires a structured approach and a variety of study methods to reinforce understanding. Implementing a combination of active learning techniques, regular reviews, and practical exercises can make all the difference in retaining complex material. The following strategies are designed to help you focus on key concepts and retain information effectively.
Study Techniques to Boost Retention
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Recall | Test yourself regularly on terms, structures, and functions to strengthen memory. |
| Spaced Repetition | Review material at increasing intervals to improve long-term retention. |
| Diagram Labeling | Practice drawing and labeling key systems to visualize their structure and function. |
| Peer Teaching | Explain concepts to a peer or study group to reinforce your own understanding. |
| Flashcards | Create flashcards for important terms and concepts to test yourself on the go. |
Maximizing Study Time
Efficiently managing your study time is just as important as the techniques you use. Break your study sessions into focused intervals, and avoid cramming the night before. Set specific goals for each session and give yourself time for breaks to prevent burnout. Additionally, ensure you are actively engaging with the material during each study session, rather than passively reading through notes.
Reviewing Musculoskeletal System for Test
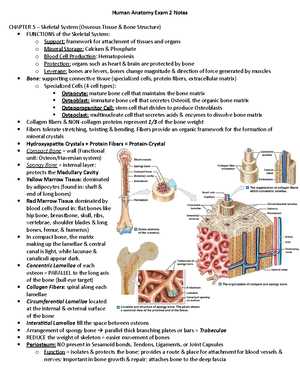
When preparing for an assessment focused on the musculoskeletal system, it’s essential to understand both its individual components and how they work together to support movement and structure. This system consists of bones, muscles, joints, and connective tissues, each with its own role in maintaining posture, enabling motion, and protecting vital organs. Reviewing these areas methodically will help reinforce key concepts and ensure you’re ready for any questions on the topic.
Key Concepts to Focus On
- Bone Structure: Understand the types of bones (long, short, flat, irregular), their composition, and functions in the body.
- Muscle Types: Know the differences between skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, and their roles in movement and function.
- Joint Classification: Review the different types of joints (synovial, cartilaginous, fibrous) and their specific functions in body movement.
- Movement Mechanics: Be familiar with how muscles and bones work together to create movement through flexion, extension, rotation, etc.
- Common Disorders: Understand common musculoskeletal conditions such as fractures, sprains, arthritis, and their effects on body movement.
Study Tips for Mastery
- Practice Labeling Diagrams: Regularly practice labeling diagrams of the skeleton and muscle groups to reinforce visual memory.
- Understand Joint Movements: Familiarize yourself with the range of movements each joint allows, such as flexion, extension, and abduction.
- Group Study Sessions: Discuss key concepts with peers to clarify difficult topics and test each other’s knowledge.
Digestive System Overview for Test Success
Understanding the digestive system is crucial for success in assessments focusing on body functions and processes. The system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. Mastering its components, from the mouth to the intestines, and knowing how each part contributes to the overall process will provide a strong foundation for answering related questions.
Key Components of the Digestive System
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Mouth | Initiates digestion through mechanical breakdown and enzyme activity (saliva). |
| Esophagus | Transports food from the mouth to the stomach through peristalsis. |
| Stomach | Breaks down food using gastric juices and enzymes, mixing it into chyme. |
| Small Intestine | Absorbs nutrients from chyme through villi and microvilli. |
| Large Intestine | Absorbs water and forms solid waste for elimination. |
| Liver | Produces bile to aid in fat digestion and processes nutrients. |
| Pancreas | Secretes digestive enzymes and regulates blood sugar through insulin production. |
Study Tips for Digestive System Mastery
- Review Process Flow: Understand the order in which food passes through the organs and how each part contributes to digestion and absorption.
- Memorize Key Enzymes: Learn the enzymes involved in digestion, their functions, and where they are secreted.
- Practice with Diagrams: Draw and label the digestive system to visualize the structure and the sequence of events in digestion.
Important Circulatory System Concepts

The circulatory system plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s internal balance by transporting nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products. Understanding its structure and function is essential for mastering the complex processes involved in circulation. This section covers the key concepts that are crucial for understanding how blood moves through the body and how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to support overall health.
To succeed in your studies, it’s important to focus on the core components of the circulatory system, such as the heart’s role in pumping blood, the structure of arteries and veins, and how oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. Reviewing these concepts will help you connect physiological processes and improve your ability to answer related questions with confidence.
Nervous System Structure and Function
The nervous system is responsible for coordinating and controlling bodily functions by transmitting electrical signals throughout the body. It acts as the communication network that links different organs and systems, enabling the body to respond to stimuli and maintain homeostasis. This system is composed of specialized cells, tissues, and organs that work together to process information and ensure proper function.
Key components of the nervous system include the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, each playing an essential role in relaying signals. Understanding the structure of these components and how they function together is critical for grasping how the body processes sensory input, regulates movement, and manages responses to internal and external changes.
The brain serves as the control center, interpreting information and issuing commands. The spinal cord acts as a relay between the brain and the rest of the body, while the peripheral nerves transmit signals from the spinal cord to muscles and organs.
Proper functioning of the nervous system is vital for overall health, as it ensures communication across systems and maintains the body’s ability to adapt to different conditions.
Preparing for Nervous System Questions
When preparing for assessments on the nervous system, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of how the body processes and responds to stimuli. The nervous system is intricate, with various components working together to manage communication between the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral structures. Focusing on these core areas will help ensure a comprehensive understanding and improve your ability to tackle related questions effectively.
Key areas to concentrate on include:
- Structure and Function of the Brain: Familiarize yourself with the regions of the brain and their specific roles, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
- Spinal Cord and Reflexes: Understand the function of the spinal cord in transmitting signals and coordinating reflex actions.
- Neurons and Synaptic Transmission: Review the structure of neurons, how they transmit signals, and the role of neurotransmitters.
- Sensory and Motor Pathways: Study the pathways through which sensory information is received and motor commands are sent from the brain to muscles.
- Disorders of the Nervous System: Be aware of common conditions that affect the nervous system, such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke.
Additionally, practicing with diagrams and quizzes can reinforce your understanding. Labeling the parts of the brain and spinal cord or answering multiple-choice questions about nerve function can be an effective way to ensure mastery of the material.
Respiratory System Key Points to Remember
The respiratory system is essential for providing oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. Understanding the structure and function of the organs involved is critical for mastering the physiological processes that sustain life. This section covers the key elements you need to remember when studying the system’s components and their roles in maintaining respiratory health.
Primary Structures and Their Functions
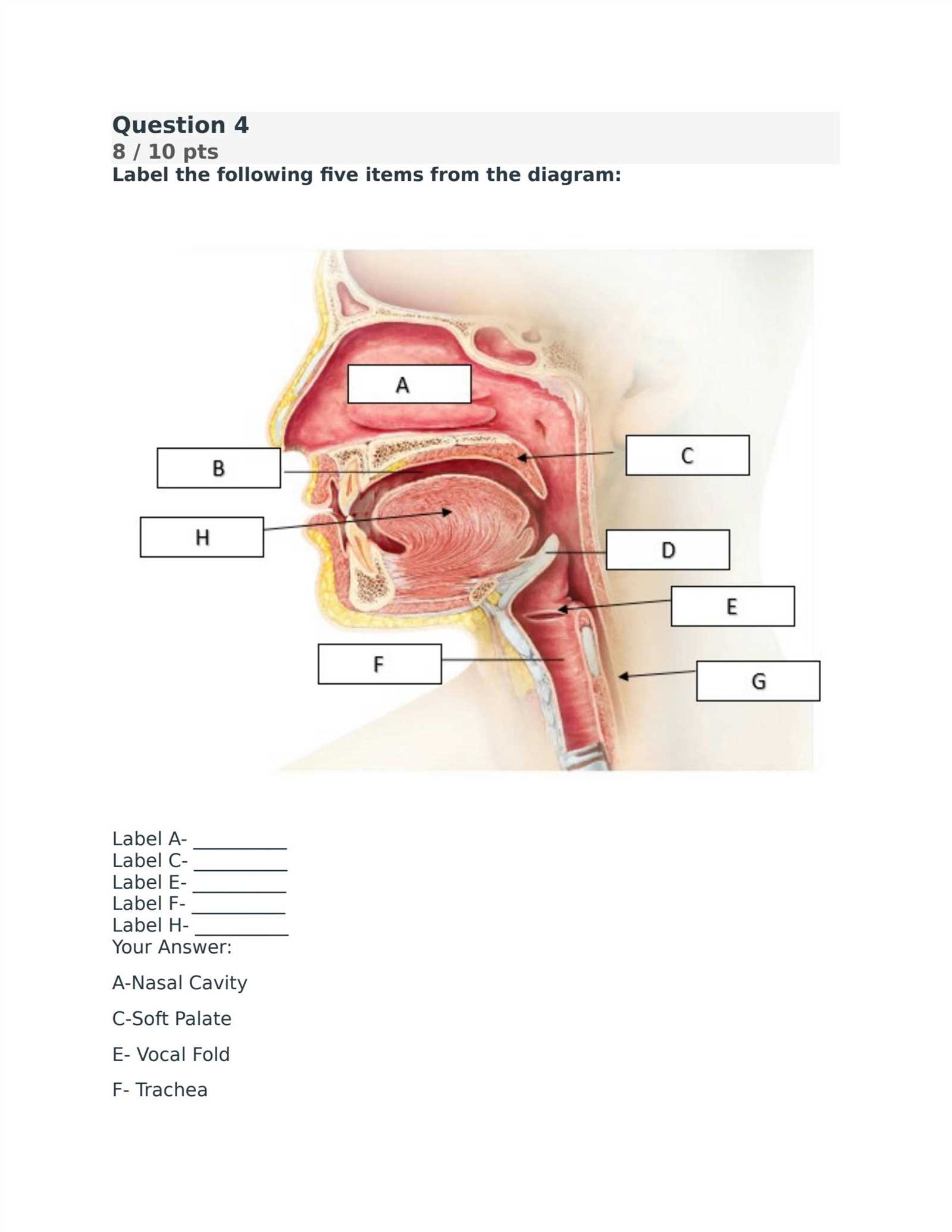
- Nose and Nasal Passages: Filter, warm, and humidify the air before it enters the lungs.
- Pharynx and Larynx: Pathways for air, also playing a role in vocalization and protecting the airway during swallowing.
- Trachea: The windpipe that channels air to the bronchi and lungs.
- Bronchi and Bronchioles: Major airways that branch from the trachea and carry air into the lungs, branching into smaller tubes.
- Alveoli: Tiny sacs where gas exchange occurs between the air and blood, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be removed.
Gas Exchange and Breathing Mechanism
- Oxygen Transport: Oxygen from the alveoli diffuses into the blood, binding with hemoglobin in red blood cells for transport to tissues.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli and is expelled from the body during exhalation.
- Breathing Cycle: The process of inhalation and exhalation controlled by the diaphragm and respiratory muscles, regulated by signals from the brain.
In addition to knowing the structures, it’s important to understand the physiological mechanisms behind the process of breathing and gas exchange. Pay attention to how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported and the regulation of breathing through signals from the brain.
Endocrine System and Hormonal Functions
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions through the release of hormones, which act as chemical messengers. These hormones influence a variety of processes, including metabolism, growth, mood, and reproductive health. Understanding how the glands of this system release and control hormones is essential for grasping its impact on the body’s homeostasis and overall well-being.
Key Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
- Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “master gland,” it controls other endocrine glands and regulates processes like growth and reproduction.
- Thyroid Gland: Responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and body temperature.
- Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which help the body respond to stress and regulate other vital functions.
- Pancreas: Releases insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels and ensure proper energy balance.
- Gonads (Ovaries and Testes): Produce sex hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone that are crucial for sexual development and reproduction.
Hormonal Regulation and Feedback Loops
- Negative Feedback Mechanism: The most common regulatory mechanism where a hormone’s effect decreases its own production, maintaining balance in the body.
- Positive Feedback Mechanism: Less common, this mechanism amplifies a specific physiological response, such as during childbirth when oxytocin increases uterine contractions.
- Endocrine Disruptors: External substances that can interfere with the production or function of hormones, leading to potential health issues.
Understanding how these glands interact and how hormones influence different bodily functions is key for mastering the concepts related to the endocrine system. Pay particular attention to the feedback mechanisms, as they help maintain hormonal balance within the body.
Tips for Retaining Detailed Information
Memorizing complex and detailed information can be challenging, especially when the material requires deep understanding and long-term retention. However, applying effective study techniques can make it easier to retain key concepts and retain them for longer periods. This section highlights practical strategies for improving memory and ensuring important details stick.
Effective Study Techniques

- Active Recall: Test yourself frequently to strengthen memory retrieval. Recalling information actively helps reinforce neural connections.
- Spaced Repetition: Review material at increasing intervals to enhance long-term retention. Spaced repetition ensures that you revisit concepts before they fade from memory.
- Visualization: Use diagrams, charts, and mental imagery to create a visual connection to the information. Visualization can make abstract concepts easier to understand and recall.
Organizing and Structuring Information
- Chunking: Break down complex information into smaller, manageable chunks. Group related pieces of information together to improve memory retention.
- Mnemonics: Create acronyms, rhymes, or other mnemonic devices to help remember complex terms or sequences.
- Mind Mapping: Create a visual representation of related concepts. A mind map can help organize information and identify connections between key topics.
Incorporating these techniques into your study routine can greatly improve your ability to remember detailed material. The key is consistency–regular review and applying different methods to engage with the material will ensure that important details remain accessible when needed.
Practicing with Past Exam Papers
Revisiting previous assessments is one of the most effective ways to prepare for upcoming evaluations. By working through past papers, you can familiarize yourself with the types of questions that may appear and identify areas where further study is needed. This method allows you to refine your test-taking strategies and build confidence.
Benefits of Using Past Papers
- Understanding Question Formats: Past papers give you insight into the typical structure of questions and how they are framed. This helps you anticipate what to expect in your upcoming evaluation.
- Time Management Practice: Practicing under timed conditions helps you manage your time more effectively during the actual assessment, ensuring you can complete all questions within the allotted time.
- Identify Weak Areas: Working through past papers helps pinpoint concepts that you may not fully understand, allowing you to focus your revision on these areas.
Strategies for Maximizing Benefits
- Review After Completion: After completing a past paper, always go back and review the answers. Understand why certain answers are correct or incorrect to reinforce your knowledge.
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Try to replicate the actual test environment by setting a timer and completing the paper in one sitting. This will help you get used to the pressure of working under time constraints.
- Group Study: Discuss past papers with peers to gain different perspectives on how to approach various questions, helping to deepen your understanding.
By incorporating past papers into your study routine, you not only increase your familiarity with the content but also enhance your ability to perform under exam conditions. Practicing regularly will improve both your speed and accuracy, setting you up for success.
Using Diagrams for Visual Learning
Incorporating visual aids such as diagrams can significantly enhance the learning process, especially when dealing with complex concepts. These tools help break down intricate systems or structures, providing a clear and organized way to absorb information. By engaging both visual and cognitive learning pathways, diagrams can aid in better retention and understanding of the material.
Visual learning allows you to see the relationships between different parts or functions, which is crucial for grasping detailed concepts. Whether it’s labeling a diagram, studying anatomical structures, or mapping out processes, these aids transform abstract ideas into tangible representations. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with subjects that require spatial awareness or understanding of interconnected systems.
Using diagrams also helps simplify challenging material by offering a visual reference point, making it easier to recall information during assessments. By practicing with these tools, students can reinforce their knowledge and improve their ability to recall key details when needed.
Managing Time During the Anatomy Exam
Effective time management is essential when preparing for and taking a test on complex biological systems. With multiple topics to cover and limited time, it is crucial to allocate your time wisely. Prioritizing questions, setting time limits for each section, and staying focused can help ensure that you answer every question with accuracy and thoroughness.
Plan Your Approach: Start by quickly scanning through the entire test. Identify the sections that you feel most confident about and those that may require more effort. Tackling easier questions first can help build momentum and give you more time for the challenging parts later. Make sure to leave time at the end for review.
Time Allocation: Break the test into sections based on the types of questions and estimate how much time you should spend on each. For example, if there are multiple-choice questions, you might allocate less time per question compared to essays or diagrams. Keep an eye on the clock, but don’t let it distract you from giving thoughtful answers.
Stay Calm and Focused: Managing stress is just as important as managing time. Staying calm and maintaining a clear focus throughout the test will help you to avoid rushing or making careless mistakes. Take deep breaths if you start feeling overwhelmed, and remember that pacing yourself is key to completing the test effectively.