
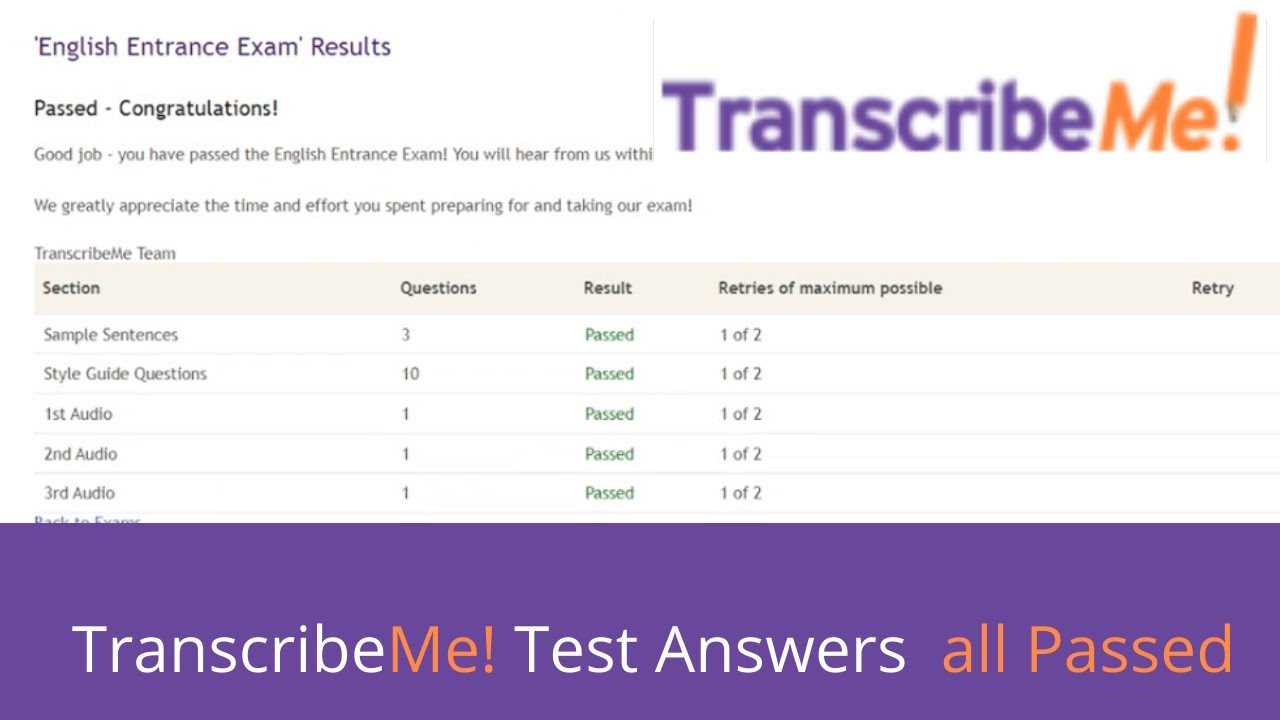
Facing difficulties in a transcription assessment can be disheartening, but it is also an opportunity to grow and improve. Understanding the reasons behind your struggles and addressing them systematically is key to achieving success in future tests. The journey from disappointment to mastery involves refining your skills and learning from your mistakes.
Many individuals encounter obstacles during transcription tests, whether it’s issues with listening accuracy, typing speed, or understanding varied accents. The process of overcoming these challenges requires both patience and practice. By focusing on specific areas of improvement, you can enhance your overall performance and increase your chances of success next time.
Rather than viewing a setback as a failure, consider it a learning experience. Embrace it as a step toward mastering the craft of transcription. With dedication and the right approach, you will be well on your way to excelling in the future.
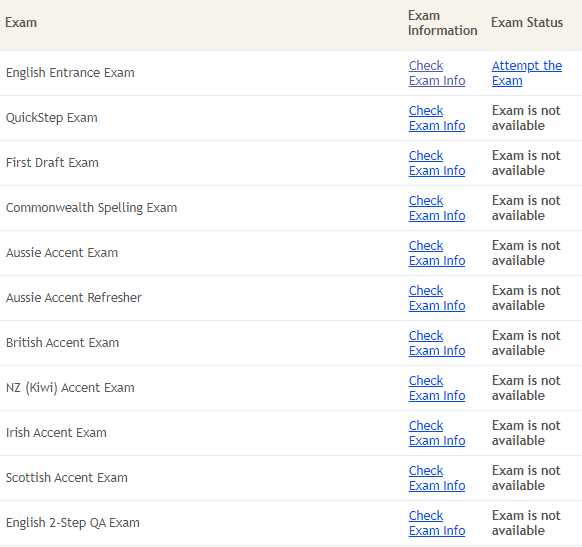
Solutions for Overcoming Transcription Test Challenges

When you encounter setbacks in a transcription assessment, it’s important to focus on actionable steps that can lead to improvement. Rather than getting discouraged, take the time to analyze your performance and identify areas that need attention. By taking a structured approach to address these weaknesses, you can significantly boost your chances of success in future assessments.
Here are some practical solutions to help you overcome common challenges:
- Review Mistakes Carefully: Go through the transcript you submitted and highlight the areas where you made errors. Whether it’s misheard words or missed punctuation, understanding where you went wrong is the first step toward improvement.
- Improve Listening Skills: Focus on improving your ability to catch every detail of the audio. Practice with different types of recordings and accents to enhance your listening accuracy. Use resources like podcasts, audiobooks, and transcription practice sites to refine this skill.
- Boost Typing Speed: Speed is crucial in transcription. Use typing software or practice touch-typing to increase your words per minute rate. A faster typing speed allows you to keep up with the audio more efficiently.
- Enhance Grammar and Punctuation: Pay attention to grammar rules, punctuation marks, and formatting. Accurate punctuation is vital for creating readable and professional transcriptions.
- Practice with Similar Content: Practice transcription with content similar to what you encountered. Use video tutorials, sample transcripts, and other materials to familiarize yourself with the types of tasks you’ll face in the future.
By focusing on these areas, you will gradually build the necessary skills to succeed in future tests. Remember, each challenge is an opportunity to learn and improve. With consistent effort, you’ll be better prepared for upcoming assessments and more confident in your transcription abilities.
Understanding Common Reasons for Failure
When faced with challenges during a transcription assessment, it is essential to understand the underlying reasons that led to the difficulties. Identifying these causes allows you to address specific areas of weakness and improve your performance in future attempts. Common issues can arise from various factors, including insufficient preparation, lack of focus, or difficulties in the transcription process itself.
Some frequent reasons for underperformance include:
- Poor Audio Quality: Low-quality recordings with background noise, unclear speech, or distorted sounds can make transcription difficult. These factors may cause errors in identifying words and phrases.
- Inadequate Listening Skills: Transcription relies heavily on being able to accurately hear and interpret speech. Difficulty in distinguishing different accents, speech patterns, or technical terms can result in missing or incorrect transcription.
- Slow Typing Speed: If your typing speed is too slow, it becomes harder to keep up with the audio. This often leads to incomplete sentences or skipped words, reducing the quality of your work.
- Lack of Focus and Concentration: Transcription requires sustained focus over long periods. Distractions or loss of concentration can cause you to miss critical parts of the audio or make careless mistakes.
- Inconsistent Formatting and Grammar: Failing to follow transcription guidelines for punctuation, spelling, and formatting can result in a poor overall assessment. Consistency is key for clarity and professionalism.
- Insufficient Practice: A lack of regular practice with different types of content can lead to unfamiliarity with specific challenges. Without adequate experience, it is easy to make mistakes or overlook important details in the transcript.
Understanding these common reasons allows you to approach future assessments with a targeted strategy for improvement. By addressing these areas, you can increase your accuracy and efficiency in transcription tasks.
How to Review Your Results
After receiving the outcome of your transcription assessment, it’s crucial to analyze the results carefully in order to understand where improvements can be made. Reviewing your performance allows you to pinpoint the areas where you struggled and provides valuable insights for better preparation in the future. This process helps identify patterns in your mistakes and develop a strategy for overcoming them.
Follow these steps to effectively review your results:
- Identify Mistakes: Look through your submitted work and mark all the mistakes, whether they’re related to spelling, grammar, missing words, or incorrect formatting. Understanding what went wrong is the first step toward improvement.
- Analyze Specific Sections: Focus on the sections where you encountered the most difficulty. Was it a particular accent or technical terminology that caused confusion? Identifying these challenges helps you target specific areas in need of practice.
- Assess Your Time Management: If you struggled with completing the task within the given time frame, take note of how long it took you to finish each section. This can help you gauge whether your typing speed or ability to focus needs improvement.
- Compare with Guidelines: Review the transcription guidelines or reference materials you were given. Were you consistent with the formatting requirements? Ensuring that you follow instructions closely can prevent future mistakes.
- Seek Feedback: If feedback is available, carefully review any comments or suggestions provided by the evaluators. Constructive criticism can highlight areas for growth that you might not have noticed on your own.
By following these steps, you can turn the review process into a learning opportunity. Recognizing your strengths and weaknesses will help you take focused action to improve your skills for future assessments.
Improving Listening Skills for Transcription
Listening is one of the most critical skills in transcription. Accurately capturing spoken words requires not only sharp hearing but also the ability to understand different accents, speech patterns, and context. To improve your transcription abilities, it’s essential to enhance your listening skills so that you can transcribe more efficiently and with fewer errors.
Practice with Varied Audio Sources
Exposure to different types of recordings will help you become more adaptable to various speaking styles. Listening to podcasts, audiobooks, interviews, and public speeches can provide a diverse range of vocabulary, accents, and pacing. Try transcribing short excerpts from these sources to challenge your skills and improve your accuracy. Gradually increase the difficulty level by working with fast-paced or technical content.
Focus on Detail and Context
Effective listening for transcription goes beyond hearing words; it’s about understanding context, tone, and implied meanings. Practice identifying key phrases and specific terms that might be difficult to hear clearly. By focusing on the overall meaning and structure of the speech, you’ll be better equipped to fill in gaps and capture nuances in the transcription process.
By making listening practice a part of your routine, you will gradually sharpen your ability to transcribe complex audio accurately and efficiently.
Mastering Accuracy in Transcribing Audio
Achieving precision in transcription is essential for producing high-quality, professional work. Accurate transcription involves more than simply typing what is heard; it requires attention to detail, a deep understanding of context, and the ability to catch every word and nuance in the audio. By refining your skills and practicing focused techniques, you can significantly enhance your accuracy and reduce errors in your transcriptions.
Here are several strategies to improve your transcription accuracy:
- Active Listening: Pay close attention to the audio, focusing on each word and phrase. Try to eliminate distractions and stay fully engaged with the content to prevent mistakes.
- Use of Pause and Replay: Don’t hesitate to pause or replay sections of the audio that are unclear. Taking the time to listen to difficult parts multiple times can help ensure that you transcribe every word correctly.
- Practice with Different Accents: To improve your ability to transcribe accurately, expose yourself to a variety of accents and speaking styles. This will help you become more adaptable and confident when transcribing unfamiliar speech patterns.
- Contextual Understanding: Understand the context of the audio to better predict words and phrases that may be difficult to hear. This can help fill in gaps when you’re unsure about a specific word or term.
- Check for Spelling and Grammar: Consistently review your work for spelling and grammatical errors. This ensures that your final transcript is not only accurate but also polished and professional.
By incorporating these practices into your transcription routine, you can greatly improve the accuracy of your work. The key is consistent practice and a dedication to fine-tuning your listening and transcription skills over time.
Building Your Transcription Speed
Increasing your transcription speed is essential for completing tasks efficiently while maintaining high accuracy. Speed and precision must go hand in hand to ensure that you can transcribe content quickly without sacrificing quality. To improve your pace, it’s important to practice regularly, enhance your typing skills, and adopt strategies that streamline your workflow.
Here are several techniques to help boost your transcription speed:
- Practice Touch Typing: One of the most effective ways to increase your speed is by mastering touch typing. This allows you to type without looking at the keyboard, improving both speed and accuracy. There are various online tools and programs that can help you practice and track your progress.
- Use Keyboard Shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with common keyboard shortcuts that can speed up the transcription process. For example, using shortcuts for pausing, rewinding, or skipping sections of audio can save valuable time.
- Transcribe Short Segments: Start by transcribing shorter audio clips and gradually increase the length as your speed improves. By breaking down tasks into manageable segments, you’ll build confidence and speed over time.
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Words: Recognizing common phrases or words that frequently appear in the audio can help you type faster. Create a list of these words to make it easier to transcribe them quickly without stopping to think about spelling.
- Minimize Distractions: Work in a quiet, focused environment to reduce interruptions. The less distracted you are, the more quickly and accurately you’ll be able to transcribe.
By applying these strategies and dedicating time to practice, you will steadily increase your transcription speed. Consistency and focused effort are key to becoming a faster and more efficient transcriber.
Tips for Handling Different Accents
When transcribing audio with various accents, it can be challenging to understand certain words or phrases. Accents can affect pronunciation, speed, and even the use of specific terms, making it essential to adjust your listening skills to capture every detail accurately. Improving your ability to transcribe content with diverse accents requires practice, patience, and a few effective strategies.
Here are some tips to help you handle different accents more effectively:
- Expose Yourself to Diverse Speakers: The more you listen to speakers with different accents, the easier it becomes to recognize variations in pronunciation. Seek out audio or video content from various regions, such as podcasts, news broadcasts, or interviews, to broaden your exposure.
- Focus on Context: Understanding the context of the conversation can help you predict difficult words or phrases. Even if certain parts of the audio are unclear, context clues often provide enough information to fill in the gaps.
- Slow Down Playback Speed: If an accent is challenging to understand, try slowing down the playback speed. This gives you more time to process the audio and catch nuances in pronunciation that might be missed at a normal pace.
- Learn Common Pronunciation Patterns: Every accent has its distinct patterns, such as how certain consonants or vowels are pronounced. Familiarizing yourself with these patterns helps you understand the speaker more easily and transcribe more accurately.
- Use Repetition to Your Advantage: Don’t hesitate to replay sections of audio when you’re having trouble understanding the accent. Repeating difficult segments allows you to catch words or phrases that may have been missed on the first listen.
By practicing these strategies, you will enhance your ability to handle different accents and improve your transcription accuracy. Over time, you’ll become more comfortable with diverse speakers, making the process faster and more efficient.
How to Manage Time During the Test
Effective time management is crucial when working on a transcription task under time constraints. Balancing speed with accuracy can be challenging, especially when there’s pressure to finish within a set period. By adopting a strategic approach to managing your time, you can increase both your productivity and the quality of your work.
Break the Task into Segments
Instead of focusing on completing the entire task at once, break it into smaller, more manageable segments. Divide the audio into sections and set a specific amount of time to transcribe each one. This will help you stay focused and prevent you from feeling overwhelmed by the overall length of the task. Allow extra time for the more difficult parts, and keep a steady pace for the easier sections.
Prioritize and Stay Flexible

Start by transcribing the easiest sections first, as these are likely to take less time. If you encounter particularly difficult segments, don’t get stuck trying to perfect them immediately. Move on to other parts of the audio and come back to the challenging sections later if needed. This will ensure that you make steady progress without wasting too much time on a single part.
By managing your time effectively, you can work more efficiently and reduce stress. With practice, you will learn to gauge how long different types of content take to transcribe and become more confident in meeting deadlines.
Analyzing Your Mistakes for Growth
When faced with challenges or errors in your transcription work, the key to improvement lies in understanding what went wrong. Analyzing your mistakes carefully allows you to identify areas for growth and develop strategies to avoid repeating the same errors. Rather than viewing mistakes as setbacks, they should be seen as opportunities to refine your skills and enhance your future performance.
Here are some steps to help you analyze your mistakes effectively:
- Review Your Work Thoroughly: Go back to the transcription you completed and identify each mistake. Look for patterns in the errors, such as specific words, phrases, or sections that caused difficulty. This will give you valuable insight into where you need improvement.
- Ask for Feedback: If possible, seek feedback from others who can offer a fresh perspective on your work. Constructive criticism can help you spot mistakes that you might have overlooked and provide advice on how to avoid them in the future.
- Identify Root Causes: Focus on understanding why mistakes occurred. Was it due to lack of focus, mishearing a word, or insufficient familiarity with the subject matter? Identifying the root causes will help you address the specific areas that need more attention.
- Take Action on Your Findings: Once you’ve identified your weaknesses, create a plan to address them. Whether it’s improving listening skills, practicing typing speed, or studying specific terminology, having a targeted approach will help you build better habits.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice, the more you’ll reinforce your strengths and correct your weaknesses. Consistent practice helps you internalize improvements and build confidence in your abilities.
By taking the time to analyze your mistakes and learn from them, you will see continuous improvement in your transcription work. With dedication and persistence, you will turn every mistake into a valuable learning experience that brings you closer to your goals.
Improving Grammar and Punctuation
Strong grammar and correct punctuation are essential for producing clear and professional transcriptions. Even small errors can change the meaning of a sentence, making it crucial to pay close attention to these details. Improving your understanding and application of grammar rules, as well as mastering punctuation, can enhance the overall quality of your work and reduce mistakes.
Focus on Grammar Fundamentals
To ensure accuracy in transcription, it’s important to review and strengthen your knowledge of grammar rules. Pay attention to the following key areas:
- Sentence Structure: Understand how to construct clear and complete sentences. Avoid fragments and run-on sentences, and ensure each thought is properly expressed.
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Ensure that the subject and verb in each sentence match in number and tense. This is a common area where errors can occur, particularly in complex sentences.
- Use of Pronouns: Ensure that pronouns are used correctly and clearly refer to the intended nouns. This avoids ambiguity in your transcription.
Mastering Punctuation

Correct punctuation helps to organize thoughts and convey the intended meaning. Focus on these areas to improve your punctuation skills:
- Commas: Use commas to separate items in a list, after introductory phrases, and to set off non-essential information. Avoid overusing commas, as this can disrupt the flow of a sentence.
- Periods and Question Marks: Ensure that every sentence ends with the appropriate punctuation mark. This is critical for clarity, especially when distinguishing between statements and questions.
- Quotation Marks: Properly use quotation marks when transcribing direct speech or quotations. This helps differentiate between spoken words and the transcription text.
By continually practicing and applying these grammar and punctuation rules, you can refine your transcription skills and create more accurate, professional results. Regular review of grammar and punctuation will help you avoid common mistakes and improve the clarity of your work.
Enhancing Your Vocabulary for Transcription
Having a broad and diverse vocabulary is an essential tool for any transcriptionist. The more words you know and understand, the easier it becomes to accurately capture the spoken content, particularly when dealing with specialized or complex terminology. Expanding your vocabulary not only improves your transcription accuracy but also boosts your confidence in handling a variety of topics and speakers.
Here are some practical ways to enhance your vocabulary for transcription tasks:
- Read Regularly: Reading books, articles, and research papers in various fields exposes you to a wide range of words and expressions. The more you read, the more words you’ll encounter, which will help you familiarize yourself with different contexts and meanings.
- Listen to Different Types of Audio: Listening to podcasts, interviews, and lectures on diverse topics can introduce you to new words and phrases. This exposure allows you to become familiar with the pronunciation and usage of specialized terms.
- Use a Thesaurus: A thesaurus is a valuable tool for finding synonyms and expanding your vocabulary. When you encounter a word you frequently use, look for alternatives to avoid repetition and enhance the variety in your transcriptions.
- Make Vocabulary Lists: Keep a list of new words you encounter during your transcription work or reading. Review these lists regularly and try to incorporate the words into your own vocabulary. This will help you retain them for future use.
- Study Specific Terminology: For transcription in specialized fields (e.g., medical, legal, technical), focus on learning the key terms and jargon relevant to those areas. This targeted approach will help you transcribe accurately and efficiently in specific domains.
By dedicating time to building and refining your vocabulary, you’ll improve your ability to transcribe diverse content with greater ease and precision. A rich vocabulary not only aids in transcription but also helps you become more versatile and professional in your work.
Tools to Aid Your Transcription Work

In the fast-paced world of transcription, utilizing the right tools can significantly improve your efficiency and accuracy. From software that enhances playback control to specialized dictionaries, the proper tools help streamline the process, allowing you to focus on the task at hand. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, integrating the right resources into your workflow can make a noticeable difference.
Here are some essential tools that can aid you in your transcription work:
- Transcription Software: Dedicated transcription software often comes with features like adjustable playback speed, foot pedal support, and timestamp insertion. These tools make it easier to manage the audio and ensure that you can transcribe with precision and speed.
- Speech Recognition Tools: Speech-to-text software can serve as a helpful starting point for transcribing audio. While not always perfect, these tools can speed up the initial draft, which you can then refine manually.
- Text Expander Programs: These programs allow you to create shortcuts for frequently typed words or phrases. This can save time when transcribing repetitive content or specialized terminology.
- Grammar and Spell Checkers: Automated grammar and spell checkers help catch common errors and ensure that your transcription is free from spelling mistakes and grammar issues. While not foolproof, they can act as a first line of defense against basic errors.
- Foot Pedals: Foot pedals allow you to control audio playback hands-free, making it easier to pause, rewind, or fast-forward while typing. This hands-free control improves workflow efficiency, particularly in long audio files.
- Noise-Canceling Headphones: High-quality headphones that reduce background noise can make a significant difference when transcribing in noisy environments. Clearer audio leads to fewer misunderstandings and mistakes.
- Online Dictionaries and Thesauruses: Having quick access to a dictionary or thesaurus can help when you encounter unfamiliar words or need alternative phrasing. Many transcriptionists also benefit from industry-specific dictionaries for accurate terminology.
Incorporating these tools into your transcription workflow will not only make the process more efficient but will also help you deliver higher-quality results in less time. By leveraging technology, you can improve both the speed and accuracy of your work, helping you meet deadlines and exceed expectations.
Preparing for a Retake of the Test
Facing a second attempt at a challenging task can feel intimidating, but it also presents an opportunity to refine your skills and improve your performance. Preparing for a retake requires a strategic approach, focusing on areas where improvement is needed. By reviewing past mistakes, practicing targeted skills, and maintaining a positive mindset, you can set yourself up for success during your second try.
Steps to Take Before the Retake
To maximize your chances of success, consider the following steps before attempting the task again:
- Review Feedback: If feedback is available from your first attempt, use it to identify areas where you struggled. This will give you a clear understanding of where to focus your efforts during preparation.
- Practice Specific Skills: Whether it’s listening comprehension, typing speed, or grammar, target the areas where you felt weakest. Devote extra time to practicing these specific skills to build confidence.
- Simulate the Task: Recreate the conditions of the task as closely as possible. This will help you become more comfortable with the process and reduce anxiety during the actual retake.
Essential Tips for the Retake
To improve your performance, consider implementing these tips during the retake:
- Stay Calm: It’s natural to feel pressure, but maintaining composure will help you think clearly and avoid unnecessary mistakes.
- Take Breaks: If the task is lengthy, take short breaks to maintain focus and prevent fatigue. Short intervals of rest can improve concentration.
- Double-Check Your Work: If time allows, review your work before submitting it. This can help catch any overlooked mistakes and improve the overall quality of your results.
Reviewing Your Progress
Tracking your progress over time is crucial to ensuring consistent improvement. Below is a table to help you assess the areas you’ve worked on and identify where further focus is needed:
| Skill Area | Initial Performance | Improvement Focus | Final Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Listening Comprehension | Poor | Practice with varied audio sources | Improved |
| Typing Speed | Average | Typing drills, focus on accuracy | Improved |
| Grammar and Punctuation | Good | Review advanced grammar rules | Excellent |
By following a structured plan and focusing on specific areas of improvement, you can increase your chances of success in the retake. Remember that every attempt is an opportunity to learn and grow, so stay persistent and positive throughout the process.
Transcription Practice: Where to Start
Starting transcription practice can seem overwhelming, especially if you’re new to the task or aiming to improve your existing skills. However, a structured approach can help you progress steadily. The key is to begin with foundational skills and gradually build your ability to transcribe more accurately and efficiently. By practicing regularly and focusing on different aspects of transcription, you’ll be able to improve both speed and precision over time.
Here’s where to begin your transcription practice:
- Familiarize Yourself with Transcription Tools: Before diving into transcribing, get comfortable with the tools you’ll be using. This could include transcription software, foot pedals, or even simple text editors. The right tools will make your practice sessions smoother and more efficient.
- Start with Simple Audio: Begin by transcribing short, clear audio clips with straightforward content. This allows you to focus on the basics–listening accuracy and typing speed–without getting overwhelmed by complex terms or unclear speech.
- Work on Typing Speed: Speed is an essential factor in transcription, especially for longer recordings. Practice typing regularly to improve your speed and accuracy. Utilize online typing tools or take typing lessons to develop muscle memory.
- Practice Active Listening: Listening is a crucial skill for transcription. Try practicing active listening by focusing on spoken words without distractions. You can start with podcasts or audiobooks that cover a wide range of topics to expand your vocabulary.
- Focus on Grammar and Punctuation: An important part of transcription is ensuring that your text is grammatically correct. Regularly review grammar rules, punctuation usage, and sentence structure to improve the quality of your transcriptions.
As you gain confidence in these foundational skills, gradually challenge yourself with more complex material. The key is to take small, consistent steps and progressively tackle more difficult audio files as your abilities grow. Regular practice will not only enhance your transcription skills but also increase your overall proficiency.
Building Confidence After a Setback
Facing a challenging outcome can be discouraging, but it’s also a powerful opportunity for growth. Building confidence after a setback requires focusing on learning from the experience rather than on the failure itself. By reflecting on the situation, identifying areas for improvement, and creating a plan for the future, you can regain your self-assurance and approach your next challenge with greater resilience and clarity.
Strategies to Regain Confidence
To restore your confidence and prepare for future attempts, consider implementing these approaches:
- Analyze the Situation: Reflect on what happened without self-judgment. What went well? What could have been improved? Understanding both your strengths and weaknesses helps you gain perspective.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your progress into smaller, achievable goals. Each small success will reinforce your confidence and help you build momentum.
- Focus on Skills Development: Identify the areas where you struggled and dedicate time to improving those skills. Regular practice and focused improvement will gradually boost your abilities.
- Positive Self-Talk: Combat negative thoughts by practicing affirmations and reminding yourself of past successes. A positive mindset can help you overcome doubts and stay motivated.
- Seek Support and Feedback: Don’t hesitate to reach out to peers or mentors for advice. Constructive feedback can provide valuable insights into areas you might overlook on your own.
Tracking Your Progress
Keeping track of your improvement over time can help you stay focused and motivated. The following table outlines key areas to evaluate and set goals for:
| Focus Area | Initial Performance | Current Performance | Target for Next Attempt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Listening Comprehension | Moderate | Improved | Increase accuracy by 15% |
| Typing Speed | Slow | Faster | Increase by 5 WPM |
| Grammar and Punctuation | Basic | Improved | Refine punctuation use |
By regularly reviewing your progress and setting specific, measurable goals, you’ll steadily build your confidence. Remember that growth is a process, and each step forward, no matter how small, is an achievement. Keep learning, practicing, and staying positive, and you’ll see improvement in both your skills and self-assurance.
What to Do Before Retaking the Exam
Preparing for another attempt after an unsuccessful one requires careful planning and focus. It’s important to use the time leading up to your next opportunity wisely, ensuring that you address areas where improvement is needed. By reflecting on past mistakes, practicing key skills, and managing your time effectively, you can approach the next challenge with confidence and a clear strategy for success.
Steps to Take Before Your Next Attempt
Consider the following actions to maximize your chances of success on your next try:
- Review Your Previous Performance: Take time to reflect on your past results. Identify the specific areas where you struggled and analyze what could have been done differently. This will help you target your efforts more effectively.
- Focus on Key Skill Development: Identify the critical skills required for success. Whether it’s improving your listening comprehension, increasing your typing speed, or enhancing your accuracy, dedicate time to practicing and mastering these skills.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice, the more confident and efficient you will become. Try to simulate real test conditions during practice sessions to build familiarity and reduce anxiety.
- Seek Feedback: If possible, seek advice or feedback from peers, mentors, or experts who can help you identify blind spots or areas that need improvement.
- Plan Your Time Wisely: Create a study schedule that allocates time to all areas you need to focus on. Prioritize difficult areas while also ensuring that you stay balanced in your preparation.
Mindset and Mental Preparation
Having the right mindset is crucial. Before your next attempt, ensure that you are mentally prepared:
- Stay Positive: A positive mindset can make a huge difference. Avoid focusing on past setbacks and instead remind yourself of your progress and your capability to improve.
- Build Self-Confidence: Confidence comes from consistent practice and reflection. Celebrate small victories along the way to keep your motivation high.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or stretching to help calm your nerves and ensure that you are in the best possible mental state for the task ahead.
By taking these steps, you will not only be better prepared for your next attempt but also feel more confident in your ability to succeed. The key is to focus on steady improvement, practice consistently, and approach the challenge with the right mindset.