Understanding the core principles of networking is essential for anyone pursuing a career in the field. In this section, we focus on critical areas that lay the foundation for more advanced concepts and practical applications. A strong grasp of these topics is vital for building a solid skill set in network configuration and troubleshooting.
We will explore fundamental topics such as addressing schemes, network protocols, and the structure of communication between devices. These are the building blocks for anyone aiming to work with networks and will be tested in various real-world scenarios. By mastering these concepts, you will be better prepared for the challenges ahead in your networking journey.
Efficient study and preparation are key to success. This guide provides insights into mastering essential networking techniques, helping you strengthen your theoretical knowledge and practical abilities. Stay focused and take your time to understand the interconnections between the concepts for a comprehensive learning experience.
CCNA Chapter 3 Exam Overview
In this section, we will explore the core concepts that form the foundation of networking. These principles are essential for anyone looking to excel in the field of network administration. The focus will be on understanding the structure and operation of networks, including key techniques for configuration and management. Building a solid knowledge of these basics is crucial for tackling more advanced topics later on.
While this part emphasizes theoretical understanding, it also incorporates practical aspects to ensure a well-rounded approach. Candidates will be tested on their ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios, making it important to focus on both the conceptual and hands-on elements. The knowledge gained here is critical for anyone pursuing a career in network management and troubleshooting.
Throughout this section, various tools, protocols, and best practices will be introduced. These are not just theoretical concepts but are actively used in the industry. Understanding their real-life applications will be key to achieving success and advancing to more complex networking challenges.
Key Topics Covered in Chapter 3
In this section, we delve into the fundamental areas of networking that are essential for anyone pursuing a career in this field. These topics provide a solid foundation in the principles and practical applications of network setup, management, and troubleshooting. Understanding these concepts is vital for anyone aiming to work with network infrastructure effectively.
The key subjects include network addressing, where the structure of IP addresses and subnetting techniques are covered in depth. You’ll also explore various network protocols, learning how devices communicate and exchange data across different systems. Additionally, the section highlights the OSI model and its relevance in breaking down complex network processes into understandable layers.
Other critical areas include the role of routing and switching in network design, which is essential for managing traffic flow. The section also addresses troubleshooting strategies, ensuring you’re equipped to diagnose and resolve network issues quickly. Understanding these topics provides the necessary skills to excel in both theoretical assessments and practical network configurations.
Essential Skills for the CCNA Exam
To succeed in the networking field, it is crucial to develop a comprehensive set of practical and theoretical skills. These abilities will help you effectively manage and configure networks while troubleshooting issues that may arise. Mastering these skills is not only important for passing assessments but also for applying knowledge in real-world network environments.
One of the most vital skills is understanding IP addressing and subnetting. Being able to correctly assign addresses and divide networks efficiently is foundational to any network design. Additionally, routing and switching knowledge is key to ensuring that data flows smoothly across different parts of a network, making them critical areas to master.
Another essential skill is the ability to work with network protocols. A deep understanding of how devices communicate, including the use of protocols like TCP/IP, is necessary for managing and configuring devices on a network. Additionally, troubleshooting techniques, including how to diagnose and resolve connectivity issues, are crucial for ensuring network reliability and performance.
Understanding Routing and Switching Concepts
Routing and switching are fundamental concepts in network communication, ensuring that data travels efficiently between devices and across various network segments. These concepts are at the heart of designing and maintaining reliable and fast networks. Understanding how routers and switches operate, as well as how they differ, is essential for configuring and troubleshooting networks effectively.
What is Routing?
Routing involves directing network traffic between different networks based on destination IP addresses. Routers make decisions about the best path for data to travel, ensuring that it reaches its destination efficiently. This is particularly important when dealing with large, complex networks with multiple interconnected subnets.
- Routers use routing tables to determine the best route for packets.
- They support various protocols, such as RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP, to dynamically adjust routes based on network changes.
- Routing helps prevent congestion by distributing traffic across the most optimal paths.
What is Switching?
Switching, on the other hand, occurs within a single network segment. It involves the forwarding of data between devices on the same local network. Switches operate at the data link layer and use MAC addresses to forward traffic efficiently within the network.
- Switches create a direct communication path between devices, improving speed and reducing collisions.
- They maintain MAC address tables that map devices to specific ports, allowing fast data forwarding.
- Switching plays a critical role in segmenting networks and enhancing security by isolating broadcast traffic.
Both routing and switching are indispensable for managing data flow and maintaining network performance. Mastery of these concepts is essential for anyone looking to build, manage, or troubleshoot modern networks.
OSI Model and Its Relevance
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that defines the different stages of network communication. It breaks down complex processes into seven distinct layers, each responsible for specific functions in the transmission of data. Understanding the OSI model is essential for troubleshooting, designing, and optimizing network systems, as it provides a structured approach to network communication.
Each layer of the OSI model represents a different aspect of the communication process, from the physical transmission of data to the application-level protocols that users interact with. By learning how data moves through each layer, network professionals can more easily identify where issues occur and how to resolve them. The model serves as a universal guide for network design and helps ensure compatibility between various technologies and devices.
- Physical Layer – Deals with the physical transmission of data over hardware like cables and switches.
- Data Link Layer – Ensures error-free transfer of data between devices on the same network.
- Network Layer – Responsible for routing data across multiple networks using logical addressing like IP addresses.
- Transport Layer – Manages end-to-end data transfer, ensuring reliability and proper data sequencing.
- Session Layer – Manages sessions or connections between applications, ensuring proper communication.
- Presentation Layer – Translates data formats for proper interpretation between different systems.
- Application Layer – The layer closest to the end-user, where applications and protocols interact with the network.
While the OSI model is a theoretical tool, its relevance remains clear in real-world networking. It provides a consistent framework for understanding how data flows and allows professionals to design networks more efficiently, troubleshoot issues effectively, and ensure robust network security across various systems and protocols.
Importance of Subnetting in Networking
Subnetting is a critical technique used in network design to divide a large network into smaller, more manageable sub-networks. By doing so, it helps optimize performance, enhances security, and simplifies the administration of a network. Proper subnetting ensures that resources are used efficiently, and it allows administrators to have more control over network traffic and routing.
One of the primary benefits of subnetting is improved network performance. By segmenting a network, administrators can reduce congestion by limiting broadcast traffic to specific subnets, ensuring faster communication and more efficient data flow. It also provides greater flexibility when assigning IP addresses, making it easier to scale and accommodate network growth.
Subnetting also plays a vital role in network security. By isolating sensitive systems or departments into their own subnets, organizations can enforce stricter security policies and prevent unauthorized access between different parts of the network. This segmentation limits the scope of potential attacks and ensures that vulnerabilities in one subnet do not compromise the entire network.
Finally, subnetting simplifies network management by allowing administrators to organize and maintain networks more effectively. It enables better allocation of resources, easier troubleshooting, and clearer network hierarchies. Understanding how to implement and manage subnets is essential for any network professional aiming to ensure optimal network performance and security.
Configuring IP Addresses Efficiently
Efficient configuration of IP addresses is crucial for ensuring seamless communication between devices within a network. Proper allocation not only prevents address conflicts but also helps optimize the network’s performance and scalability. By following systematic methods and best practices, network administrators can make the most of available address spaces while maintaining network integrity.
When configuring IP addresses, it is essential to consider the size and structure of the network. Whether assigning addresses manually (static) or automatically (dynamic), the approach should align with the specific requirements of the network. Below is a table illustrating how different subnet masks influence the number of available hosts within a network:
| Subnet Mask | Number of Hosts | Range of IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| 255.255.255.0 | 254 Hosts | 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 |
| 255.255.255.128 | 126 Hosts | 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126 |
| 255.255.255.192 | 62 Hosts | 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.62 |
Deciding whether to use static or dynamic IP addressing depends on the type of device and its role in the network. Static addresses are best suited for devices that require a consistent and permanent address, such as servers or network infrastructure equipment. In contrast, dynamic IP addresses, typically assigned by a DHCP server, are ideal for devices like laptops and mobile phones that frequently join and leave the network.
By efficiently assigning IP addresses and using appropriate methods, administrators can reduce network congestion, avoid address conflicts, and create a more scalable and organized network infrastructure. Proper planning and configuration ensure that devices are assigned the right addresses based on their roles and network requirements.
Routing Protocols You Should Know
Routing protocols are essential for directing traffic across networks, ensuring that data packets find the most efficient path from source to destination. These protocols enable routers to communicate with one another, share information about network topology, and adjust to changes such as network failures or congestion. Understanding the key routing protocols is vital for any network professional, as they determine the reliability and efficiency of a network’s communication.
There are several popular routing protocols, each with unique characteristics and use cases. Below are the most important ones you should be familiar with:
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol) – One of the oldest and simplest distance-vector protocols. RIP uses hop count as its metric to determine the best path. It is easy to configure but not as efficient in larger networks.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) – A link-state protocol that uses a more sophisticated algorithm for path selection. OSPF is scalable and commonly used in larger, more complex networks. It divides a network into areas to optimize performance.
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) – A hybrid protocol that combines the best features of distance-vector and link-state protocols. It offers faster convergence and is more efficient in larger networks compared to RIP.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) – A path-vector protocol primarily used for routing between different networks (i.e., inter-domain routing). BGP is crucial for internet routing, allowing ISPs and large organizations to exchange routing information.
Each of these protocols has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the size and type of network. While RIP is suitable for smaller networks, OSPF and EIGRP provide greater flexibility and scalability. BGP, on the other hand, is indispensable for routing data across the global internet. A good understanding of these protocols is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring robust connectivity.
Common Networking Errors to Avoid
In networking, errors and misconfigurations can lead to major disruptions, slow performance, or even complete service outages. By being aware of common mistakes, network administrators can take proactive steps to avoid issues that affect network reliability and security. Understanding these common pitfalls and knowing how to address them is essential for maintaining a robust and efficient network.
Misconfiguring IP Addressing
One of the most frequent issues arises from incorrectly assigning IP addresses. Common mistakes include assigning duplicate IPs within the same subnet or failing to properly configure subnet masks. This can lead to network conflicts and unreachable devices. It is important to ensure each device has a unique IP address and that subnetting is done according to the network’s requirements. Always double-check address assignments and validate them using network tools.
Neglecting Proper Routing Setup
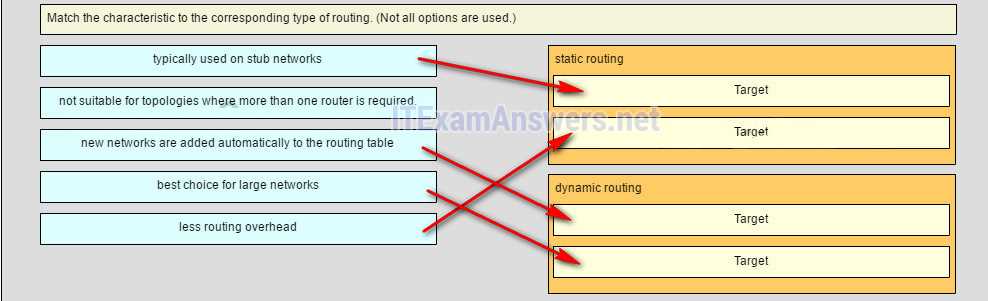
Improper routing configuration is another common error that can cause data packets to be misdirected or dropped. This could happen due to incorrect routing table entries or missing routes. Ensuring that all routers are properly configured to handle routing decisions and that all routes are accurate and up to date is crucial. Additionally, relying solely on static routes in a dynamic network can cause inefficiencies and make the network difficult to scale.
Other common errors include failure to secure network devices, overlooking firmware updates, and incorrectly configuring VLANs. Each of these mistakes can introduce vulnerabilities or reduce the overall efficiency of the network. Regularly auditing and testing the network, along with following best practices, can help prevent these issues from impacting network performance.
Preparing for Exam Day

Successfully passing a certification test requires more than just knowledge; it also demands proper preparation, focus, and strategy. The day before the test is crucial, as it allows you to ensure that you are physically and mentally ready. Organizing everything in advance can help reduce stress and boost confidence when you walk into the testing center.
Start by reviewing your study materials and notes one last time. Focus on areas where you feel less confident, but avoid cramming new information. It’s important to get enough rest the night before, as fatigue can impair your ability to think clearly and make decisions under pressure. Eating a balanced meal in the morning can also improve focus and energy levels.
Key tips for success on test day:
- Arrive early to the testing center to avoid unnecessary stress.
- Bring the required identification and any necessary paperwork to the test center.
- Stay calm and manage your time effectively during the test.
- Read each question carefully and eliminate obviously incorrect answers.
- If unsure about a question, move on and return to it later with a clearer mind.
On test day, maintaining a positive attitude and a clear focus is key. Being well-prepared and mentally sharp will help you stay composed and perform your best throughout the assessment.
Best Study Resources for Certification Preparation
Preparing for a networking certification requires access to high-quality resources that help reinforce theoretical knowledge and offer practical experience. A combination of books, online courses, practice exams, and hands-on labs can significantly boost your understanding and retention of key concepts. The right study tools can make the difference between just passing and truly mastering the material.
Books and Study Guides
Books are essential for a structured and detailed understanding of the topics. Popular study guides often break down complex subjects into digestible sections with practice questions and case studies. Some of the most recommended resources include:
- Routing and Switching Study Guide by Todd Lammle – A comprehensive guide with clear explanations and practice questions.
- Network+ Guide to Managing and Troubleshooting Networks by Mike Meyers – Great for foundational knowledge and troubleshooting techniques.
- Mastering Network Administration by Ed Tittel – A detailed book covering everything from basic networking concepts to advanced configurations.
Online Courses and Videos
Online courses and video tutorials offer flexibility and a hands-on approach to learning. Many platforms provide a mix of theory and practice with instructors guiding you through key topics. Some of the best options include:
- Udemy – Offers a variety of courses that are highly rated by learners, covering everything from networking fundamentals to advanced configurations.
- LinkedIn Learning – Provides a wide range of video courses, including certification preparation tracks with real-world examples.
- Pluralsight – Known for in-depth technical courses and interactive exercises that help reinforce concepts.
Using a combination of these resources will provide a well-rounded preparation strategy, helping you gain both the theoretical understanding and practical experience needed to succeed.
Time Management During the Test
Effective time management is a crucial skill when it comes to taking any professional assessment. Allocating your time wisely during the test can help ensure you complete all questions with enough attention to detail, while also avoiding unnecessary stress. Without proper planning, you may run out of time or rush through important sections. The key is balancing speed with accuracy.
Strategies for Managing Time Effectively
To make the most of your available time, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Know the Time Limit: Before you begin, familiarize yourself with the total time allotted for the test and the number of questions. This will help you gauge how much time to spend on each question.
- Start with the Easy Questions: Begin by answering the questions you find easiest. This helps you build confidence and ensures that you secure points on simpler topics before tackling more challenging ones.
- Keep Track of Time: Regularly check the clock to ensure you’re staying on schedule. If a question is taking too long, it’s better to move on and return to it later if time allows.
Dealing with Time Pressure

Sometimes, time can become a source of pressure during the test. If you feel stressed, here are a few tips to keep you focused:
- Stay Calm: If you encounter a difficult question, take a deep breath and remain calm. Panic can cloud your judgment and waste valuable time.
- Use the Process of Elimination: If unsure about an answer, use elimination techniques to rule out incorrect options. This saves time compared to second-guessing every answer.
- Leave Tough Questions for Later: If you’re stuck on a question, mark it and move on. This ensures you don’t waste too much time on a single item.
By managing your time effectively, you can approach each section of the test with confidence and avoid the pressure of rushing through the final questions. Proper time management helps you stay focused and maximize your performance.
Commonly Tested Networking Scenarios
In many professional networking assessments, practical scenarios are used to evaluate how well you can apply theoretical knowledge in real-world situations. These scenarios often involve troubleshooting, configuring, or analyzing network designs and configurations. Being prepared for the most commonly tested networking scenarios can help you approach these questions with confidence and efficiency.
Common Network Configurations
Several network setups are frequently tested, and understanding how to configure them is crucial. These configurations often include:
- IP Addressing: Configuring static IP addresses, subnets, and network masks.
- VLAN Setup: Creating and managing virtual LANs to segment network traffic.
- Routing: Configuring static and dynamic routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP.
Common Troubleshooting Scenarios
Another common scenario involves diagnosing network issues. These could range from connectivity problems to configuration errors. Some of the most frequent troubleshooting topics include:
- Ping Tests and Connectivity Issues: Diagnosing problems with network connectivity using tools like ping and traceroute.
- Subnetting Issues: Resolving conflicts or misconfigurations related to IP addresses and subnets.
- Routing Loops: Identifying and resolving issues caused by incorrect or missing routing entries.
Example Scenario Table
Below is an example of how a typical networking scenario might be presented and how you should approach it:
| Scenario | Required Actions | Tools and Commands |
|---|---|---|
| Unable to ping a remote device | Check IP configuration, verify routing, troubleshoot using ping and traceroute | ping, tracert, show ip route |
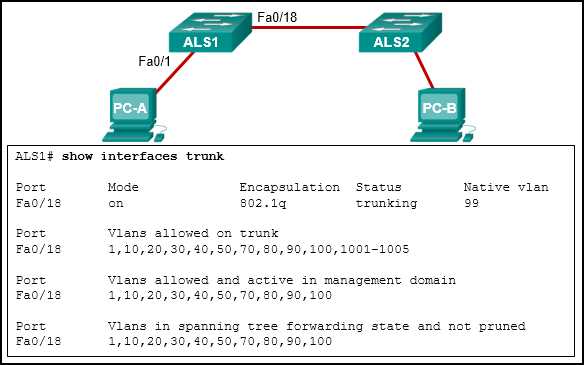
| VLAN misconfiguration | Verify VLAN assignments, check trunking configuration, ensure correct VLAN routing | show vlan brief, show interfaces trunk |
| Subnetting issue | Check IP address, subnet mask, and gateway settings | show ip interface brief, subnet calculator |
By familiarizing yourself with these typical scenarios, you can improve your ability to troubleshoot and configure networks effectively, which is often a key component of professional assessments.
Understanding the Exam Format
The format of a professional networking certification assessment plays a significant role in preparing for the test. Familiarizing yourself with the structure of the test will help you approach it strategically. These assessments typically consist of multiple types of questions that test both theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of your skills.
Question Types
Different question formats are used to assess your understanding of networking concepts. Here are the most common types:
- Multiple Choice: These questions test your theoretical knowledge on various networking protocols, technologies, and configurations.
- Simulations: Simulations test your ability to configure and troubleshoot real network scenarios, assessing your hands-on skills in practical situations.
- Drag-and-Drop: These questions require you to match concepts or arrange steps in the correct order, testing your understanding of processes and procedures.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: These are used to evaluate your ability to recall specific networking terms or commands.
Time Management and Question Strategy
Managing your time effectively during the test is crucial. Most assessments have a time limit, so it’s important to pace yourself. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Read Questions Carefully: Ensure that you fully understand the question before answering, especially in simulations and scenarios.
- Don’t Spend Too Long on One Question: If you’re unsure about a question, move on and come back to it later.
- Practice Under Time Constraints: Taking practice tests under timed conditions will help you become familiar with the pacing required for success.
By understanding the exam format and practicing different question types, you can develop a strategy that will increase your chances of passing the test on your first attempt.
Practice Labs and Simulation Questions
Hands-on experience is crucial for mastering the practical aspects of networking. Practice labs and simulation questions offer a unique opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in realistic scenarios. These exercises not only help reinforce key concepts but also improve your troubleshooting and configuration skills. Understanding how to navigate these tasks efficiently will greatly enhance your preparation.
Benefits of Practice Labs
Practice labs allow you to gain real-world experience by setting up and configuring network devices in a controlled environment. The following are key advantages of using practice labs:
- Practical Application: Practice labs enable you to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, helping solidify your understanding.
- Hands-On Troubleshooting: Labs provide opportunities to solve network issues and address common errors, which is essential for future problem-solving.
- Improved Retention: Actively engaging with hardware and software tools helps enhance long-term retention of networking concepts.
- Simulated Real-World Scenarios: These labs simulate complex network configurations, offering exposure to challenges you might encounter in a professional setting.
Simulation Questions in Practice
Simulation questions are a valuable component of the preparation process, as they mimic the practical, real-time aspects of network management. Here’s how you can benefit from practicing with simulation questions:
- Critical Thinking: These questions require you to apply your knowledge in dynamic situations, making quick decisions that directly impact the outcome.
- Technical Proficiency: Simulations test your ability to configure devices, manage IP addresses, and troubleshoot network problems efficiently.
- Time Management: Since simulations often take longer to complete, practicing under timed conditions will help you manage your time during the real test.
- Confidence Building: Consistently practicing these simulations builds confidence, ensuring that you are ready to tackle practical scenarios during the test.
By incorporating practice labs and simulation questions into your study routine, you’ll not only reinforce your theoretical knowledge but also sharpen your skills in handling real-world networking tasks. This comprehensive approach is key to excelling in any networking certification assessment.
Tips for Troubleshooting Network Issues
When network problems arise, having a systematic approach to identifying and resolving the issues is essential. Effective troubleshooting involves a combination of logical thinking, technical knowledge, and methodical testing. The ability to diagnose and solve network issues quickly is a key skill that can significantly improve network performance and minimize downtime.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
By following a structured process, you can more easily pinpoint the source of the problem and apply the correct solution. Here’s a basic troubleshooting framework:
- Identify the Problem: Begin by gathering as much information as possible about the issue. Is the problem affecting only one device or multiple users? Is the issue intermittent or constant?
- Define the Scope: Narrow down the potential causes by checking hardware connections, network configurations, and other devices in the affected area.
- Test the Network: Use network diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute to verify connectivity and identify any failed routes or lost packets.
- Isolate the Issue: Once you’ve identified potential sources of the problem, isolate them by disabling devices, changing settings, or simplifying the network topology to pinpoint the exact cause.
- Fix the Issue: After identifying the problem, implement the appropriate fix, whether it’s reconfiguring settings, replacing faulty hardware, or adjusting network parameters.
- Verify the Solution: Test the network again to ensure that the problem is resolved and that there are no side effects from the changes made.
Common Network Issues and Solutions
There are a few common network issues that professionals frequently encounter. Here are some examples and strategies for addressing them:
- IP Address Conflicts: Multiple devices on the same network having identical IP addresses can cause connectivity issues. To resolve this, ensure that DHCP is configured correctly or manually assign unique IPs.
- Slow Network Performance: Performance issues can stem from bandwidth limitations, network congestion, or outdated hardware. Identifying and prioritizing traffic, upgrading hardware, or optimizing routing protocols can help alleviate the issue.
- DNS Resolution Problems: If devices cannot resolve domain names, verify DNS server settings and ensure that DNS services are running properly.
- Disconnected Devices: Devices may lose connection due to incorrect configurations or cable issues. Check physical connections, verify device settings, and test network cables to resolve the problem.
By approaching troubleshooting methodically and focusing on common issues, you can minimize network downtime and ensure that systems run efficiently. The ability to diagnose and correct network problems quickly is a vital skill that helps maintain network stability and performance.
How to Stay Confident on Test Day
Maintaining confidence on the day of an important assessment is crucial for performing at your best. Preparation is key, but so is having the right mindset. How you approach the test itself–mentally and emotionally–can significantly impact your ability to recall information and manage time effectively during the test.
To boost your confidence and minimize anxiety, start by thoroughly reviewing the material beforehand, ensuring you’re well-prepared. But equally important is focusing on strategies that will help you stay calm and composed once the test begins. Here are a few tips to help you maintain your self-assurance on the big day:
- Review Key Concepts: Focus on the main topics you’ve studied, but avoid cramming right before the test. A quick review of your notes or key flashcards can help reinforce your knowledge.
- Practice Under Test Conditions: Simulate the test environment by taking practice quizzes or mock assessments. This will help you get used to the format, improve your time management, and reduce the element of surprise.
- Get Adequate Rest: A good night’s sleep before the test is essential for mental clarity. Avoid staying up late studying–your brain needs rest to perform optimally.
- Eat a Balanced Meal: Eating a healthy meal before the test will give you the energy and focus you need to perform well. Avoid heavy or sugary foods that may lead to an energy crash.
- Stay Positive: Remind yourself that you’re well-prepared and capable. Maintaining a positive attitude helps reduce anxiety and keeps you focused during the assessment.
- Manage Test Anxiety: If you begin to feel overwhelmed, take deep breaths to calm yourself. Break the test into smaller sections and tackle each one methodically. Confidence often builds as you move through the questions successfully.
By following these strategies and maintaining a calm, focused approach, you can enter the test with a clear mind and strong confidence. Trust in the preparation you’ve done, and know that you’re ready to handle any challenge that comes your way.